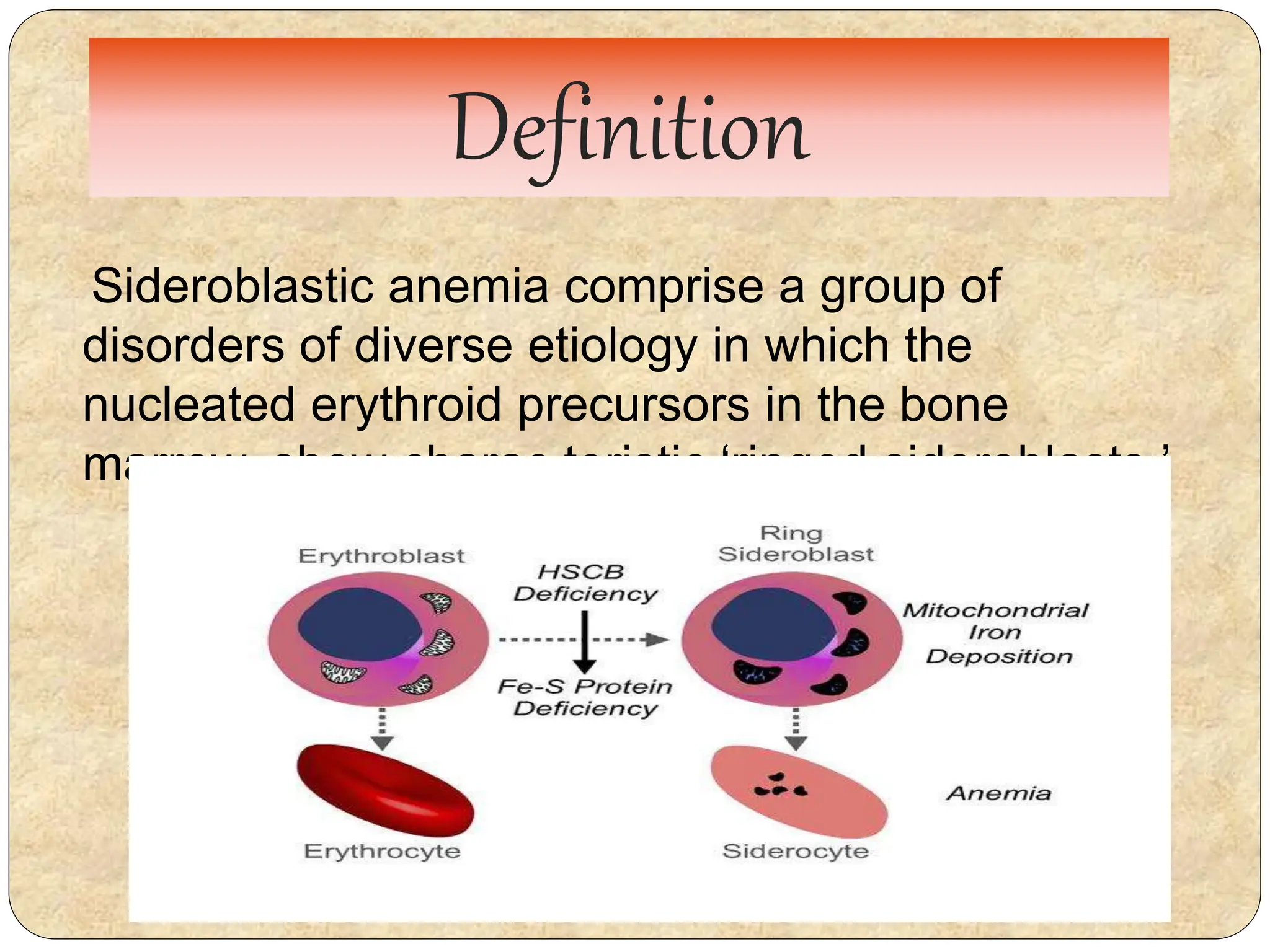
Sideroblastic anemia is a group of disorders characterized by the presence of ringed sideroblasts in bone marrow, which can be inherited or acquired from various causes. Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath, with laboratory findings indicating hypochromic anemia and elevated serum ferritin levels. While there is no cure, management involves monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, and, in some cases, treatments like stem cell transplantation and iron chelation therapy.