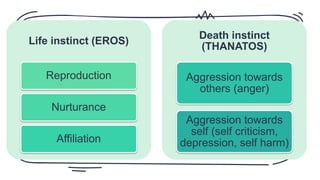
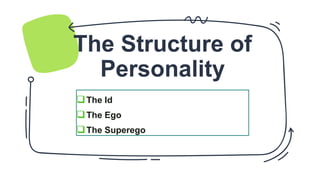
Freud's psychoanalytic perspective proposed that unconscious forces and childhood experiences influence personality development. He described personality as consisting of the id, ego, and superego. The id operates according to the pleasure principle, the ego mediates between the id and reality, and the superego incorporates societal moral standards through parental influence. Anxiety arises when these forces conflict, threatening the ego. To protect the ego, the mind employs defense mechanisms like repression, denial, reaction formation, and projection.