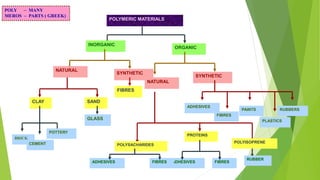
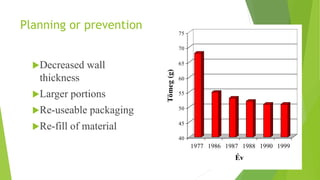
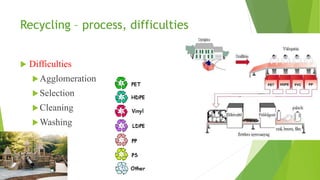
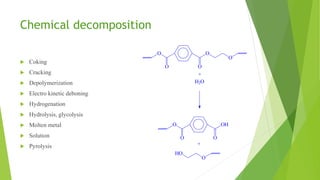
The document provides an overview of polymers, their history, and influence on daily life. It discusses how polymers are formed from monomers and lists major polymer discoveries from the 1820s to present. Polymers have widespread applications in construction, households, transportation, sports, agriculture, medicine, and more due to properties like strength, light weight, durability, and versatility. While polymers provide advantages, issues like non-biodegradability and waste disposal must be addressed. Future solutions include biodegradable polymers that break down naturally.