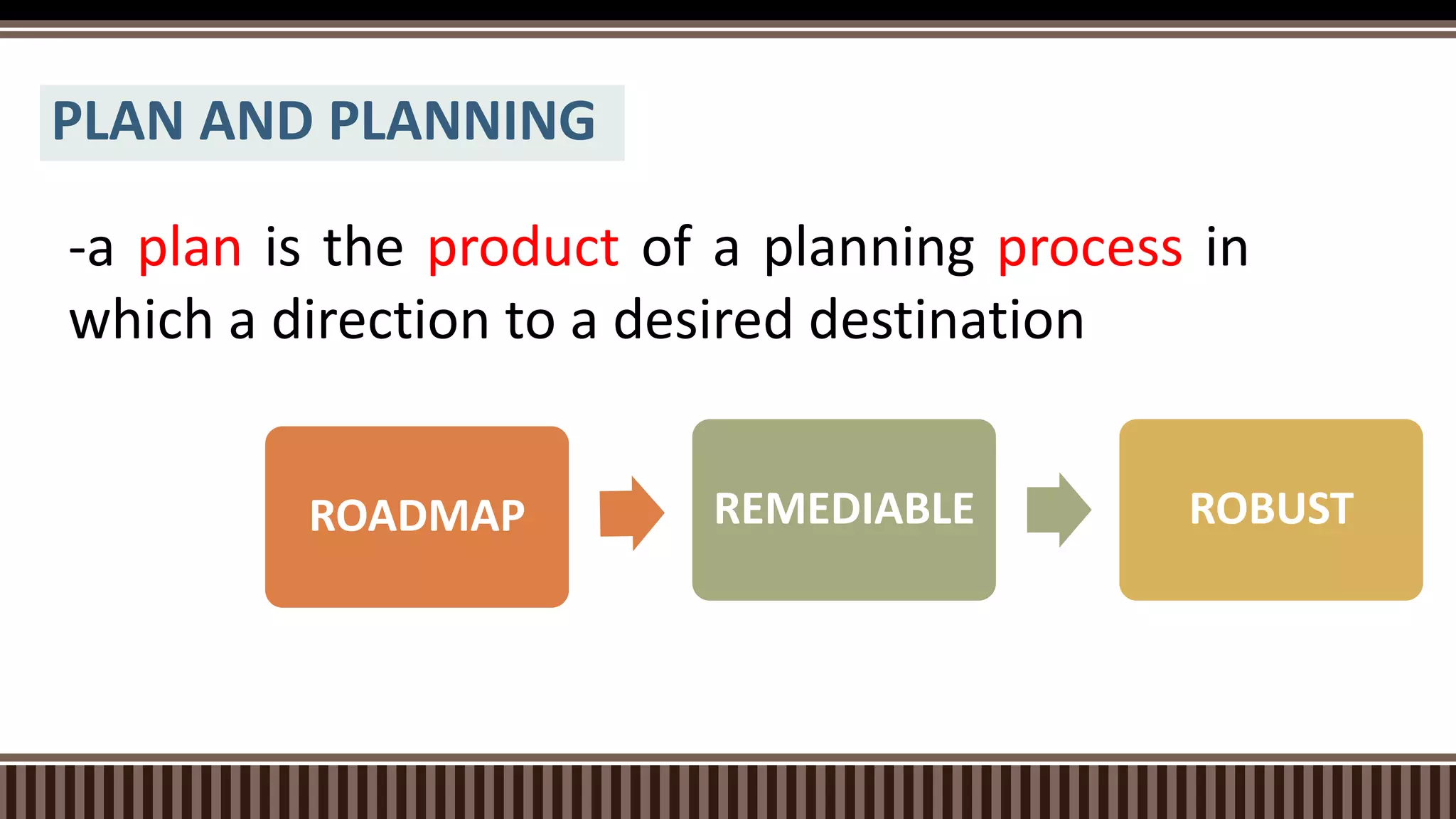
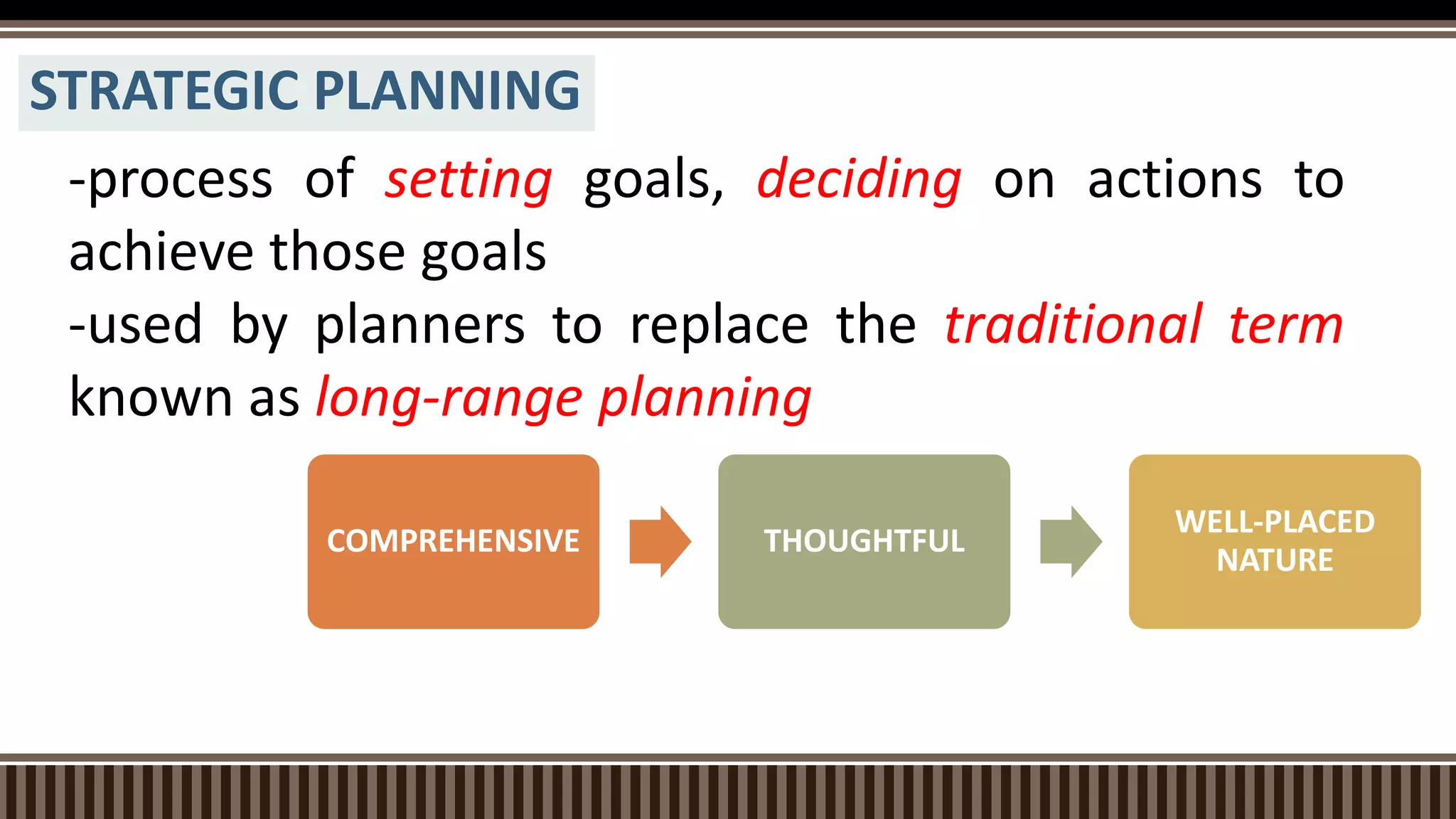
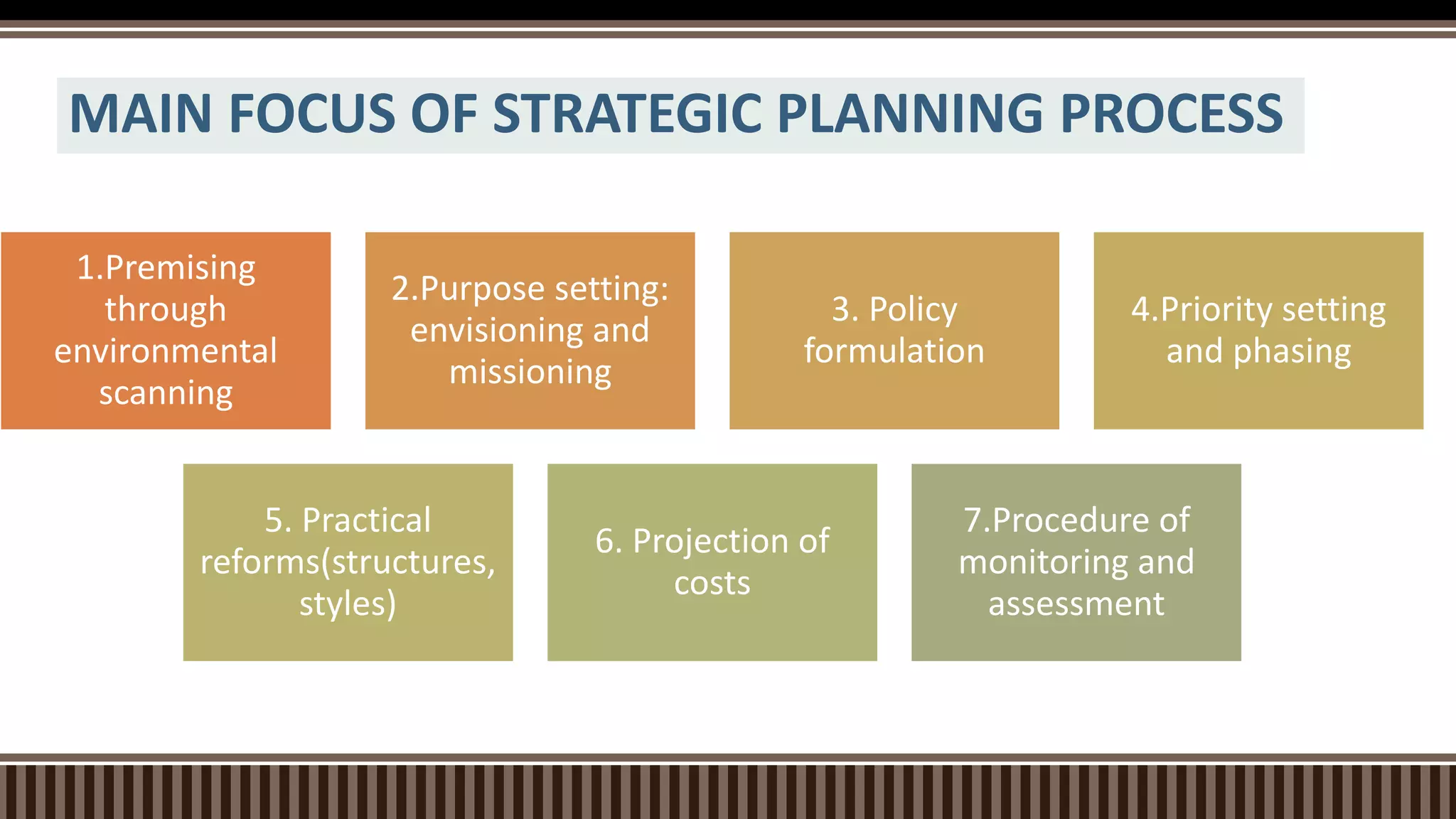
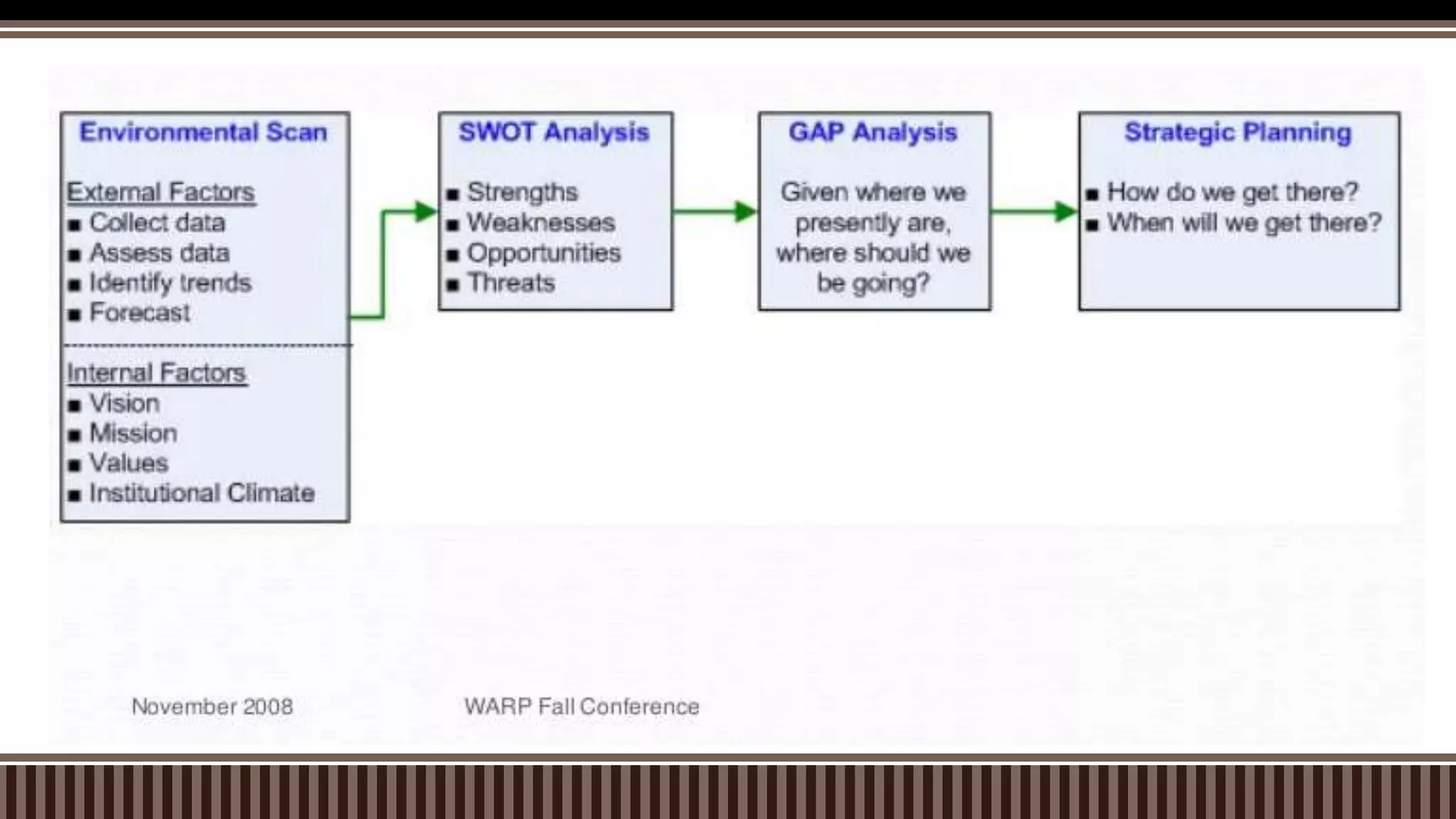
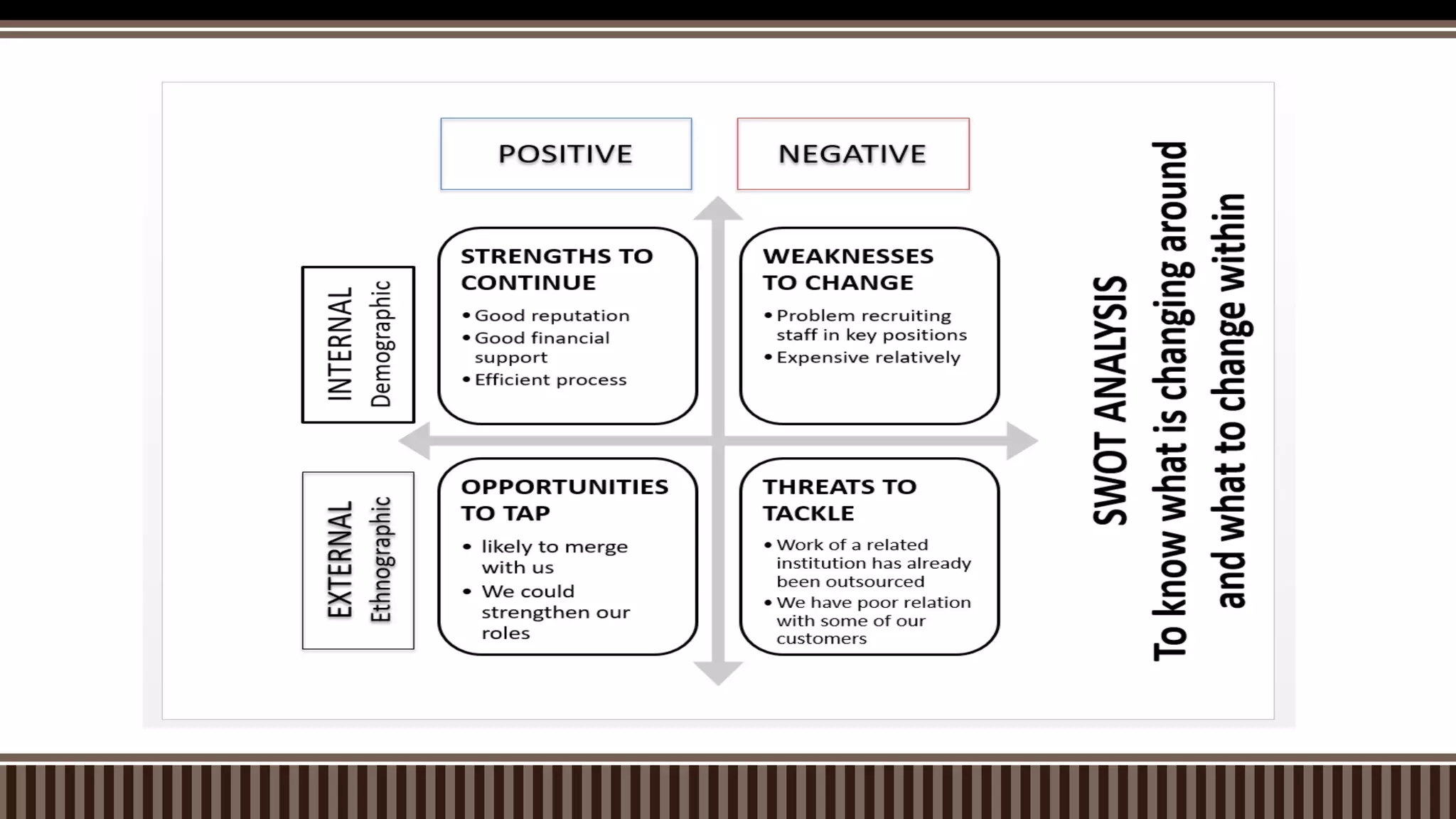
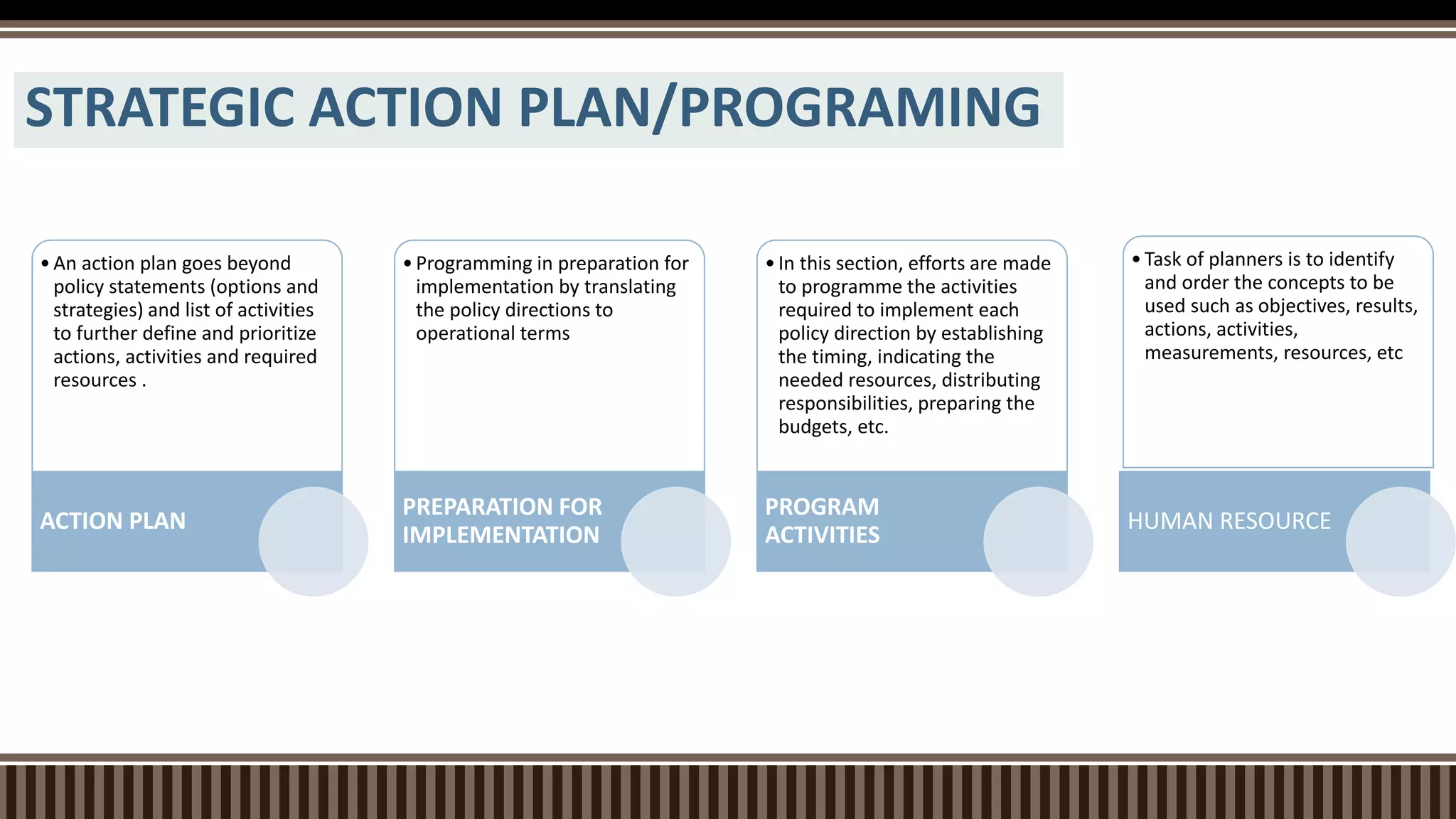
The document outlines the strategic planning process which includes analyzing the internal and external environment, setting goals and direction, and developing strategic and operational plans. It discusses key steps like environmental scanning, defining the mission and vision, setting targets, and creating action plans with objectives, strategies, timelines and responsibilities. The planning process results in strategic and operational documents that guide implementation, and it is monitored and assessed on an ongoing basis to ensure goals are achieved.