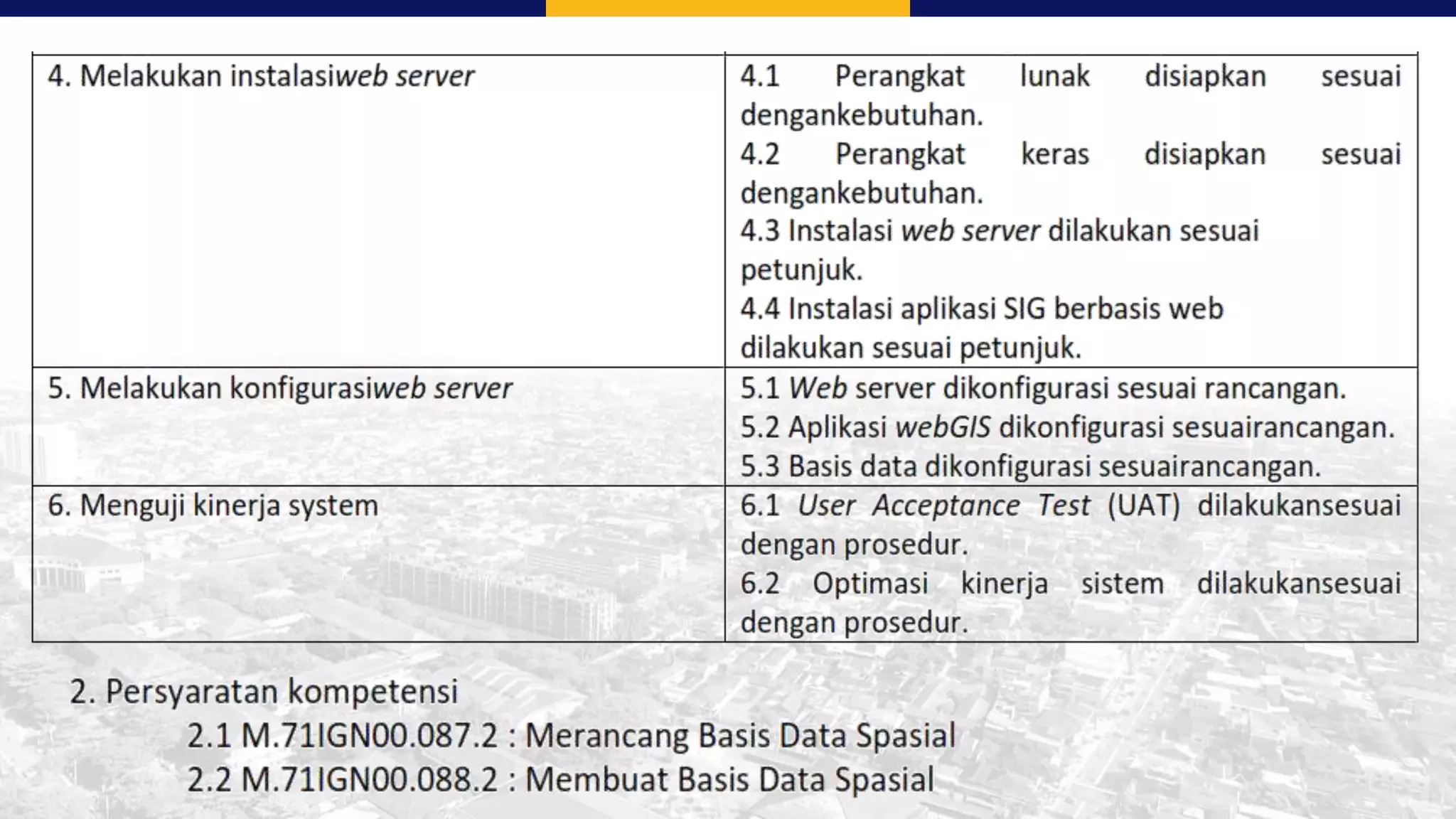
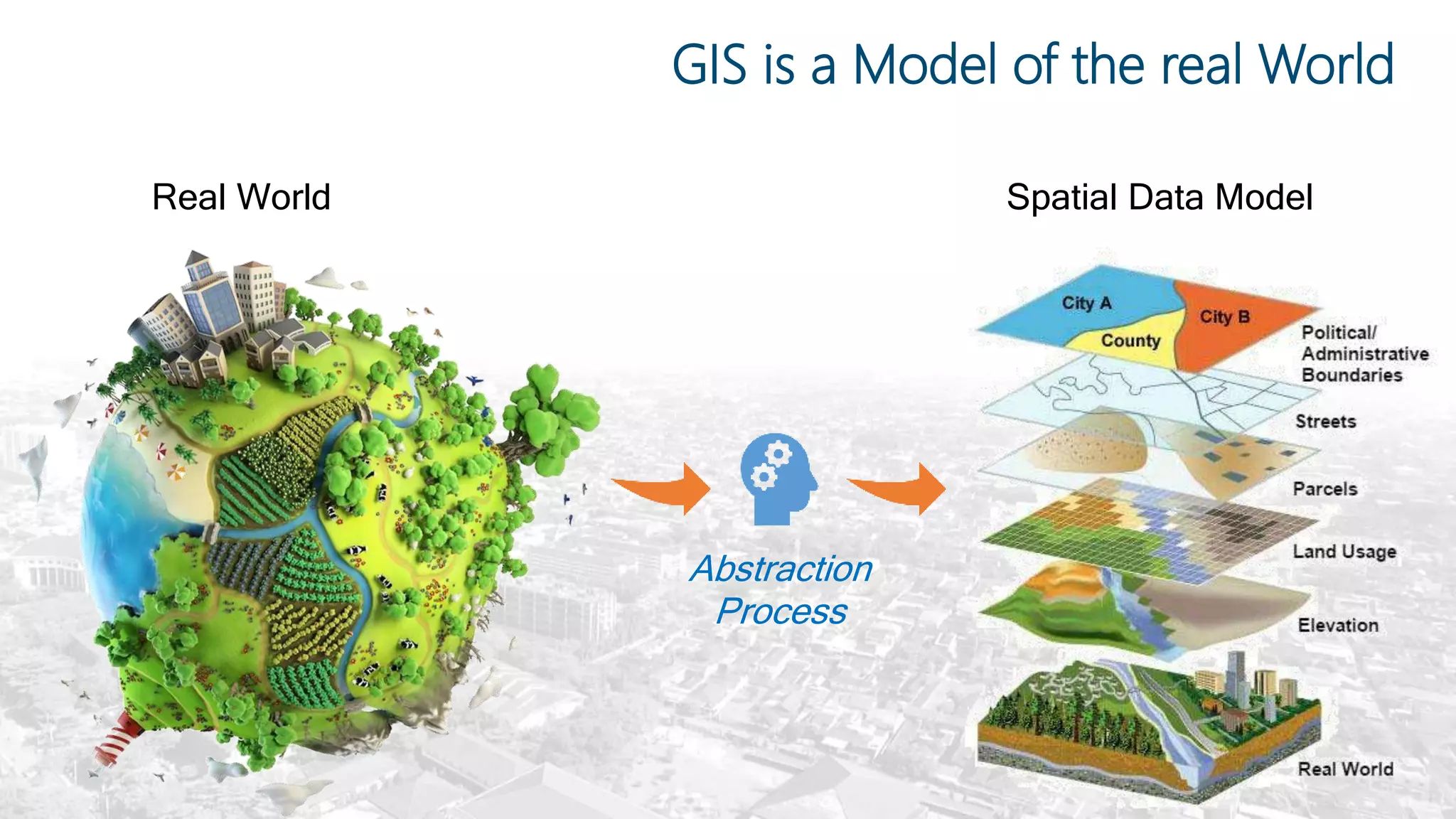
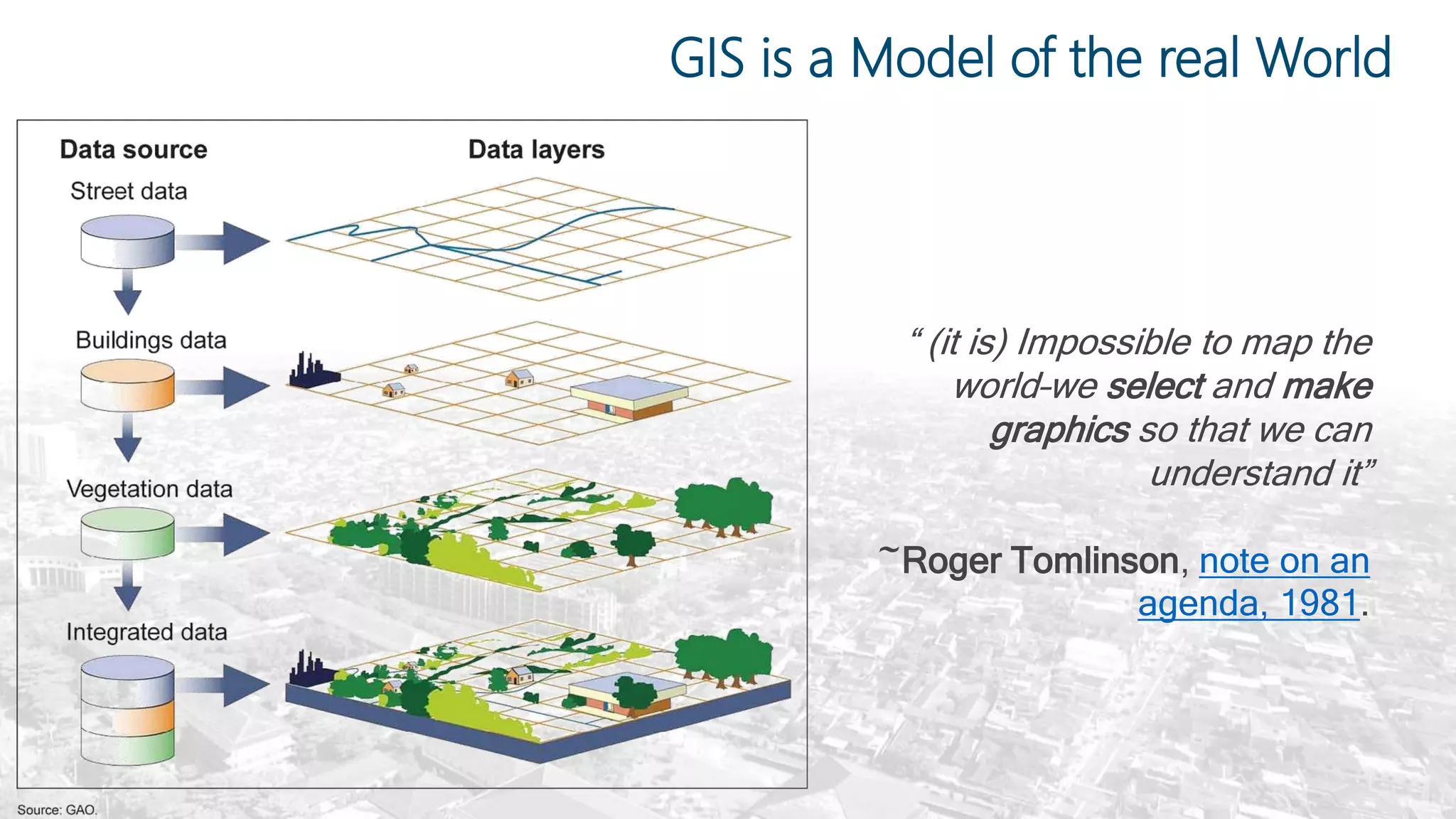
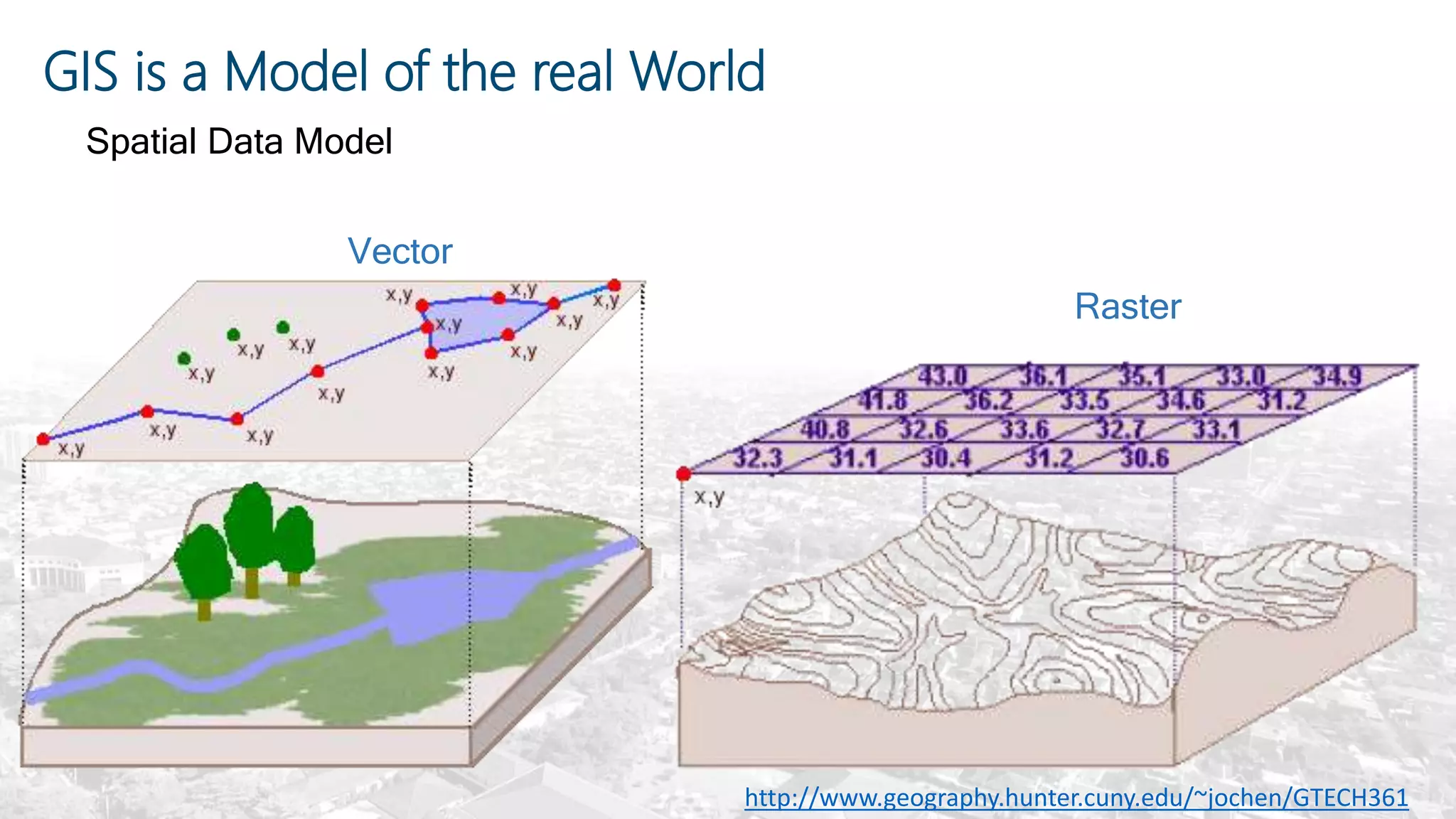
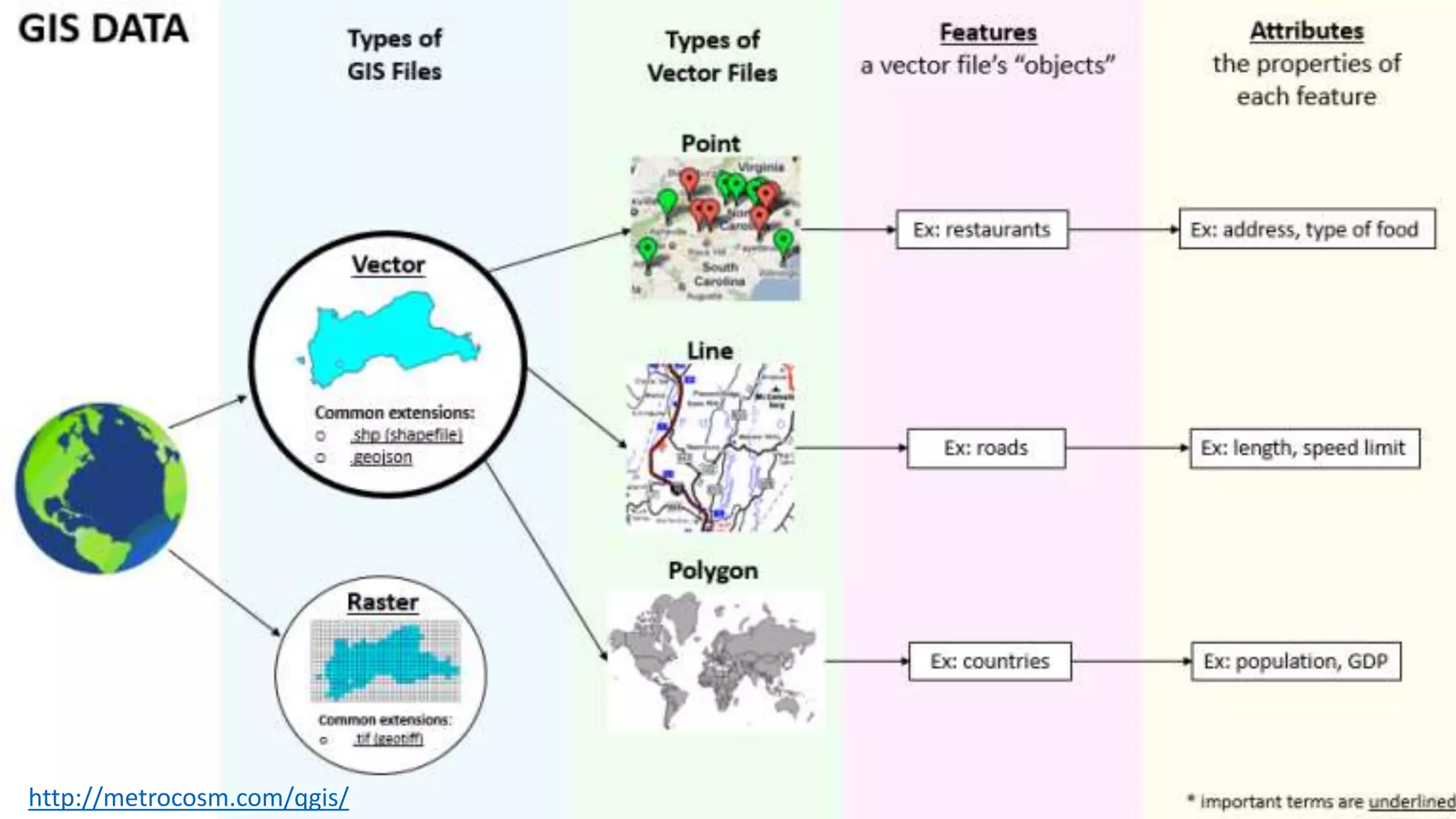
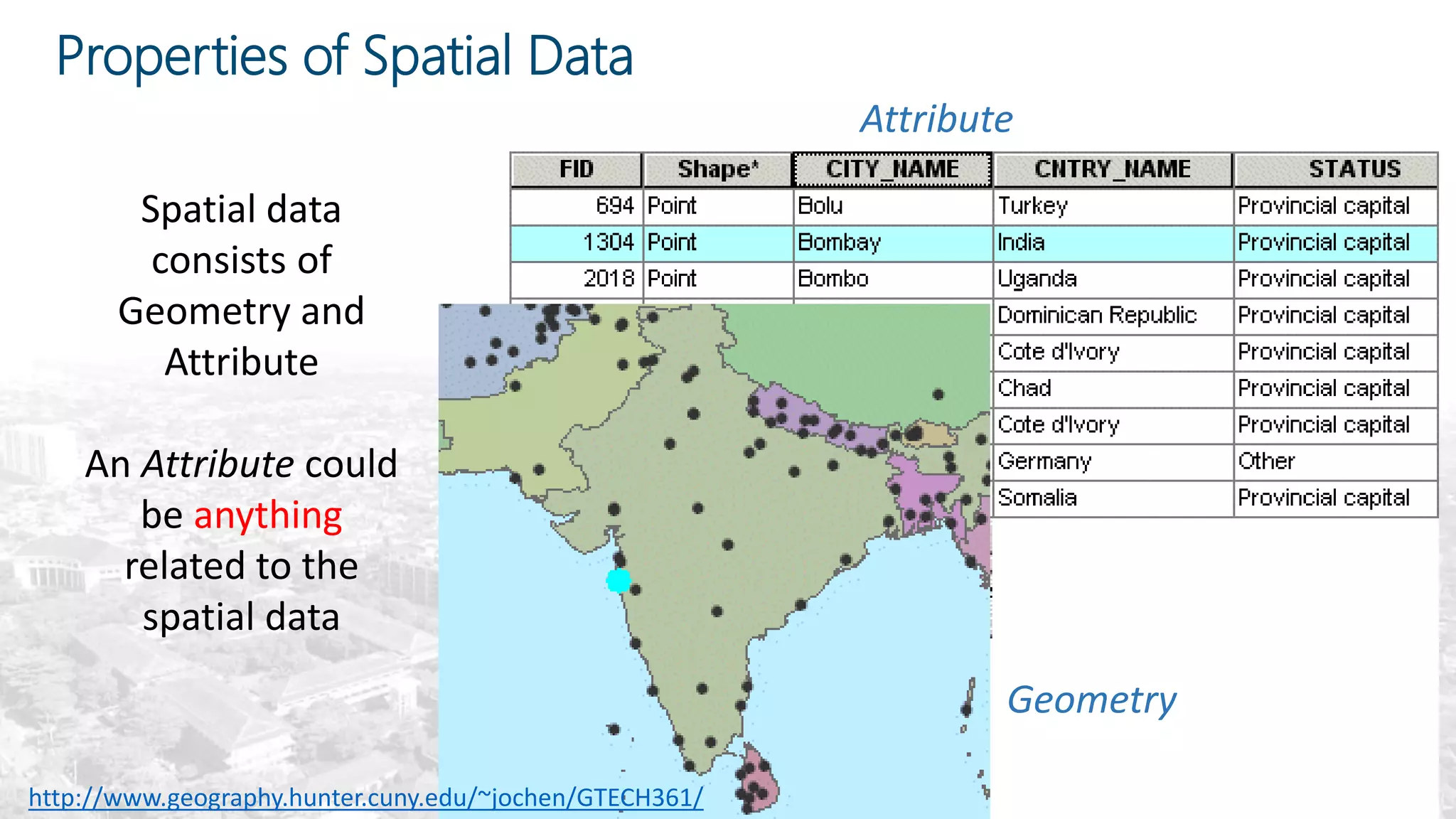
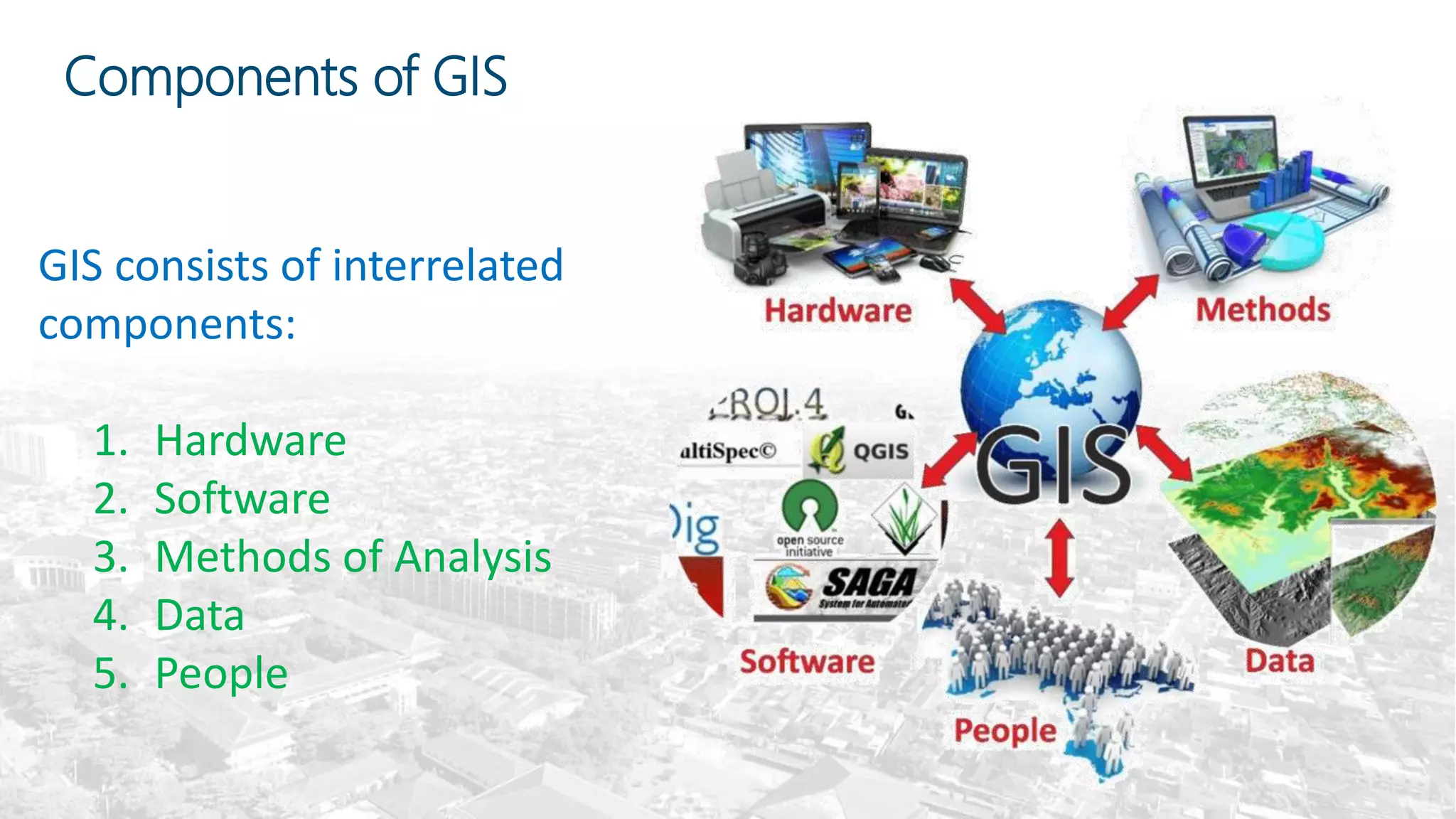
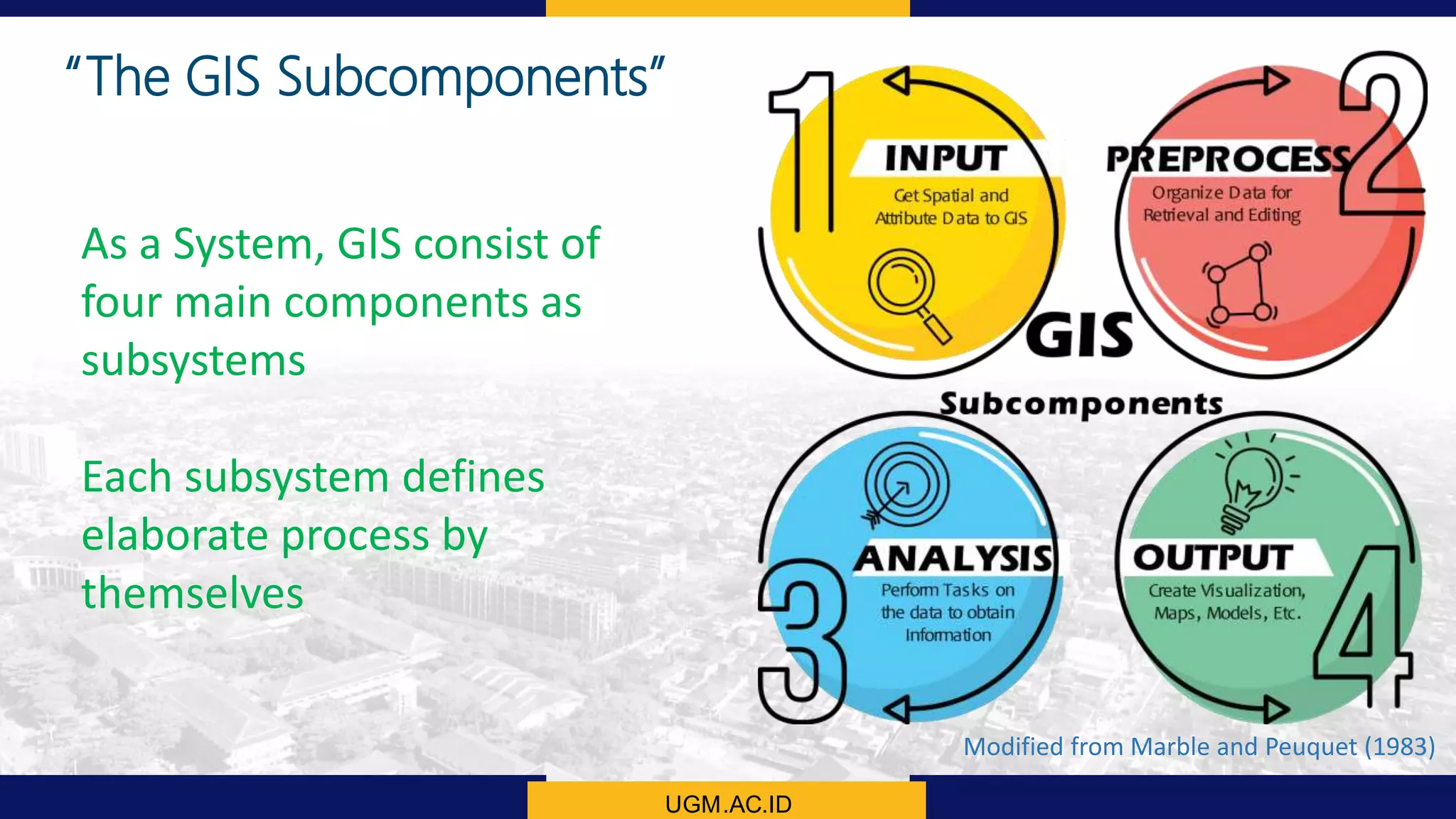
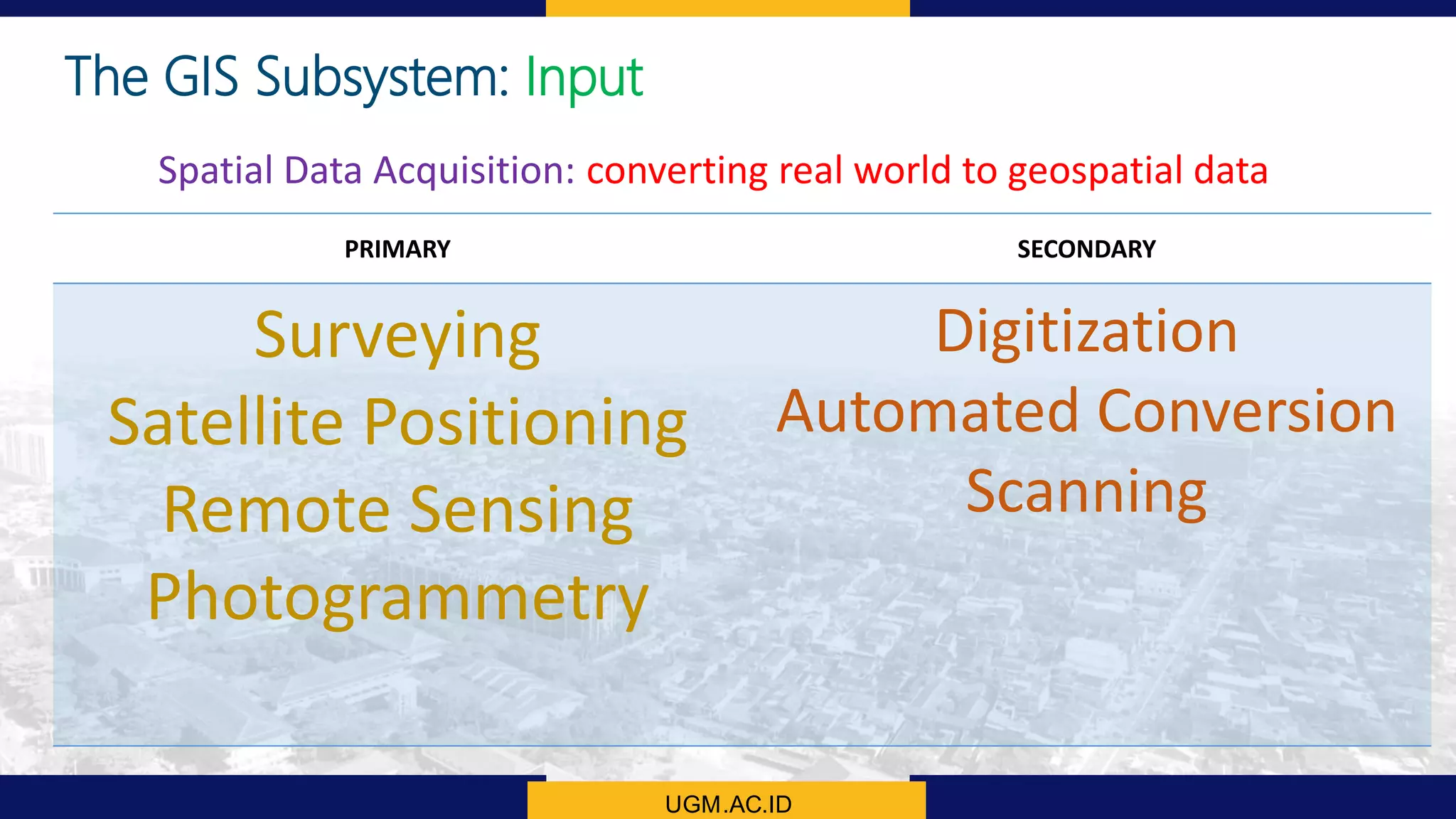
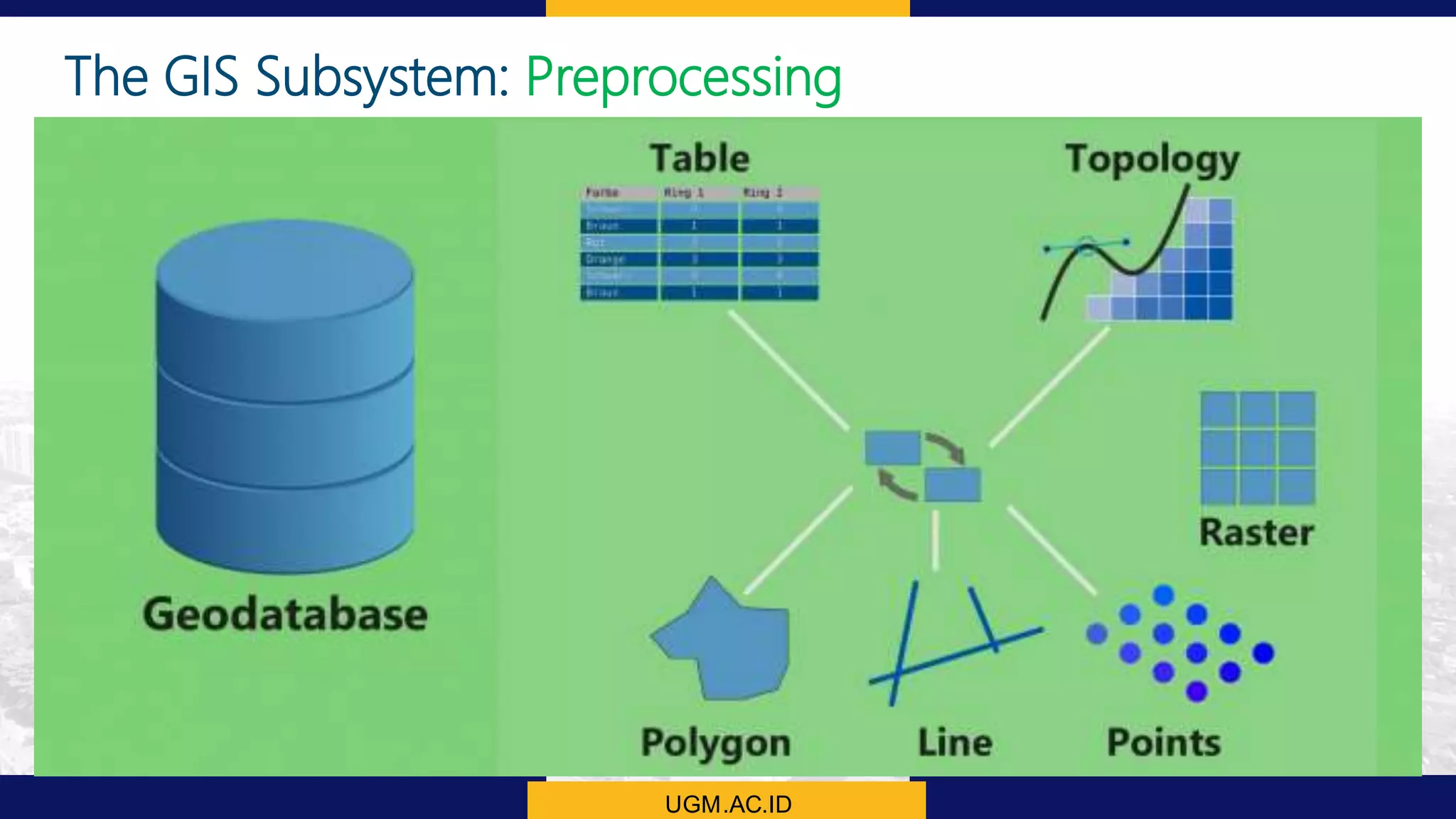
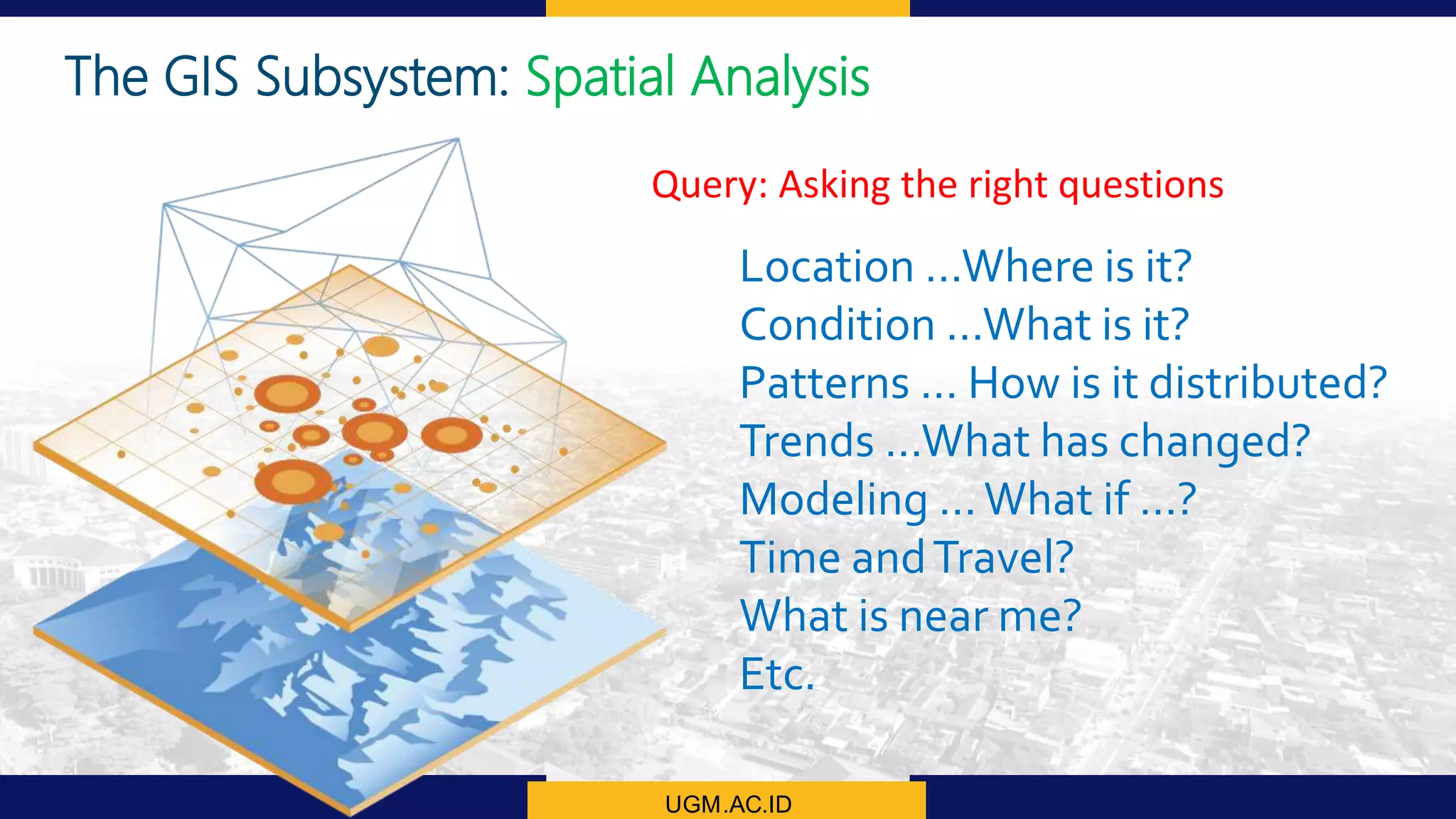
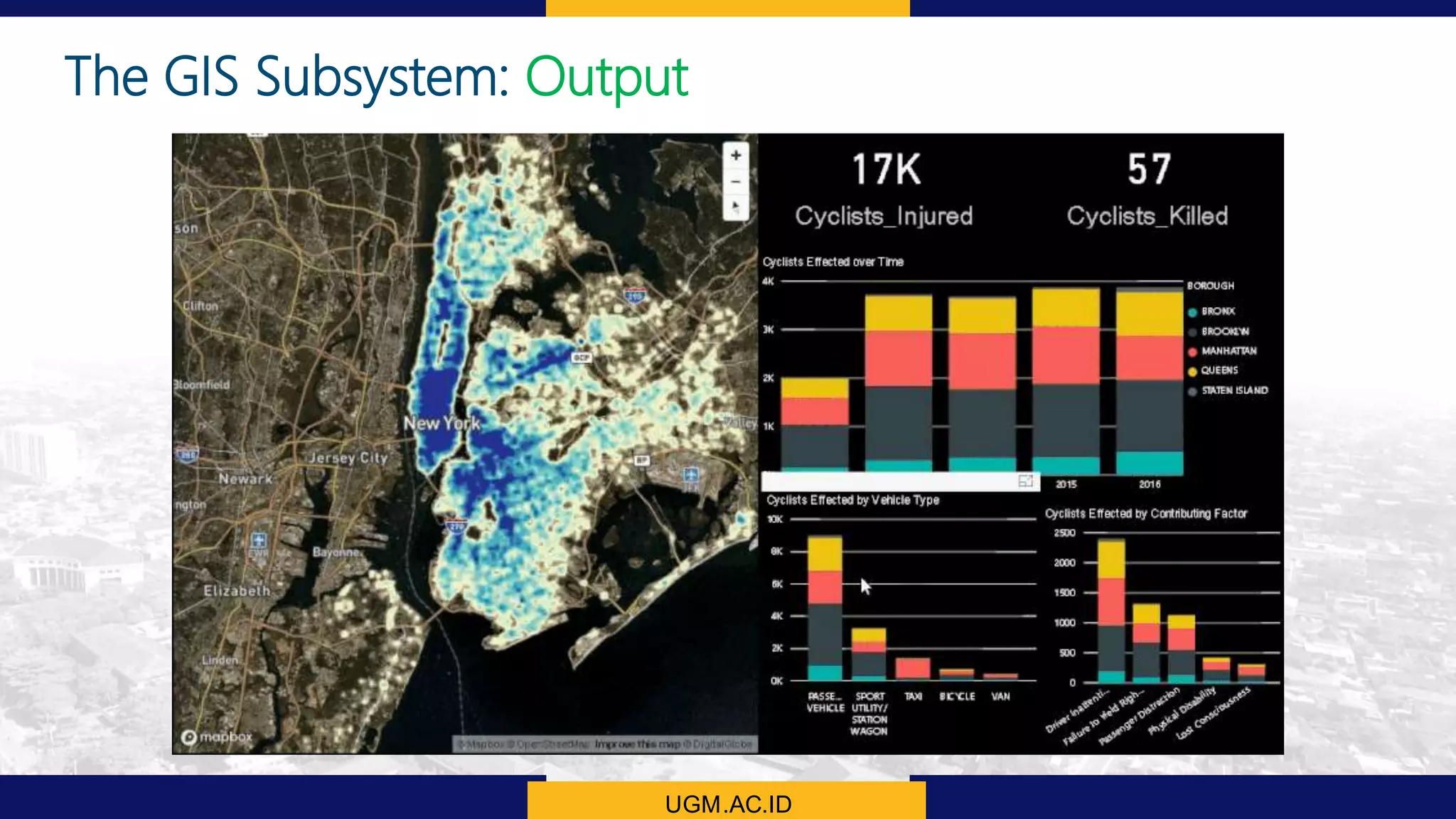
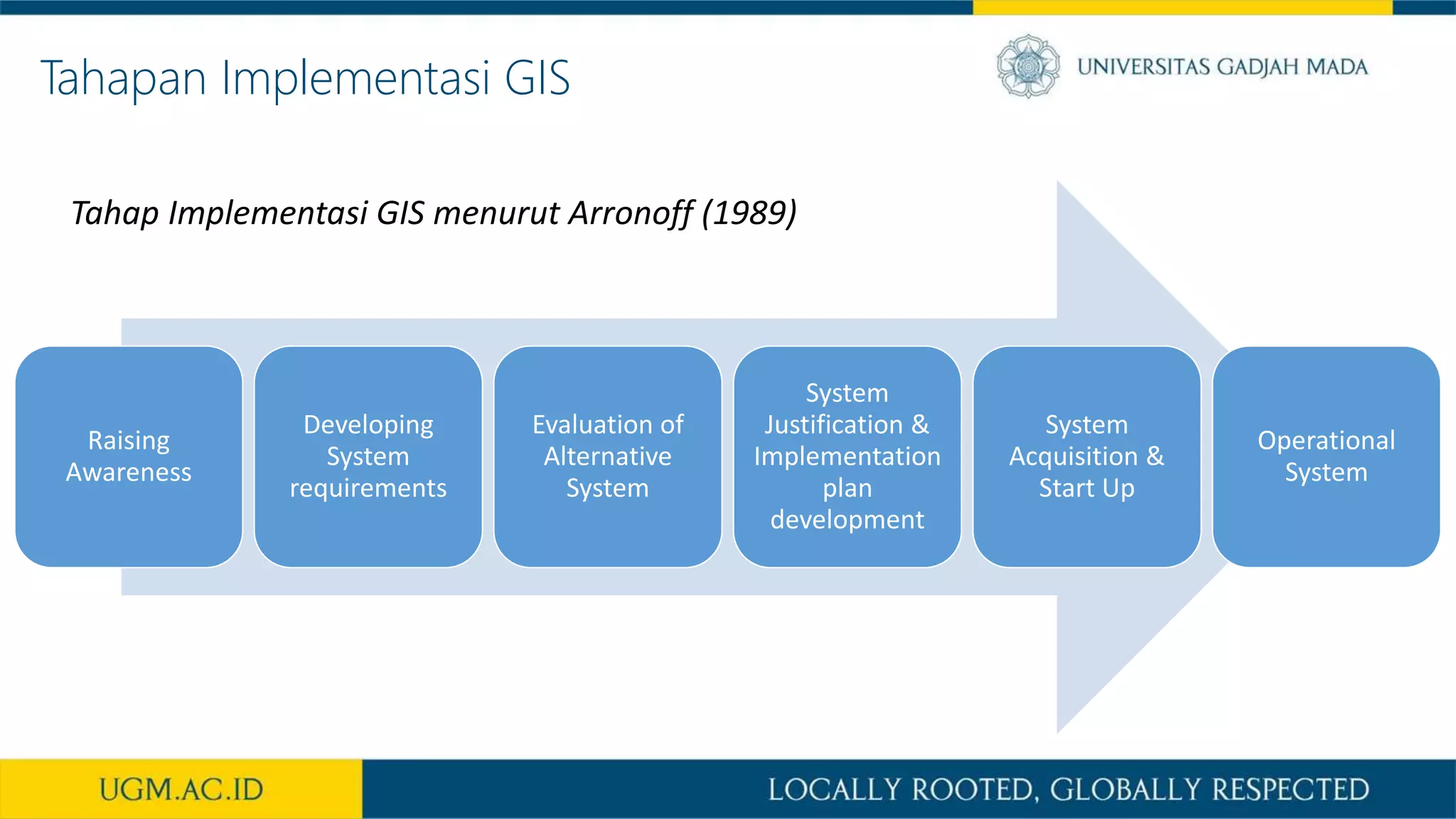
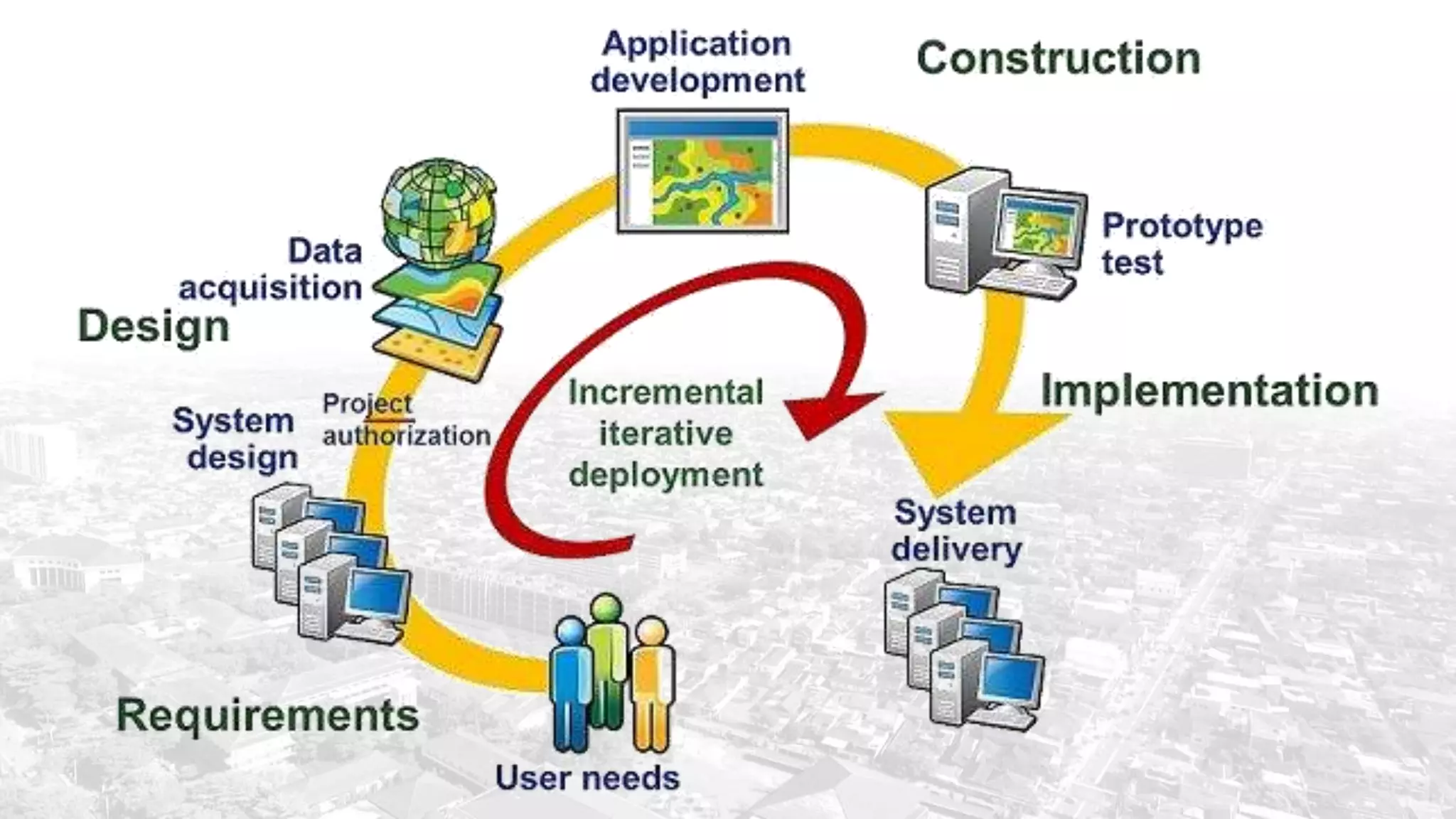
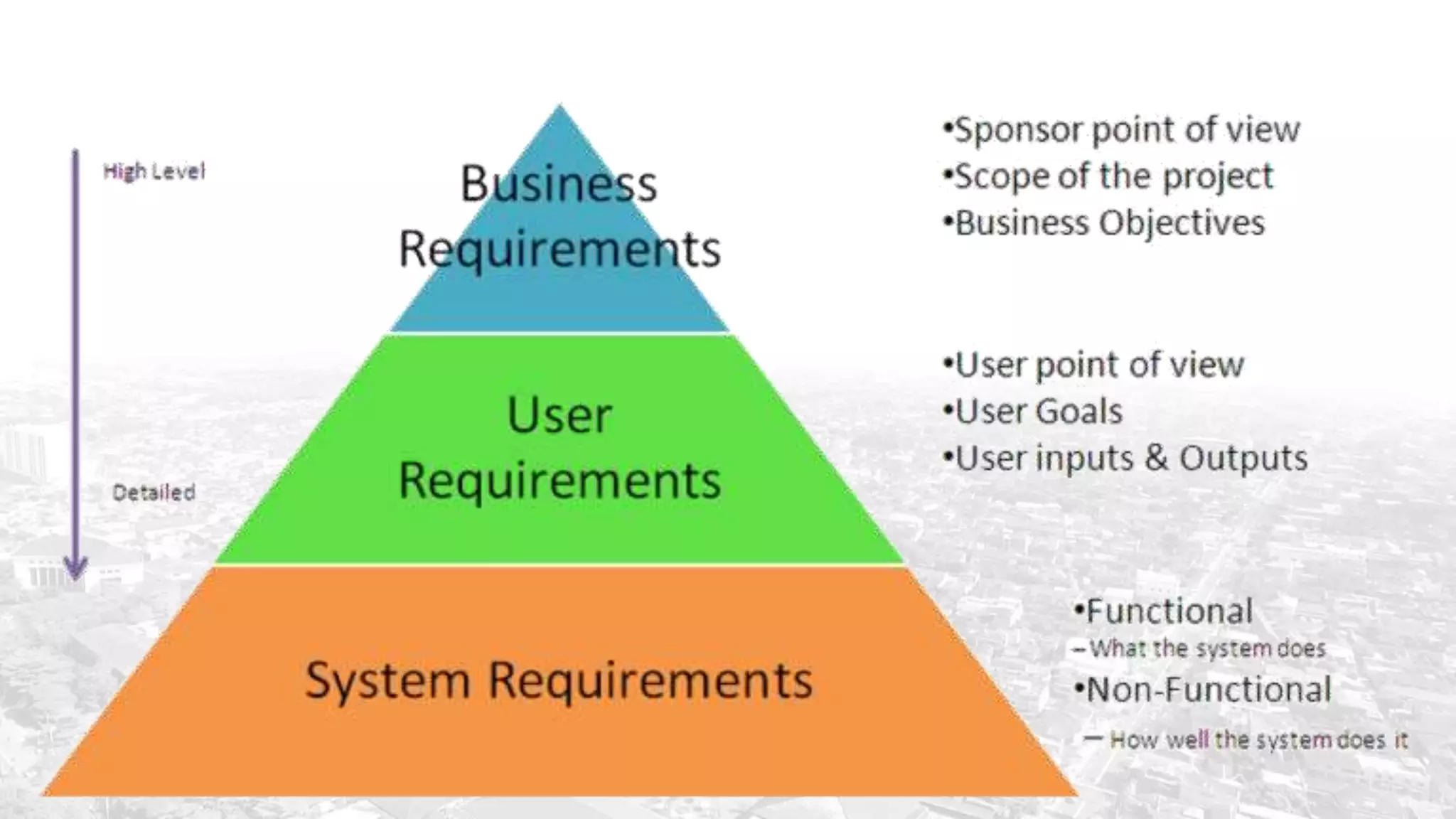
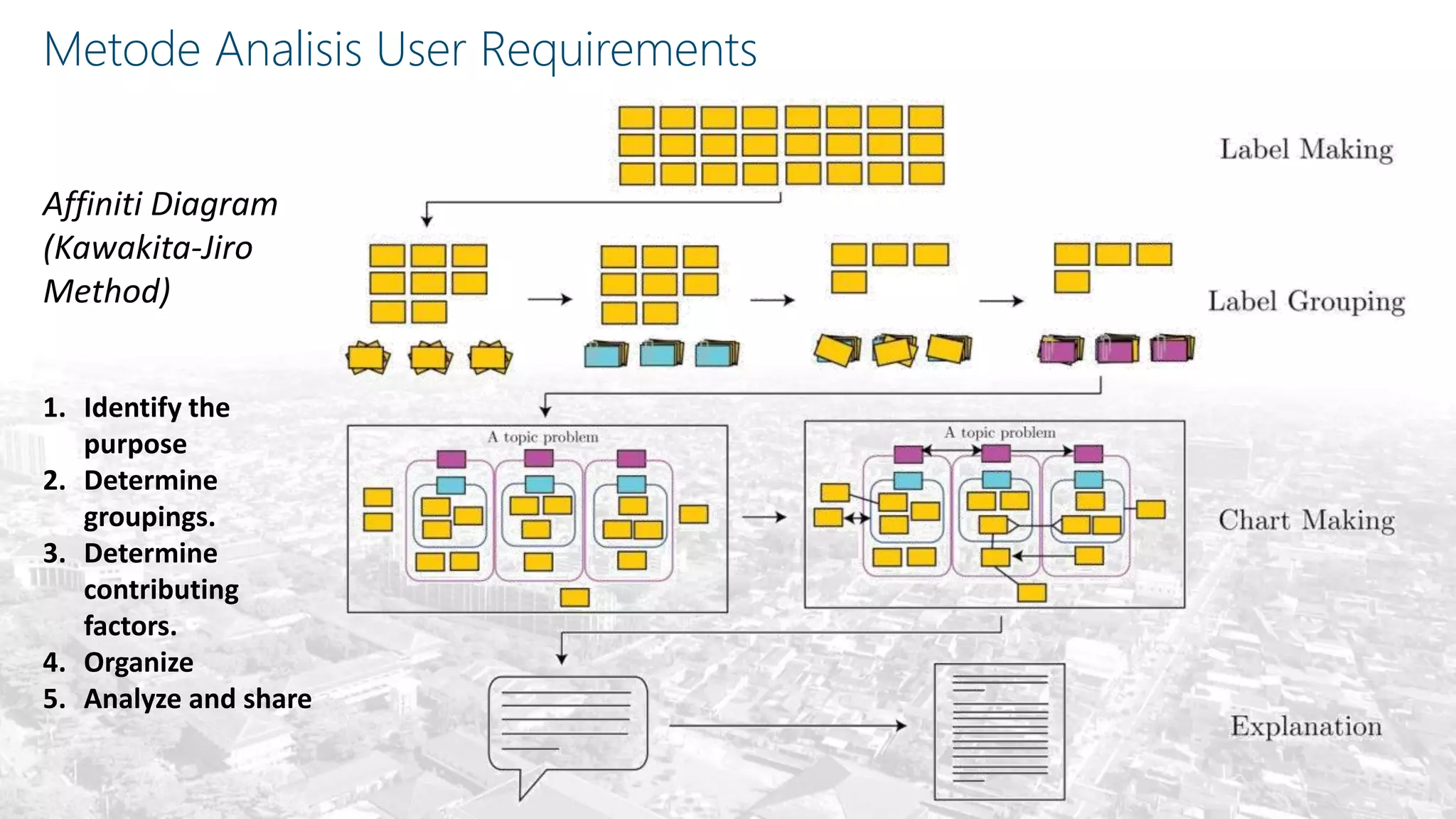
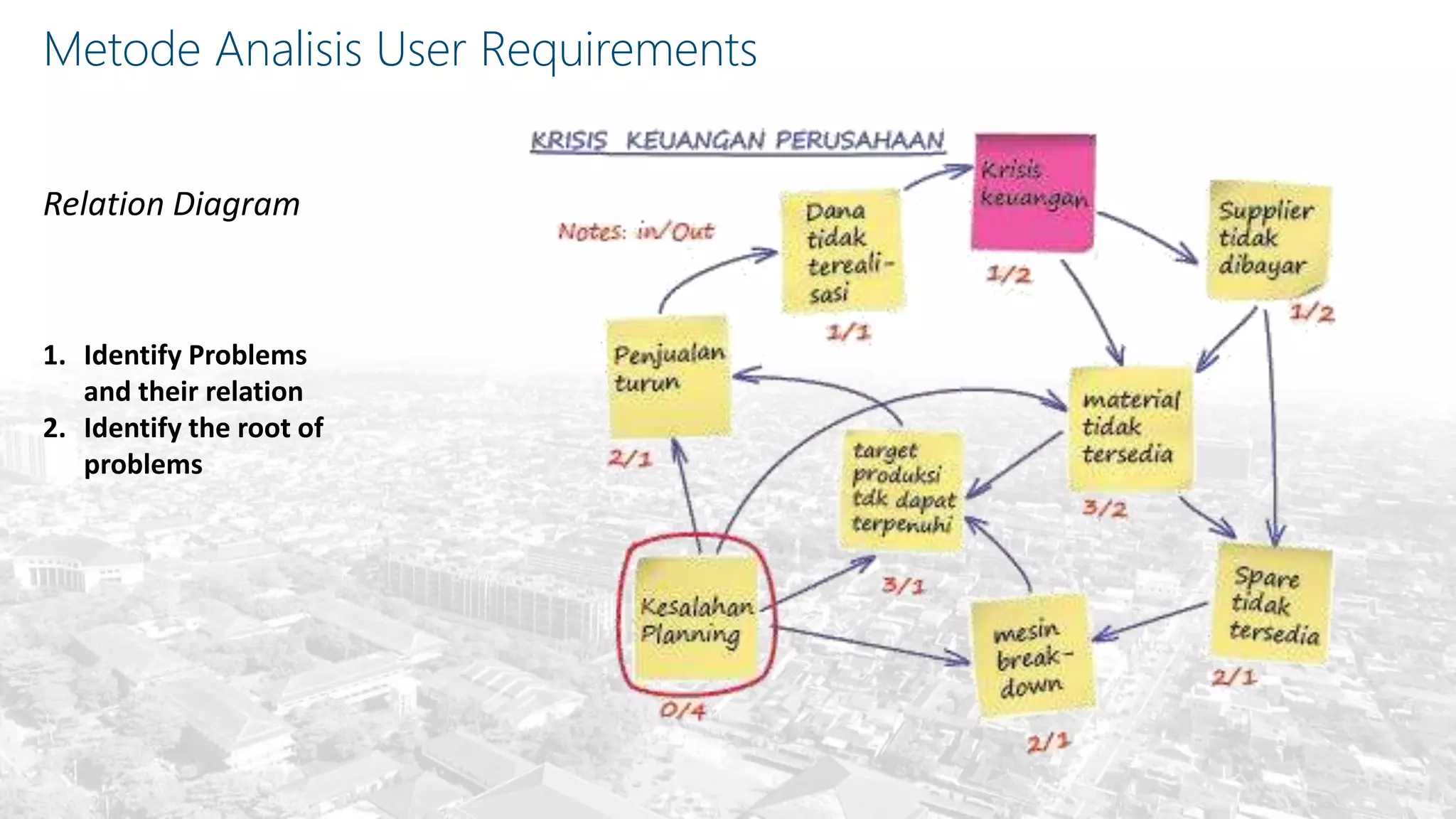
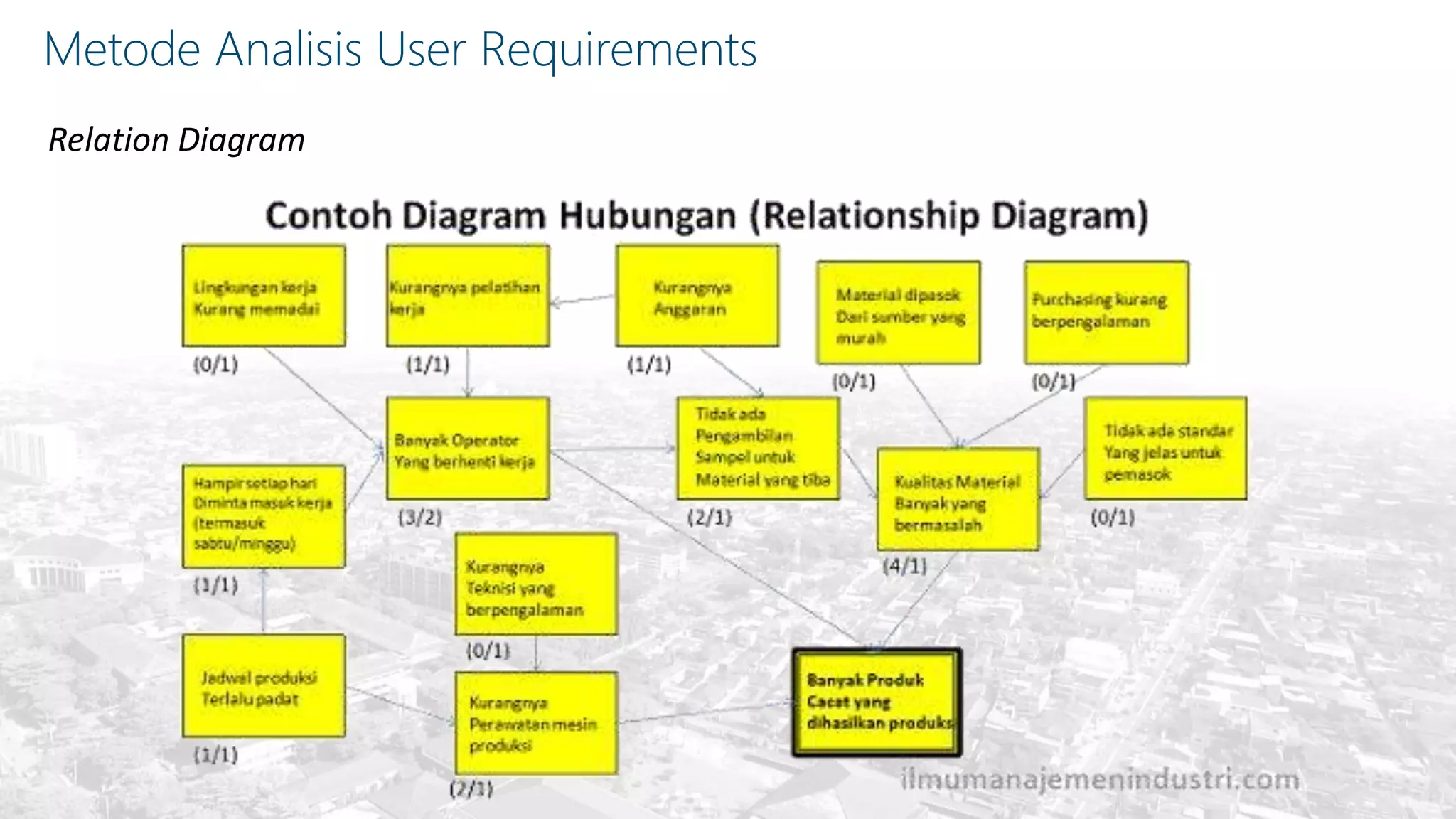
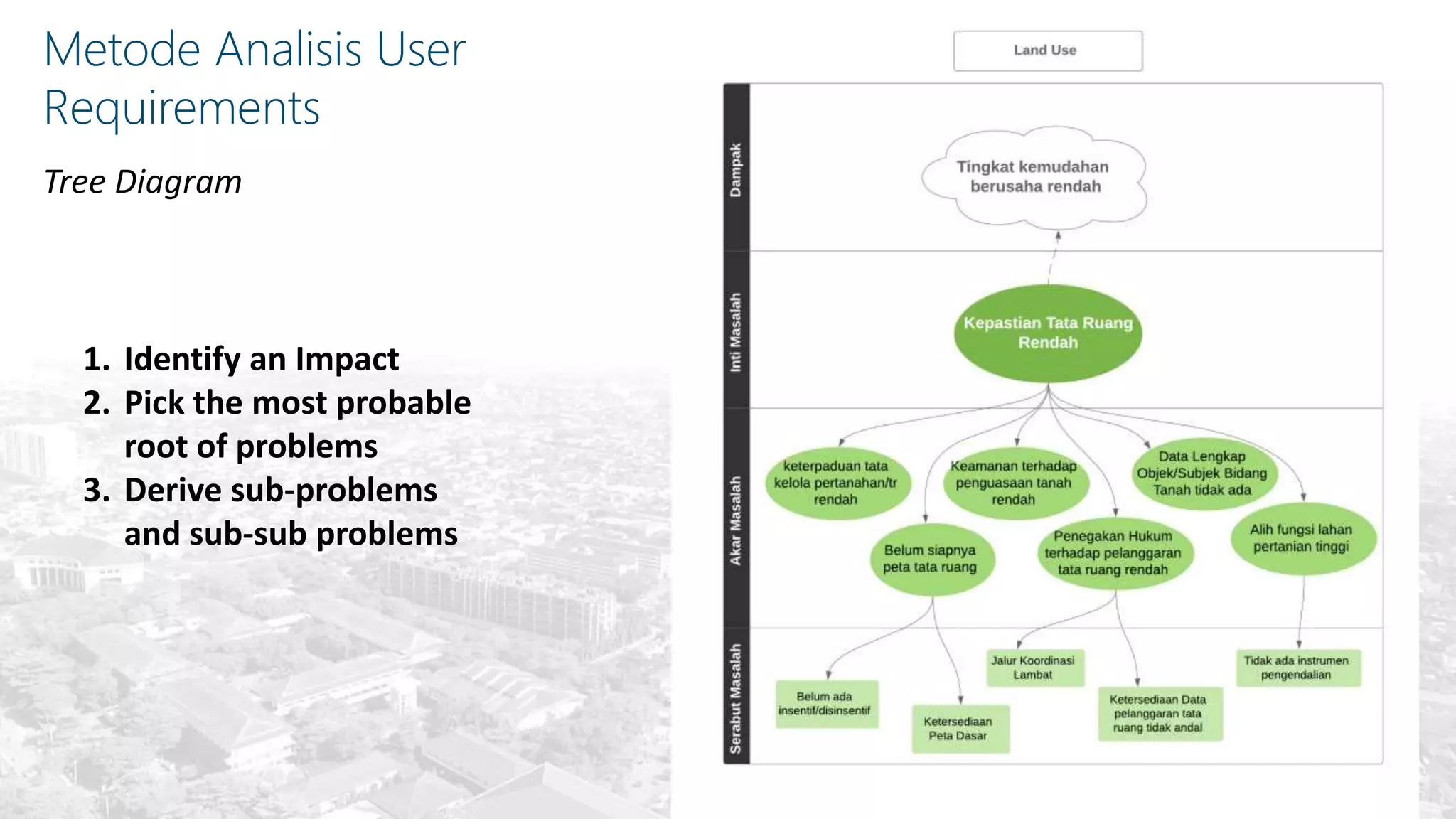
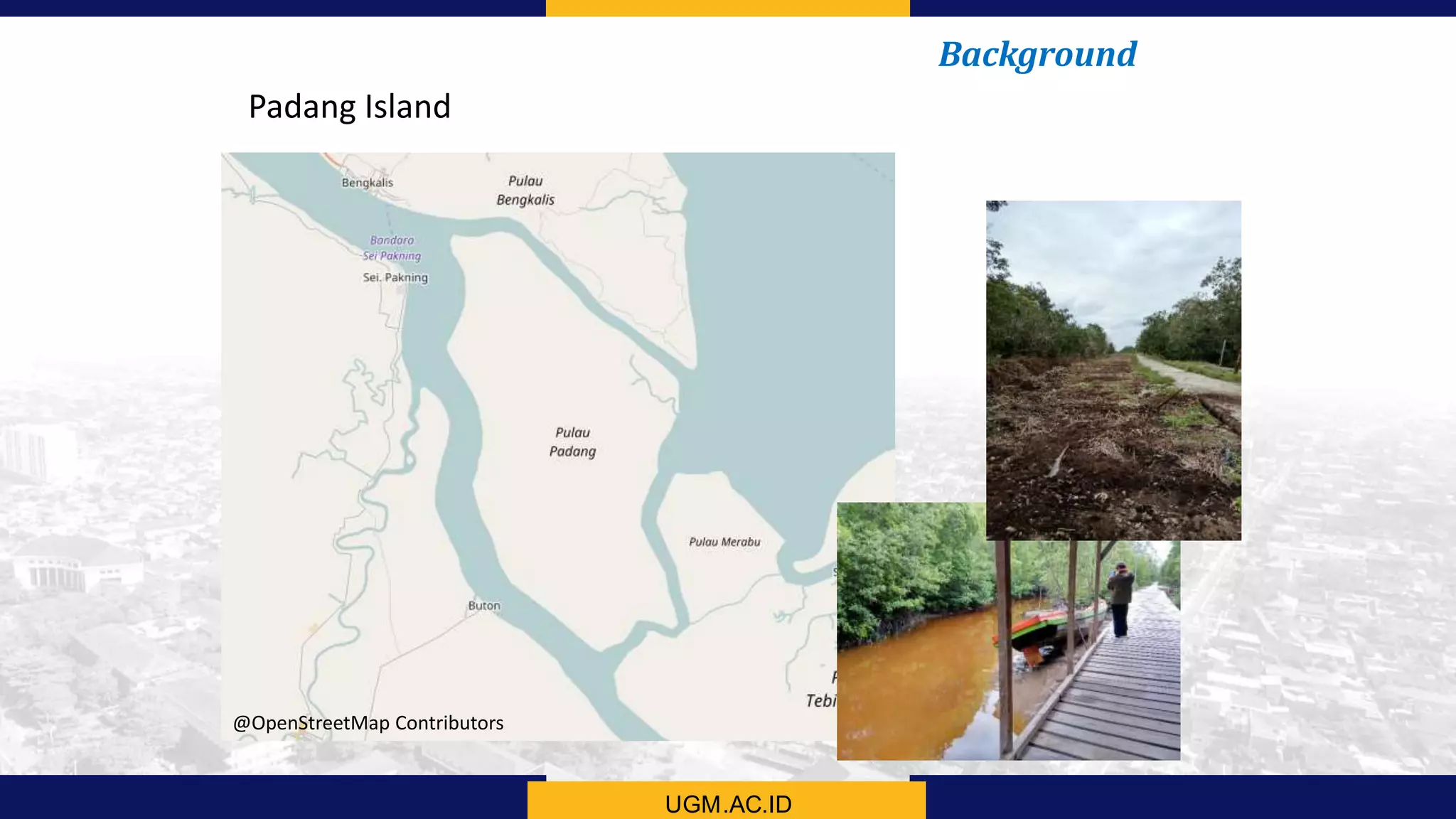
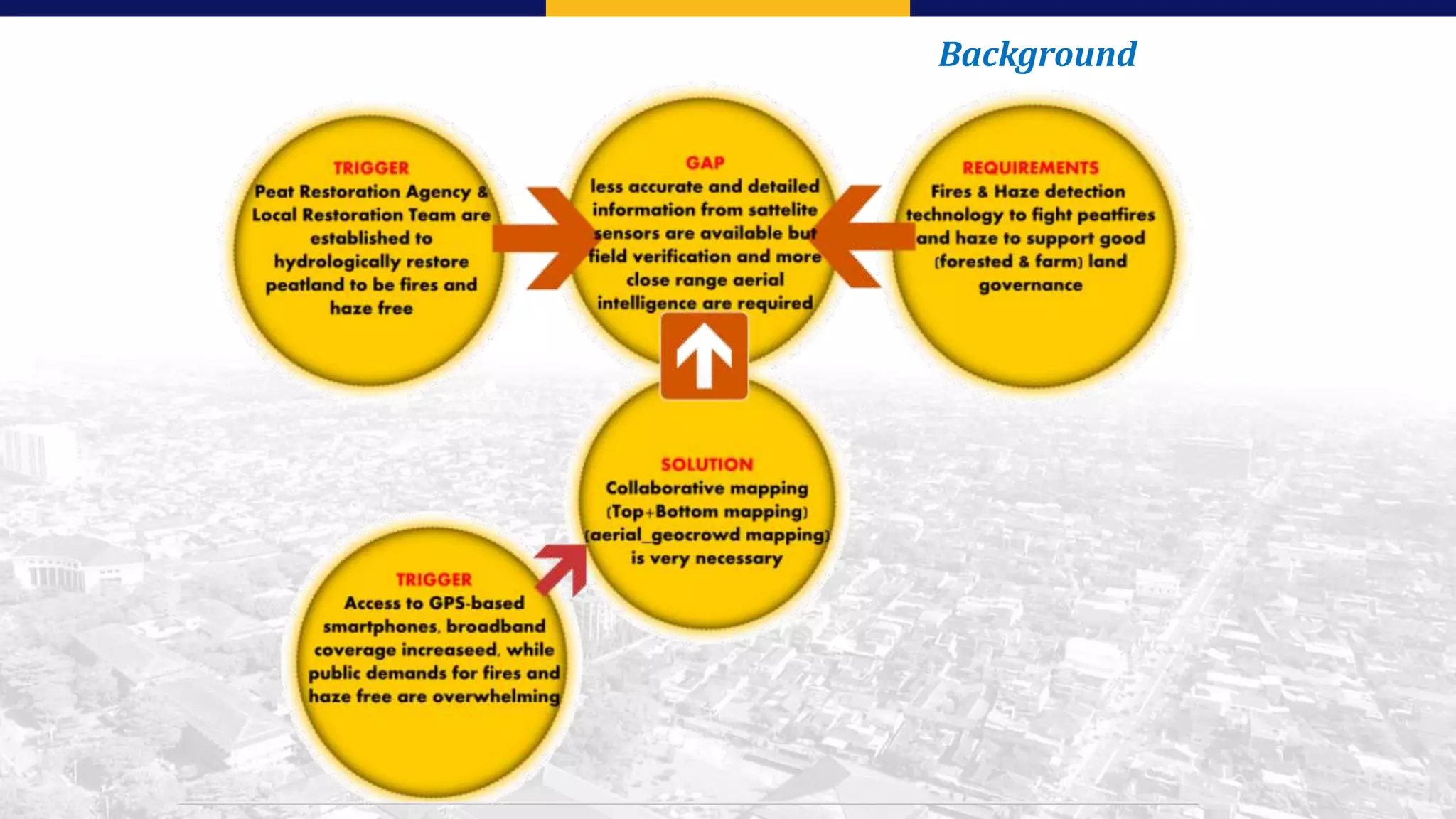
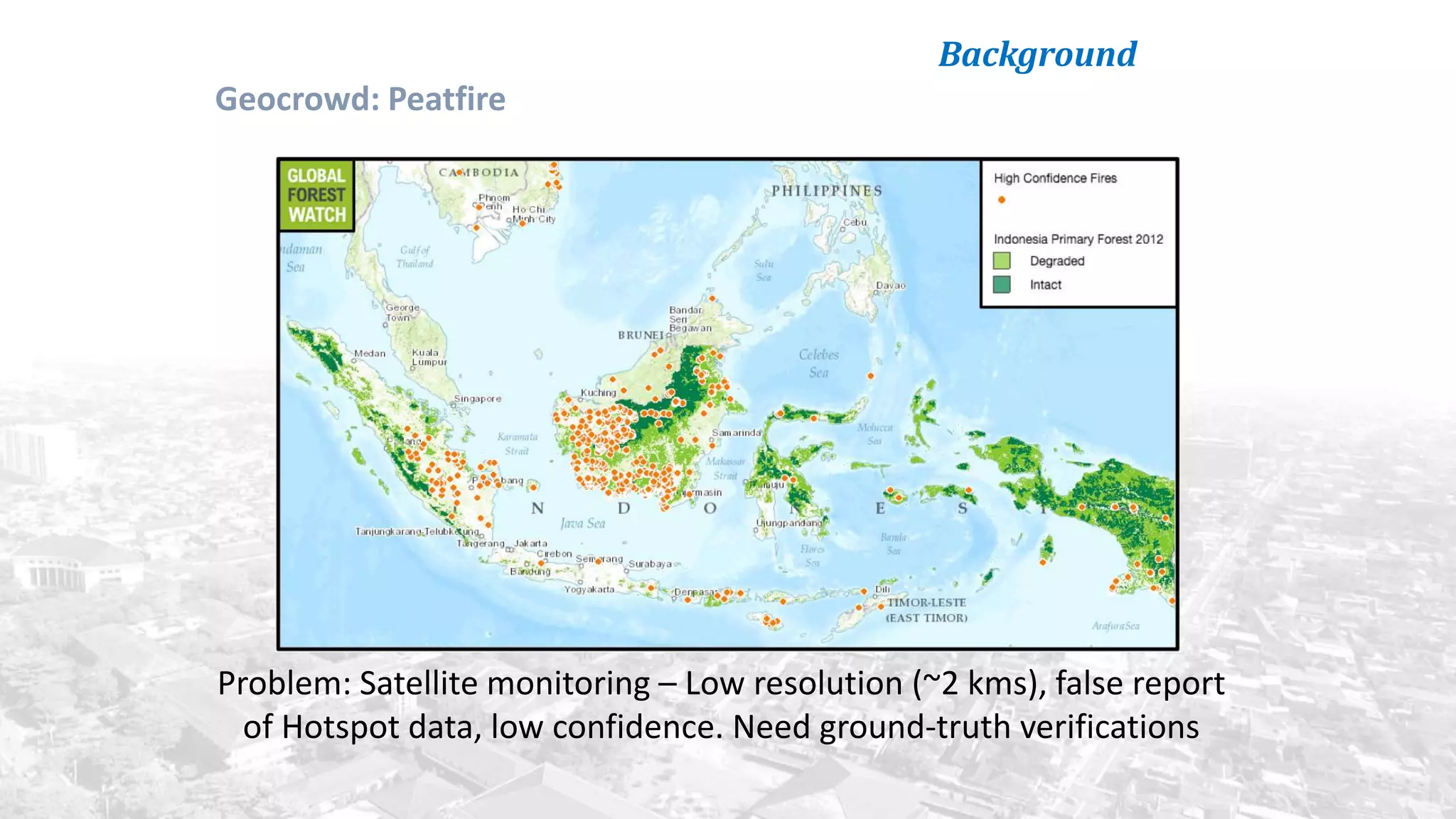
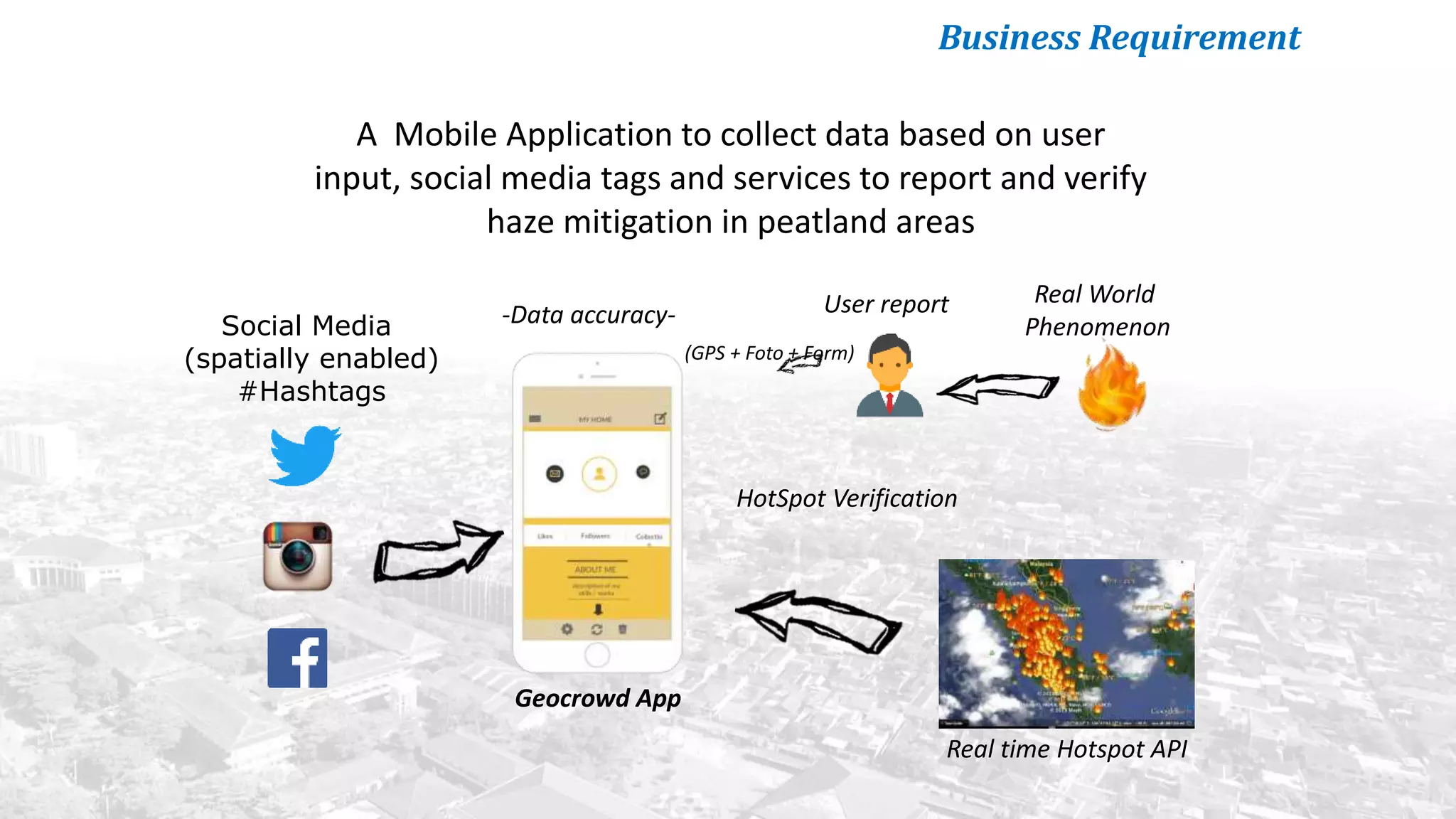
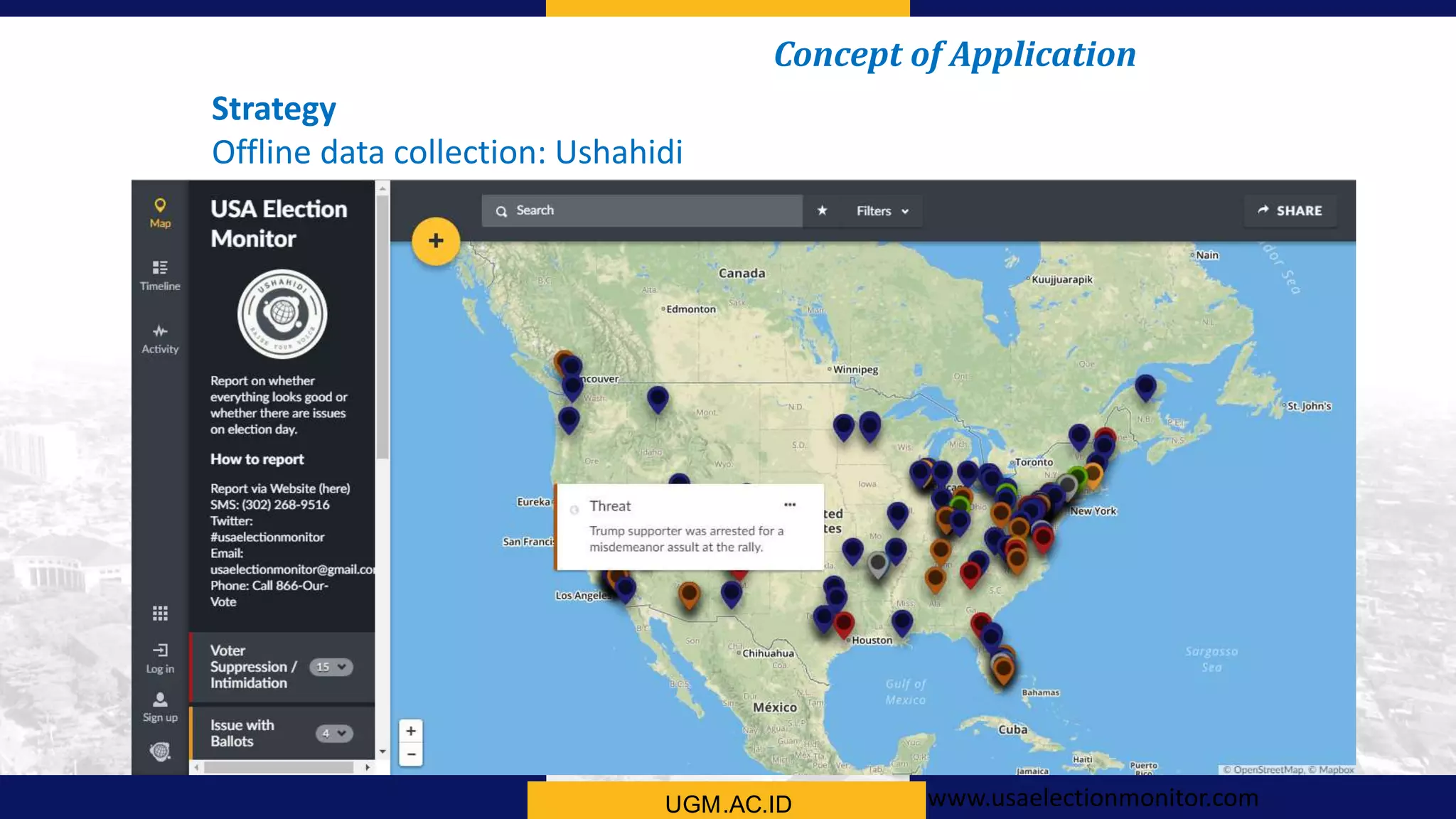
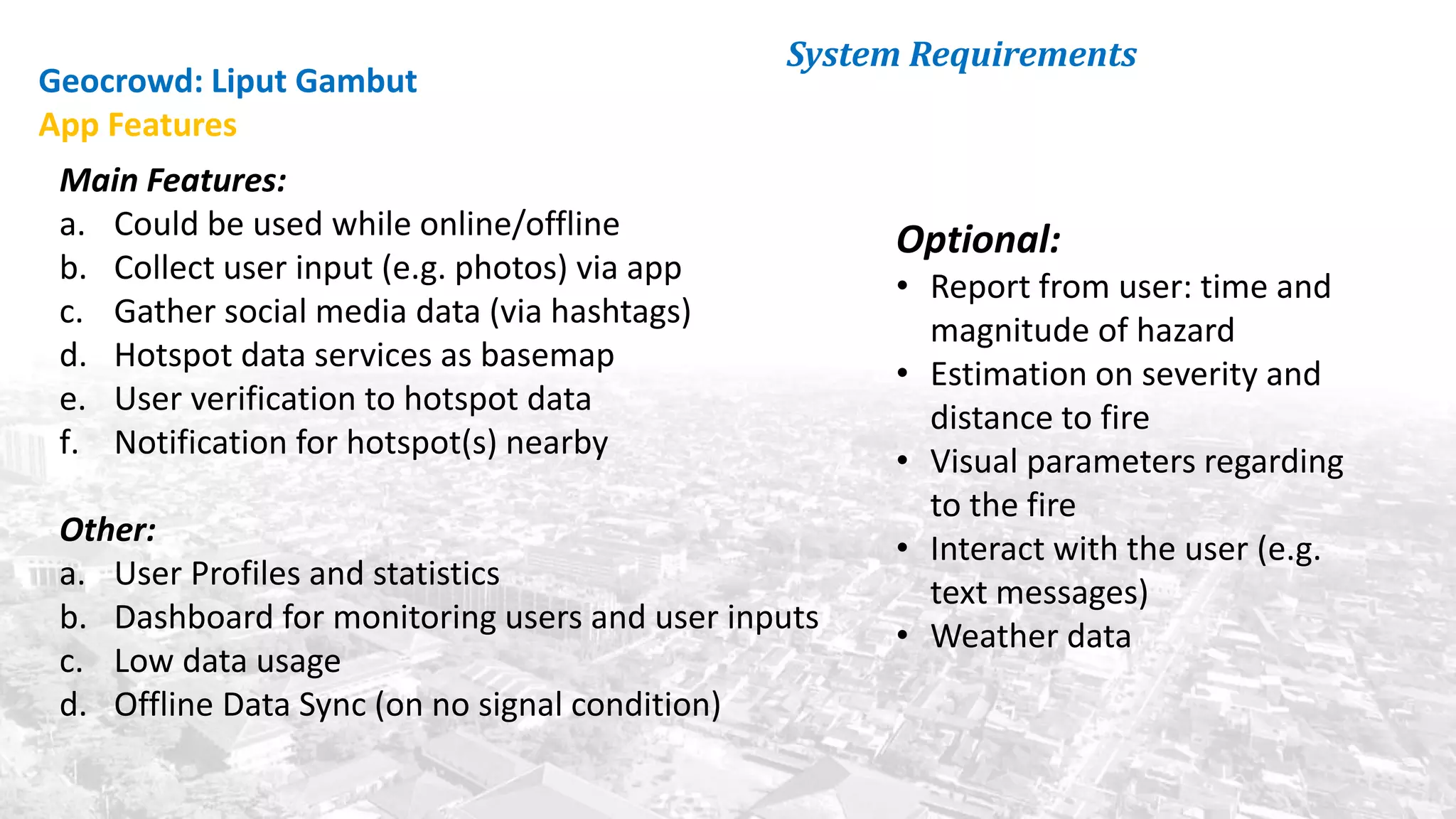
This document summarizes the key points from a training presentation on analyzing system requirements for a geographic information system (GIS). It discusses how GIS works as a model of the real world through abstraction and spatial data modeling. The components of a GIS are explained, including hardware, software, methods of analysis, data, and people. Methods for analyzing user requirements like affinity diagrams, relation diagrams, and tree diagrams are presented. The document also provides background on a project to develop a mobile application called "Geocrowd: Peatfire" to help monitor and prevent peatland fires on Padang Island through crowd-sourced reporting and satellite data verification. System and user requirements for the app are outlined, including the ability to work