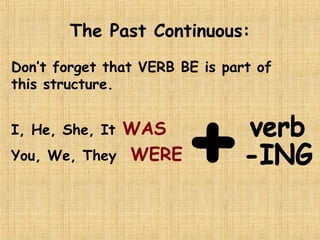
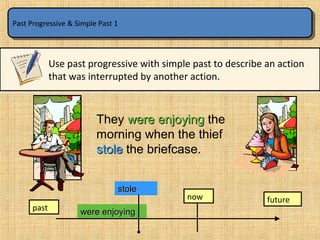
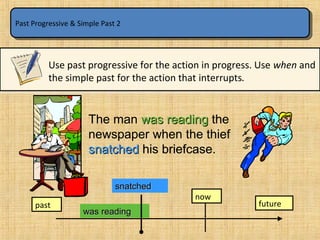
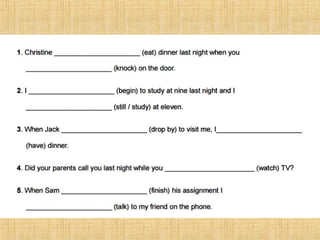
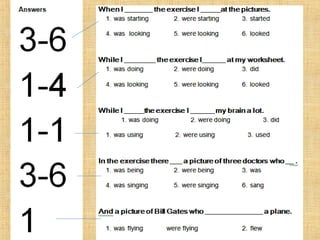
The document summarizes the difference between the simple past and past continuous tenses in English grammar. It provides examples of how to use each tense properly. The simple past is used for actions completed in the past, while the past continuous is used for actions that were ongoing or in progress at a specific time in the past. It also notes that stative verbs like "know" and "like" are not typically used in the past continuous tense.