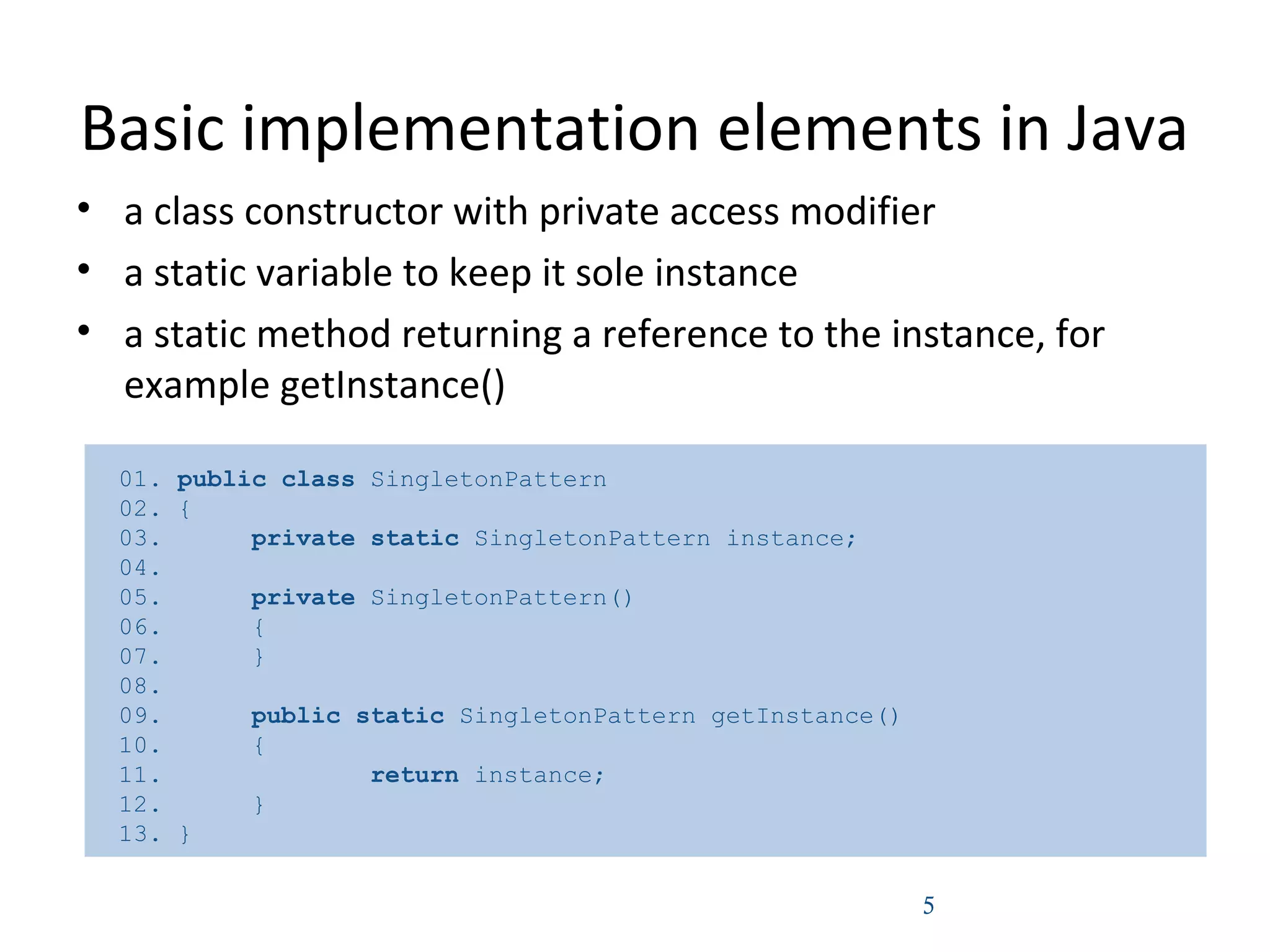
The document discusses various implementations of the Singleton design pattern in Java, including lazy initialization, eager initialization, serialization considerations, and preventing instantiation through reflection or cloning. The best approach is to use an enum singleton, as it is inherently a single instance, implements interfaces automatically, and prevents reflection attacks.