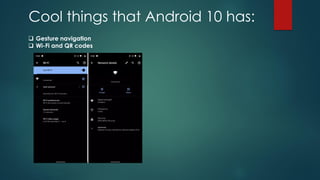
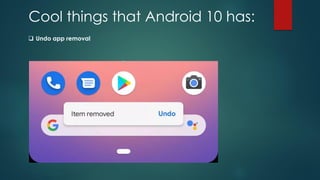
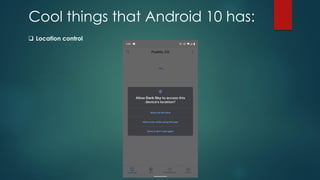
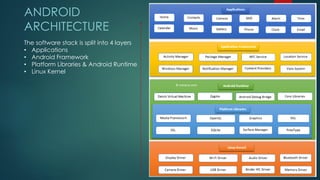
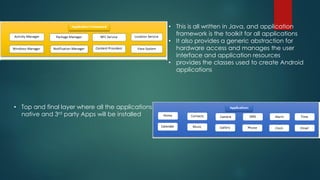
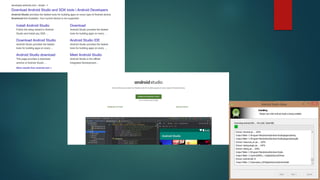
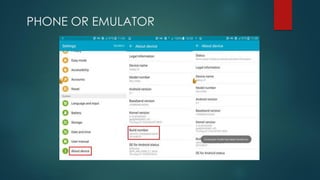
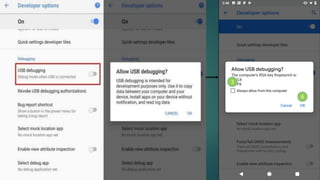
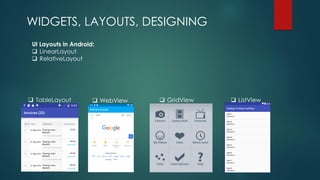
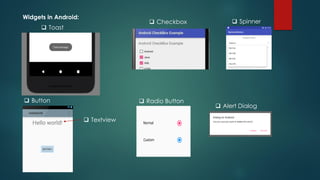
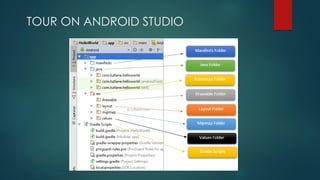
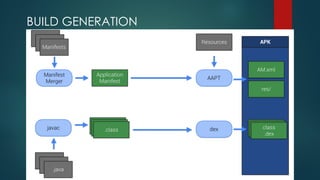
The document covers a presentation on Android application development led by M. Mukesh Kannan at Bharathiar University, detailing the history, architecture, and fundamental components of Android. It outlines the evolution of Android from its inception in 2003 to its current version, highlighting important features and tools necessary for development. Additionally, it discusses the Android framework, its installation procedures, and key elements like activities, services, and user interface components.