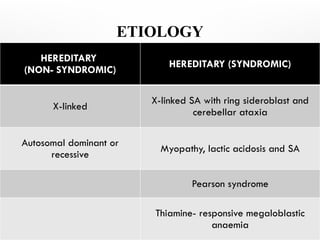
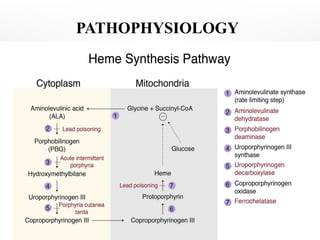
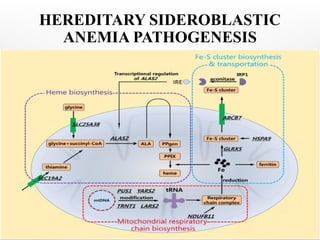
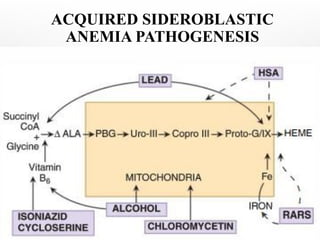
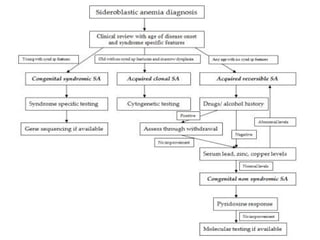
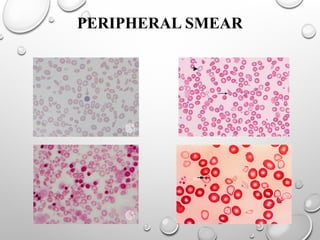
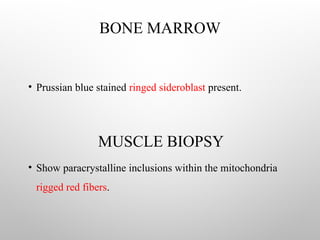
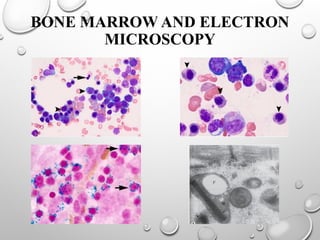
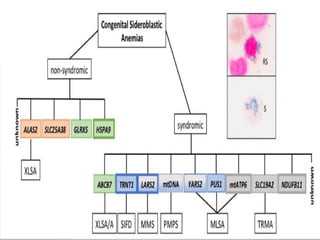
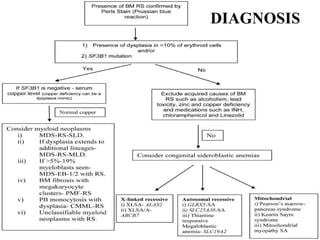
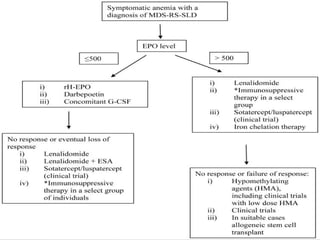
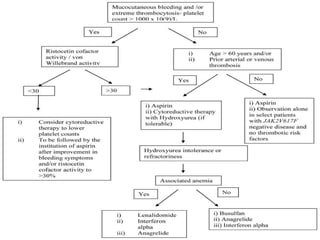
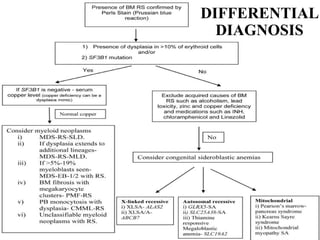
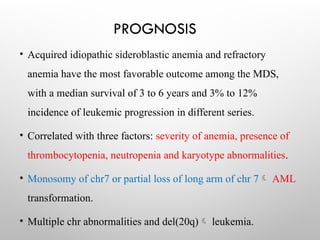
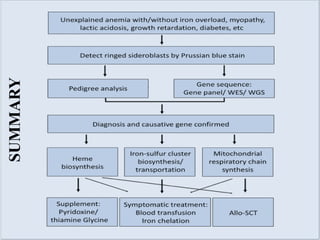
Sideroblastic anemia is a group of inherited and acquired anemias characterized by iron accumulation in erythrocyte precursors, with ring sideroblasts as a key diagnostic feature. The anemias can be hereditary, acquired, or secondary to various factors, each with distinct clinical manifestations and pathophysiology. Laboratory diagnosis includes low hemoglobin levels, characteristic peripheral smear findings, and increased iron levels, while treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the anemia.