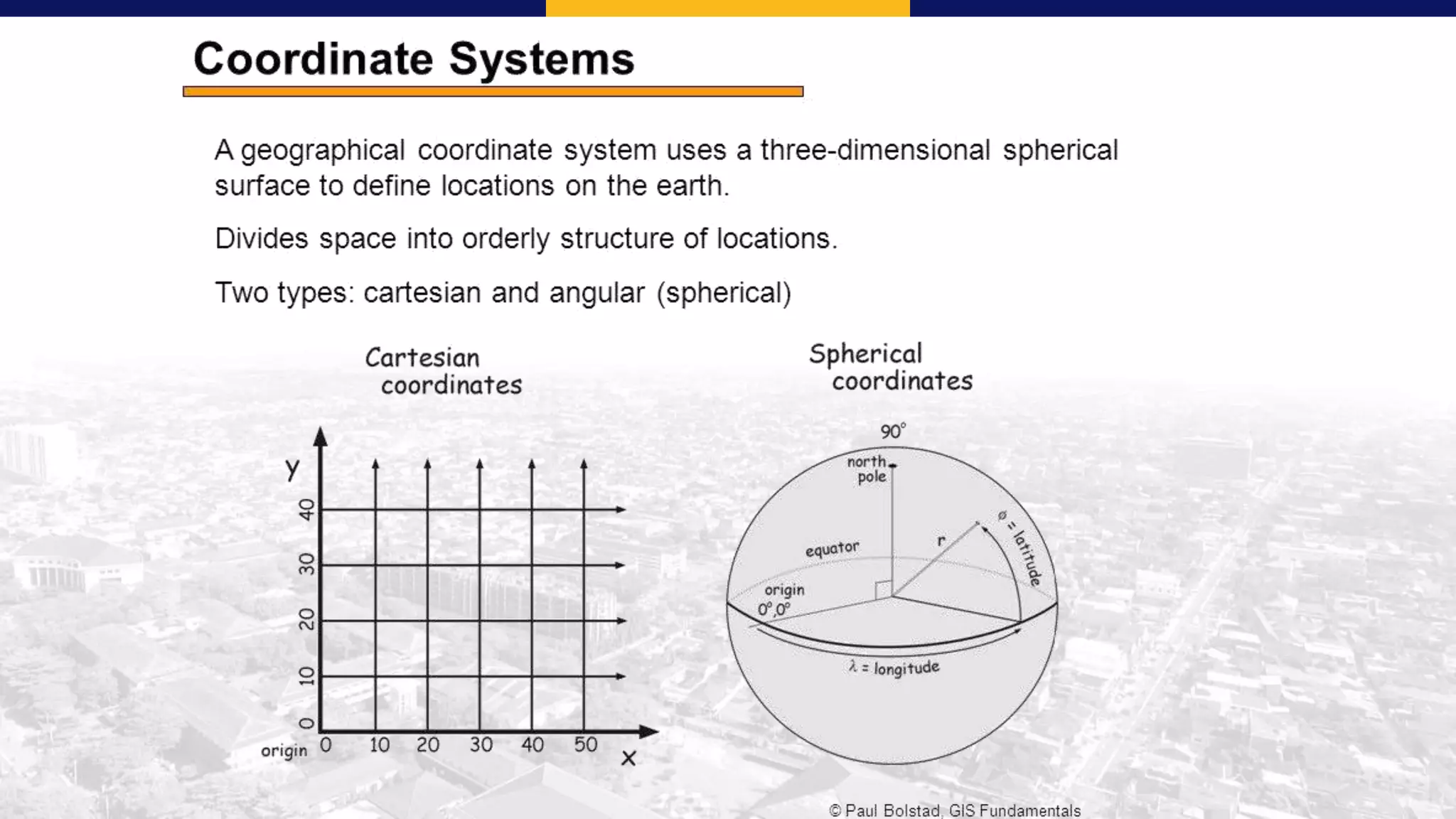
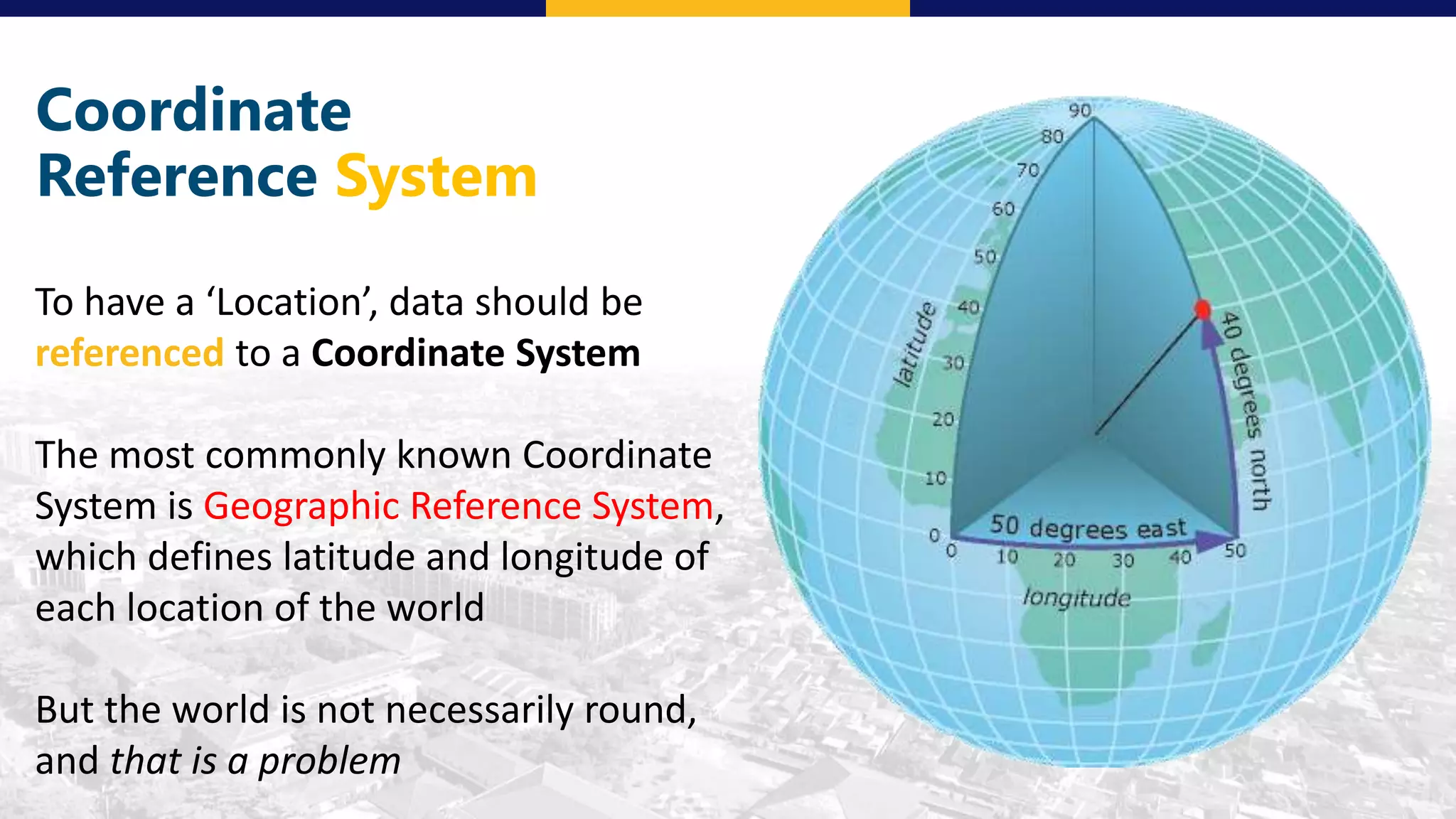
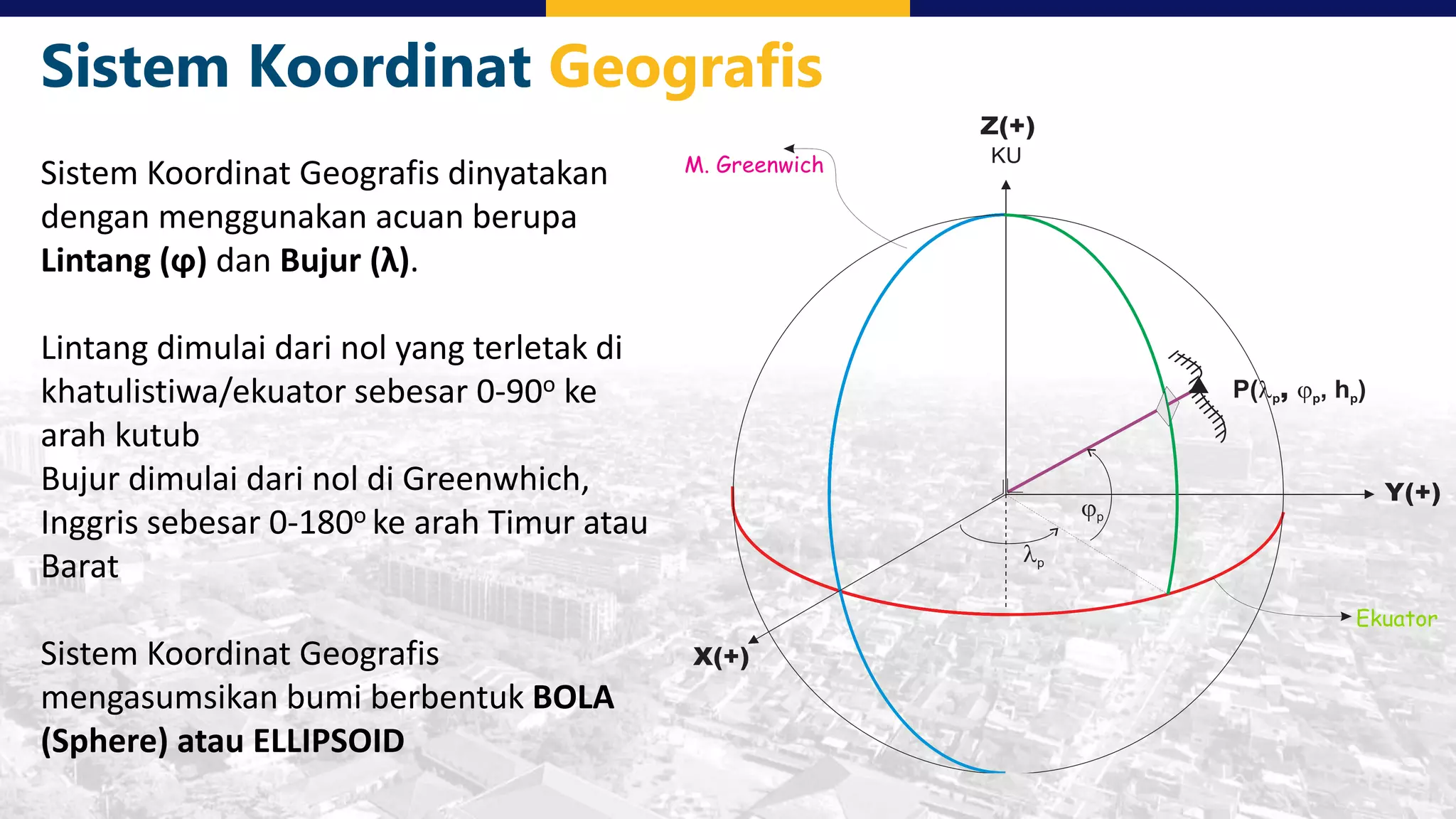
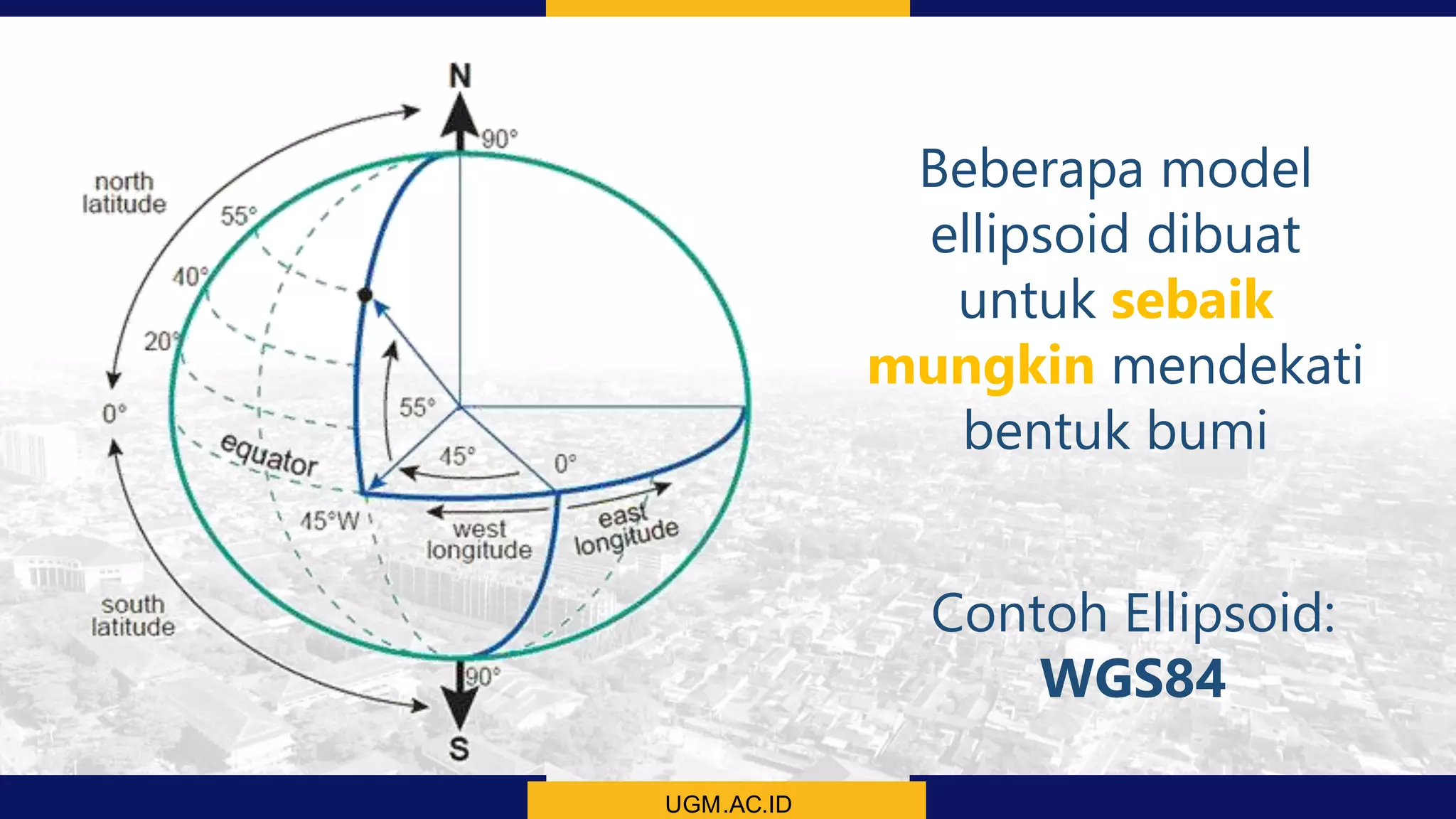
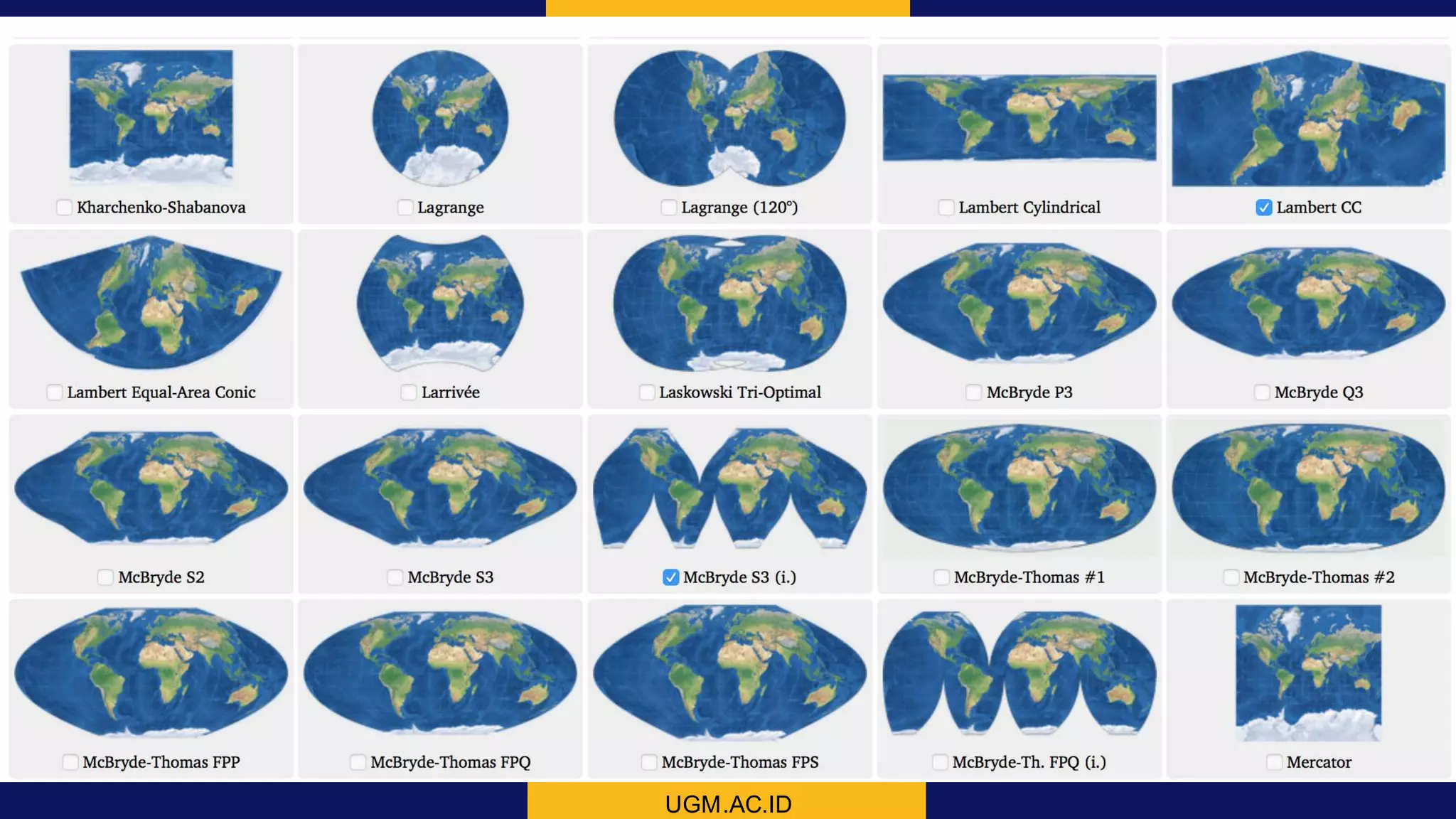
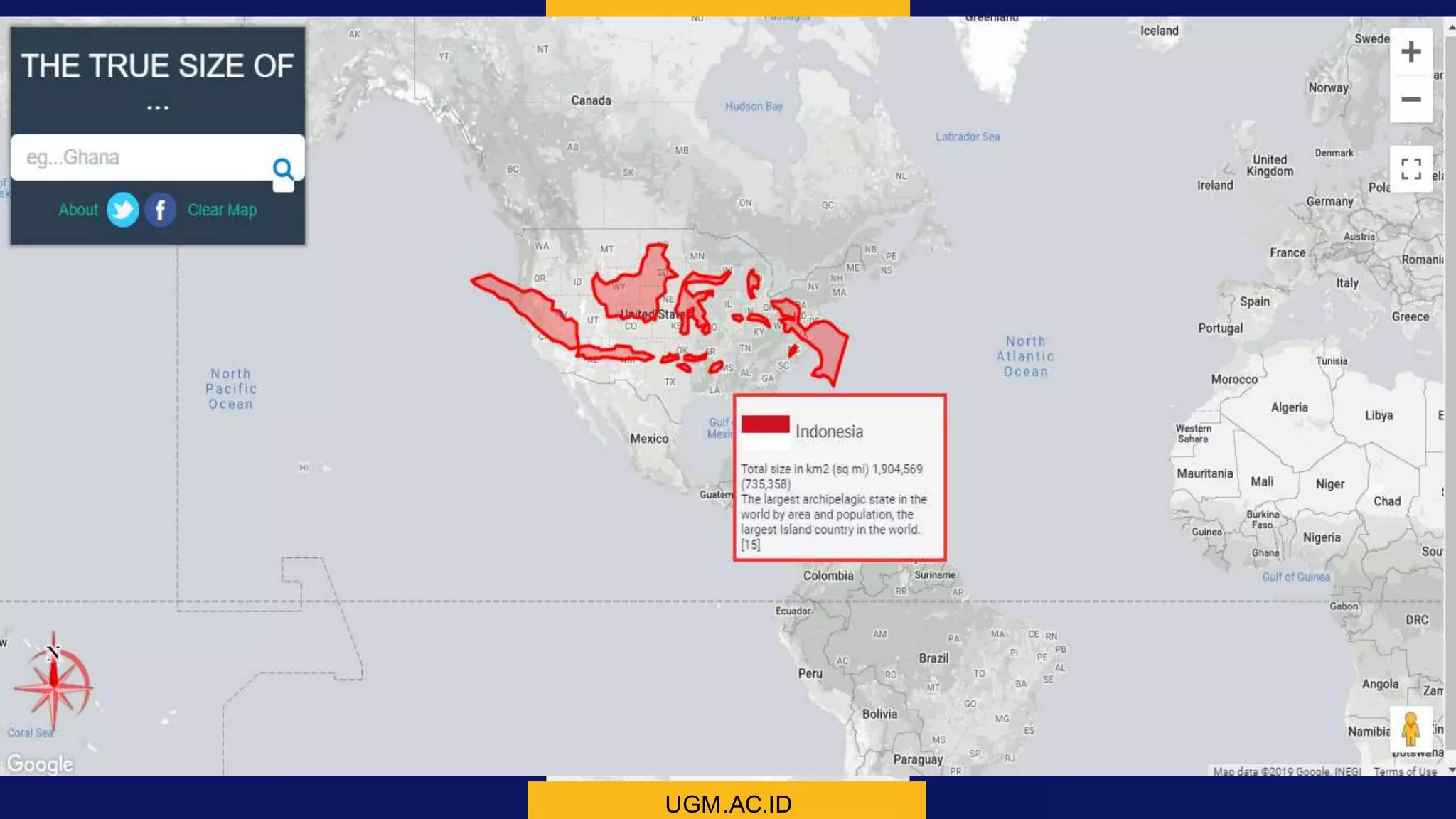
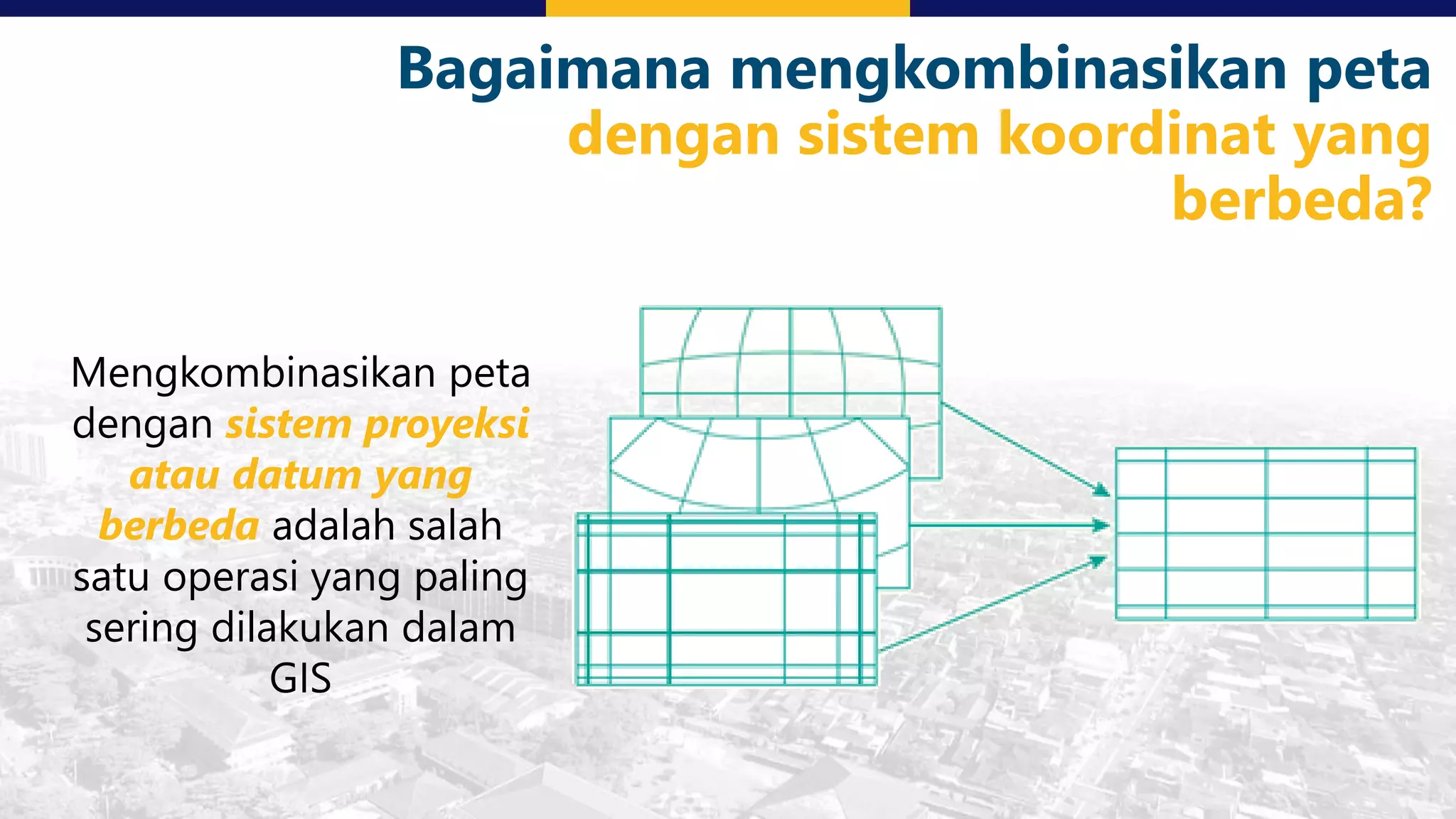
This document discusses coordinate system transformations and map projections. It begins with an introduction to coordinate systems and how they are used to give locations on maps. It then describes how the actual shape of the Earth is more like an ellipsoid than a perfect sphere. This leads to distortions when trying to represent the spherical Earth on a flat map. The document goes on to explain different map projections which try to minimize these distortions, though all projections distort some map properties. It emphasizes the importance of choosing the appropriate projection depending on what properties need to be preserved for the map's intended use. Transformations between different coordinate systems and projections are also covered.