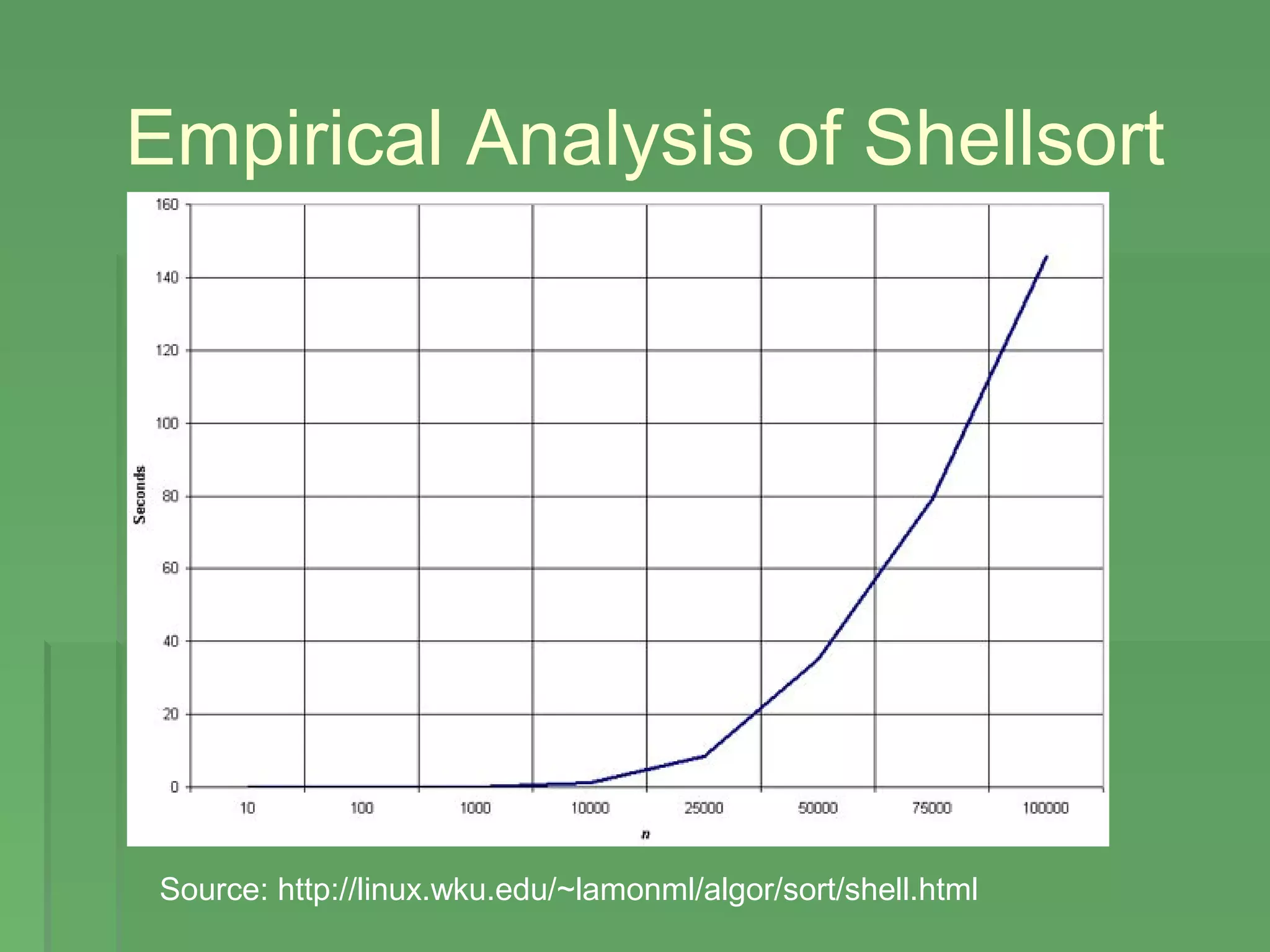
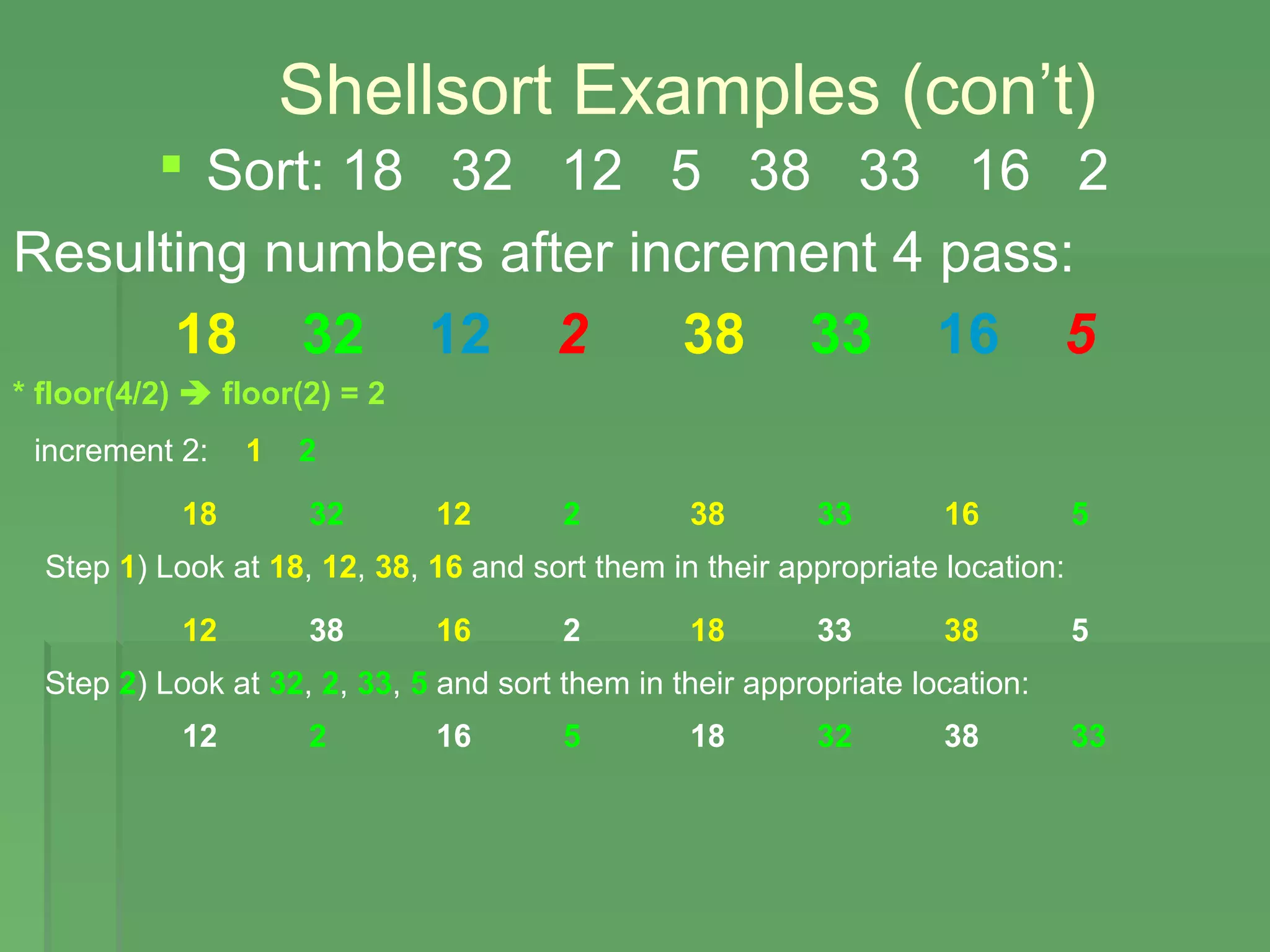
This document discusses Shellsort, an algorithm developed by Donald Shell in 1959 that improves on insertion sort. Shellsort works by comparing elements that are farther apart within an array rather than adjacent elements. It makes multiple passes through a list, sorting subsets of elements using an increment sequence that decreases until the final pass sorts adjacent elements using insertion sort. Shellsort breaks the quadratic time barrier of insertion sort and is faster for medium sized lists but is outperformed by other algorithms like merge, heap, and quick sort for large lists. Examples are provided to illustrate how Shellsort works by sorting a sample list.






![Shellsort
After each phase and some increment
hk, for every i, we have a[ i ] ≤ a [ i + hk ]
all elements spaced hk apart are sorted.
The file is said to be hk – sorted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shellsort-150701090243-lva1-app6891/75/Shell-sort-7-2048.jpg)