This document provides details about installing a turbocharger on a 125cc single cylinder motorcycle engine to increase its efficiency. It discusses designing and fabricating a turbocharger prototype that was implemented on a two-wheeler. The summary is:
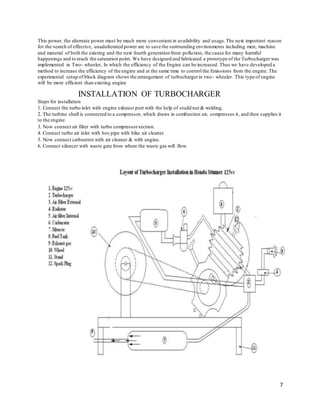
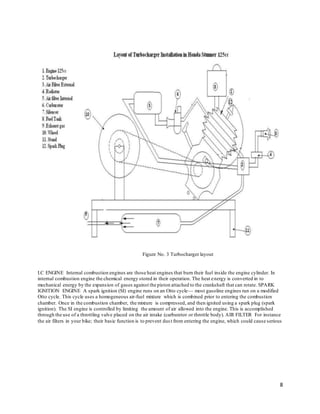
1. The document outlines the steps to install a turbocharger on a Honda Stunner CBF 125cc motorcycle, including connecting the turbocharger inlet to the exhaust port and connecting the air filter, carburetor, and intake manifold.
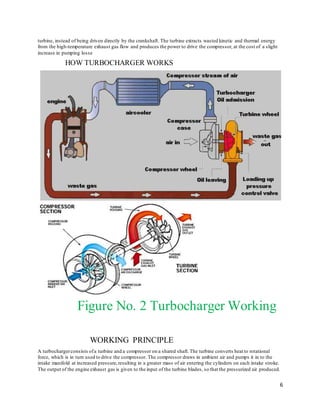
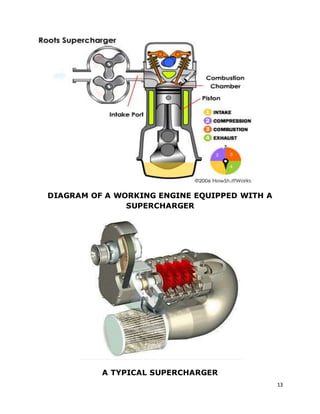
2. It explains that a turbocharger uses the engine's exhaust gases to drive a turbine, which spins a compressor to force more air into the combustion chamber, allowing more fuel and increased power output.