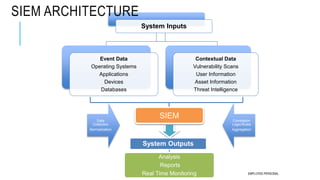
This document discusses log management and security information and event management (SIEM). It defines log management and outlines the log management challenges organizations face. It then introduces SIEM, describing what it is, why it is necessary, its typical features and process flow. The document outlines eight critical features of an effective SIEM solution including log collection, user activity monitoring, event correlation, log retention, compliance reports, file integrity monitoring, log forensics and dashboards. It also discusses typical SIEM products, uses cases for PCI DSS compliance and reasons why SIEM implementations may fail.









![CONTEXT
14
“User Broberts Successfully Authenticated to 10.100.52.105 from
client 10.10.8.22 “
“10.100.52.105 New Client Connection 10.10.8.22 on account:
Broberts: Success”
Long story short: what needs to be done is to break down every
known log message out there, and put it into a normalized format,
like this:
“User [USERNAME] [STATUS] Authenticated to [DESTIP] from client
[SOURCEIP]”
“10.100.52.105 New Client Connection 10.10.8.22 on account:
Broberts: Success”
EMPLOYEE-PERSONAL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siemslide-160203161713/85/SIEM-Activating-Defense-through-Response-by-Ankur-Vats-14-320.jpg)