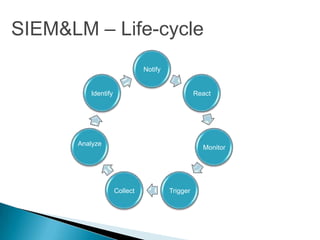
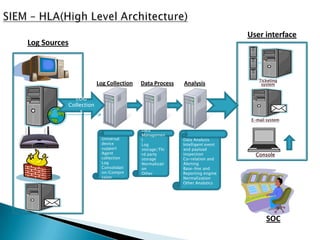
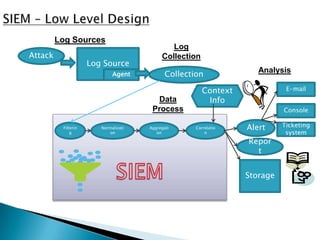
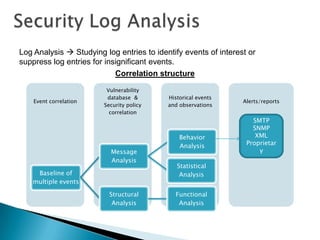
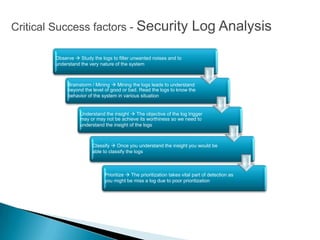
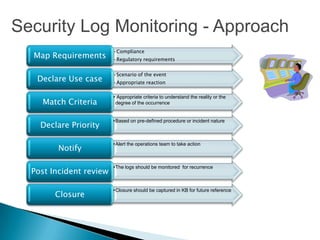
This document provides an overview of security information and event management (SIEM) systems. It discusses the types of SIEM systems, how they differ from security event management and security information management systems, and their high-level architecture and life cycle. Key topics covered include log analysis, monitoring, and National Institute of Standards and Technology guidelines for effective log management. The document aims to explain the importance of centralized log management and analysis.