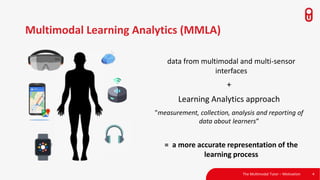
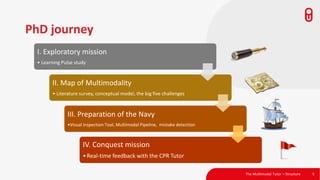
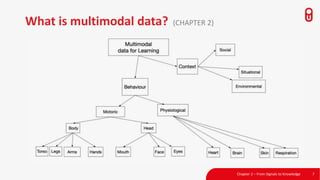
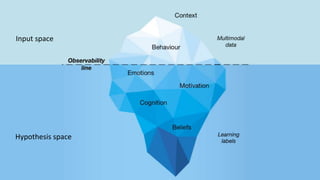
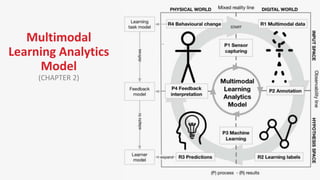
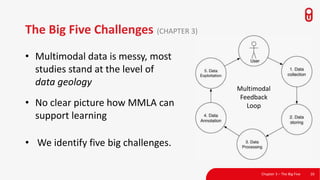
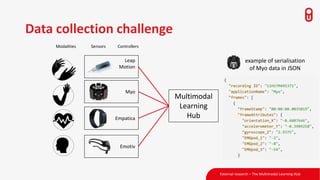
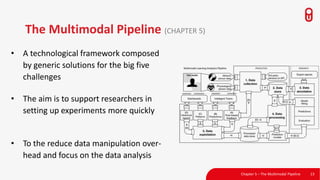
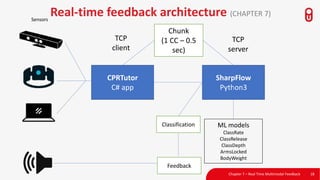
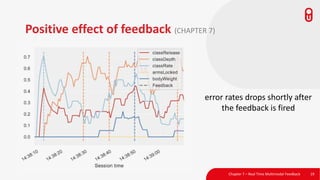
The document discusses the concept and implementation of a multimodal tutor that utilizes various sensors and analytics for enhanced learning experiences. It highlights the challenges and frameworks for effective data collection and analysis, particularly in training high-stakes skills like cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). The findings suggest that multimodal tutors can provide real-time feedback, supporting learners even in the absence of human instructors.