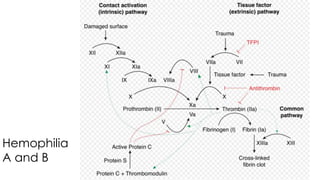
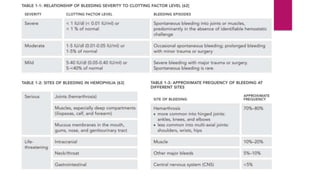
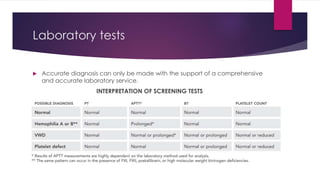
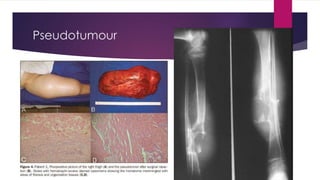
Hemophilia is a genetic bleeding disorder caused by deficiencies in coagulation factors VIII or IX. It affects males primarily and can range from mild to severe. The main types are hemophilia A (factor VIII deficiency) and hemophilia B (factor IX deficiency). Treatment involves replacing the missing clotting factor through prophylactic or on-demand regimens to prevent or treat bleeding episodes. Complications can include hemarthrosis, joint damage, fractures, and pseudotumors, so treatment seeks to maintain adequate factor levels and address medical issues promptly. Proper diagnosis and laboratory testing are needed to determine severity and guide personalized management.