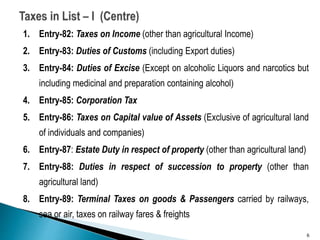
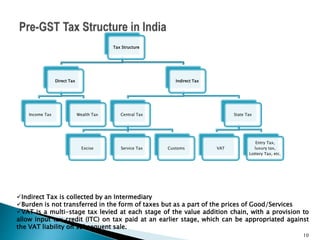
The document discusses the implementation of Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India, which came into effect on July 1, 2017, as a significant tax reform aimed at simplifying compliance with a unified tax system. It outlines the administrative framework of GST, its historical context, various tax powers detailed in the Indian Constitution, and the challenges posed by the pre-GST tax structure such as the multiplicity of taxes and compliance difficulties. The paper emphasizes the transition towards a destination-based tax model and aims to enhance inter-state trade efficiency and reduce tax evasion.




![ Is a Three Tier Federal Structure [Central, State & Local Municipal
Bodies]
Power to Levy and Collect Taxes Emerges from the Constitution of
India
Article-265 “No tax shall be levied or collected except by the authority
of Law”
Prohibits arbitrary collection of taxes
Article-246: Authority to enact law & Levy taxes and duties is
given by Article-246.
The parliament may make laws for the whole of India or any part of
the territory of India
The State legislature may make laws for whole or part of the state
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pre-gstscenarioinindia-introduction-190729095002/85/Pre-GST-Era-in-India-5-320.jpg)