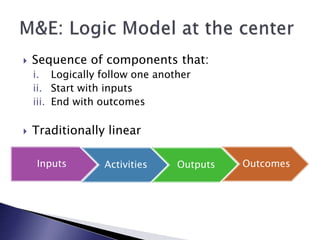
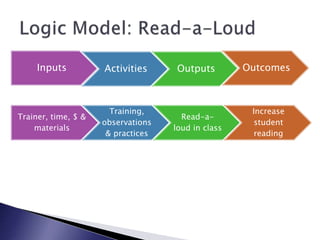
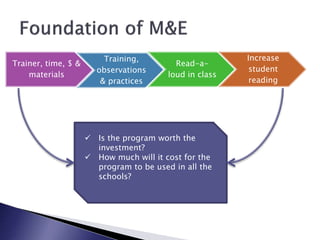
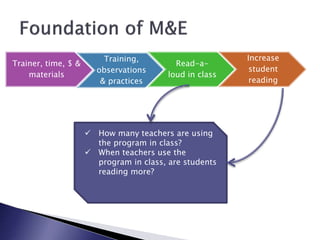
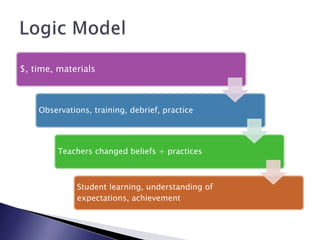
This document discusses monitoring and evaluation in schools. It defines key terms like school improvement, school effectiveness, and monitoring and evaluation. It explains that monitoring and evaluation provide essential data for decision making by tracking progress, demonstrating impact, and informing stakeholders. Logic models are presented as a way to visually map how a program's inputs and activities lead to intended outputs and outcomes. The importance of school culture that supports data-driven, evidence-based decision making is also emphasized.