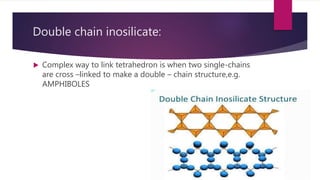
The document discusses rock-forming minerals, detailing their composition, formation processes, and classifications. It describes primary minerals, such as ferromagnesians and non-ferromagnesians, and secondary minerals formed from weathering of primary minerals. Additionally, it outlines various mineral classifications based on origin, quantity, specific gravity, and chemical composition.