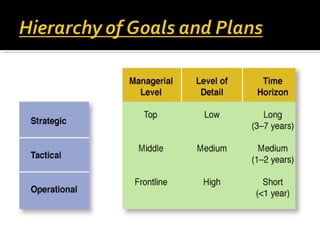
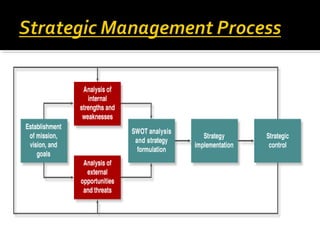
The document outlines the importance of strategic planning for organizations, detailing its components such as development plans, environmental scans, and gap analysis. It emphasizes the need for a clear vision and mission as foundational elements for effective planning and includes practical steps for setting strategic goals, implementing action plans, and evaluating progress. The document also highlights the need for flexibility and continuous assessment to adapt strategies as necessary.