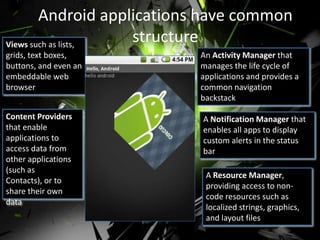
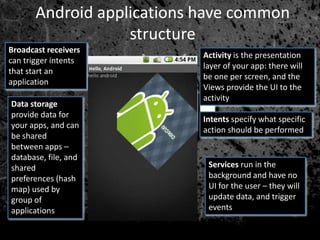
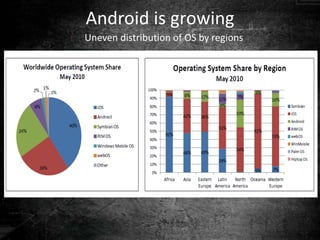
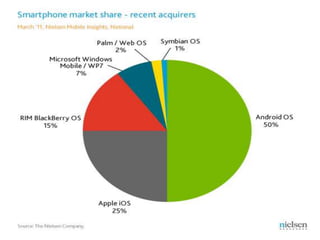
Android is an open source operating system used widely in mobile phones and tablets. It includes features like an application framework, Dalvik virtual machine, integrated browser, media support, and preinstalled applications from Google. The OS is updated every few months with new versions adding features and compatibility. Applications have a common structure including activities, intents, services, and data storage. Android is developed through the Open Handset Alliance and is growing rapidly as the dominant mobile OS. It provides security through process isolation and permission-based controls.