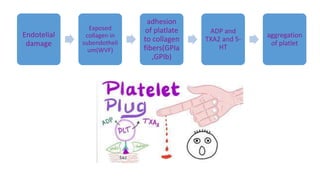
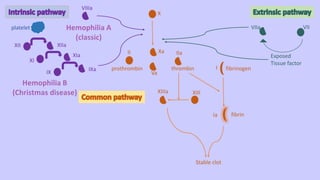
1. Hemostasis involves vasoconstriction, platelet plug formation, coagulation, and fibrinolysis.
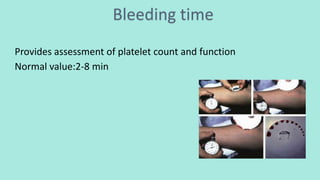
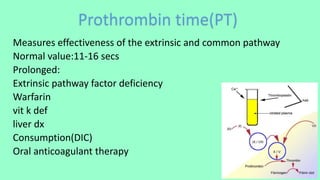
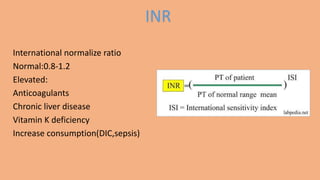
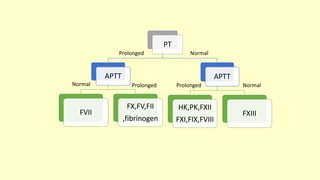
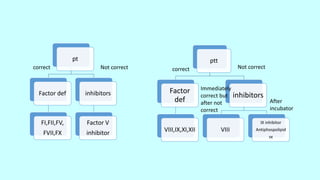
2. Tests like bleeding time, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and thrombin time are used to assess the coagulation pathway.
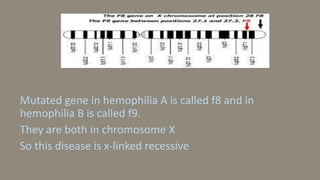
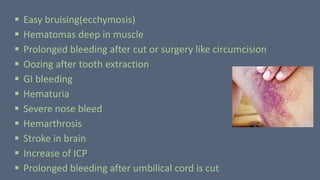
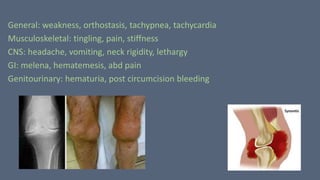
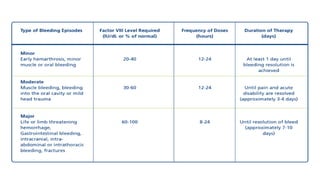
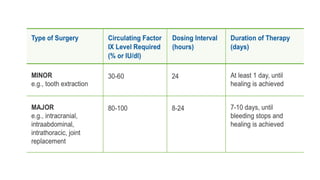
3. Hemophilia is an inherited bleeding disorder caused by factor VIII or IX deficiency that impairs hemostasis and causes easy bruising and prolonged bleeding.