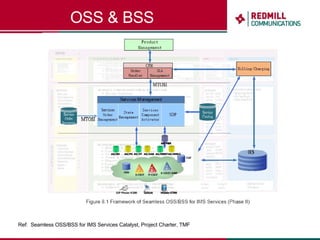
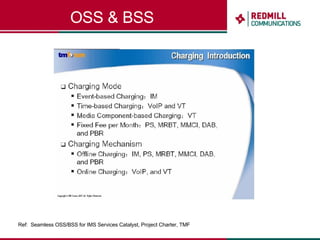
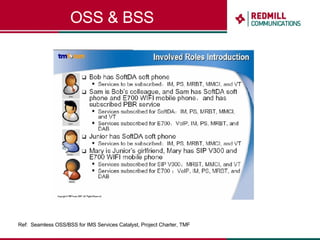
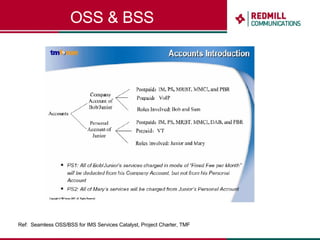
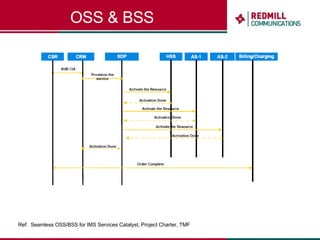
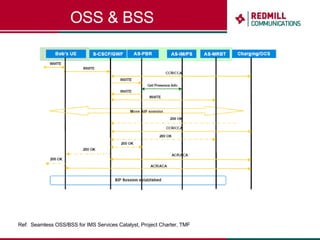
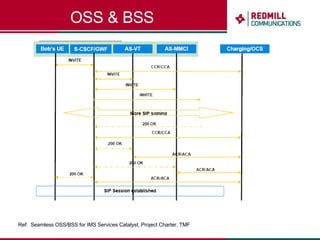
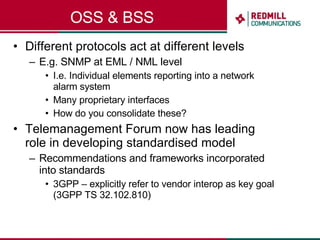
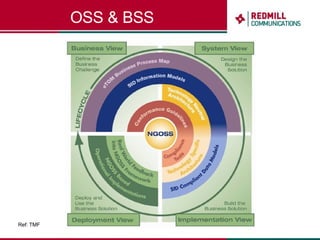
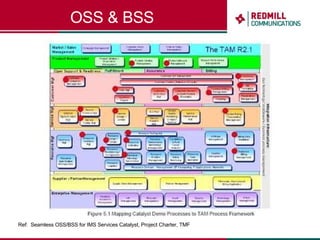
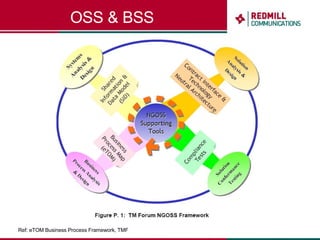
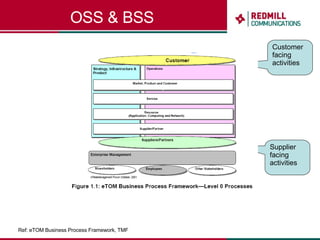
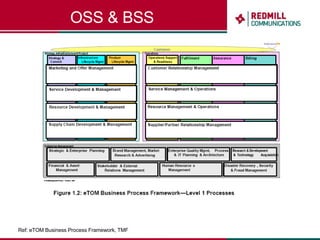
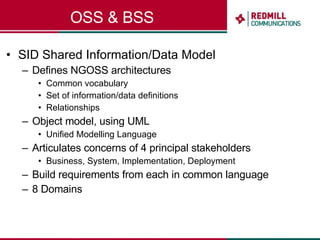
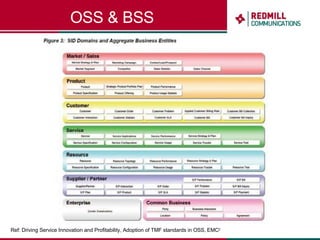
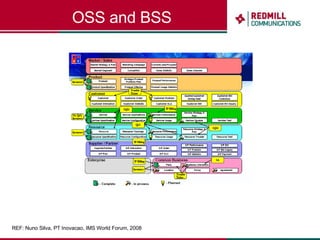
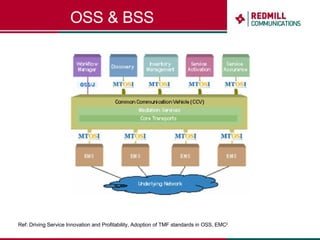
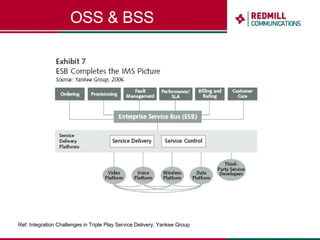
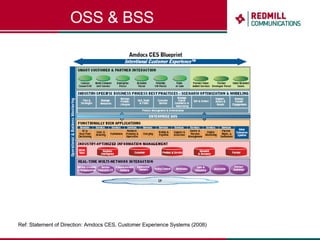
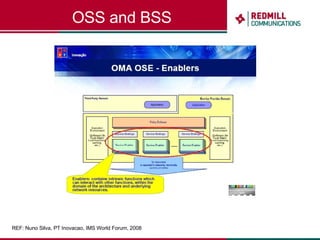
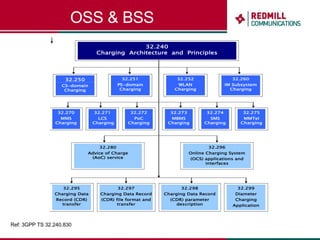
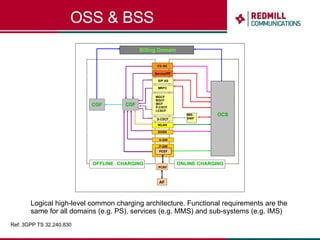
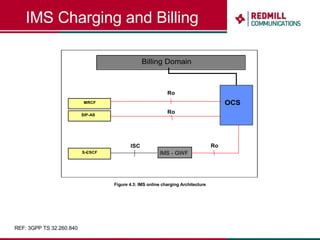
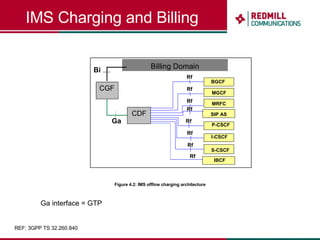
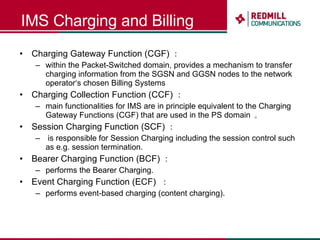
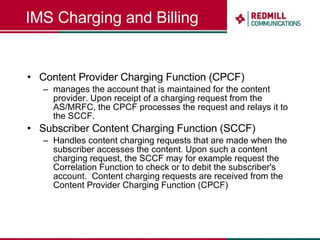
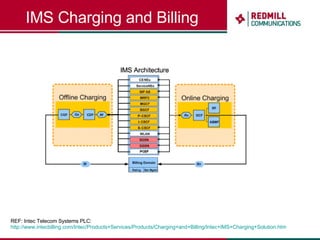
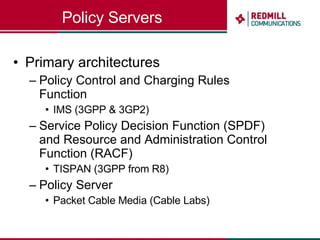
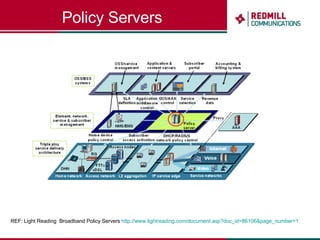
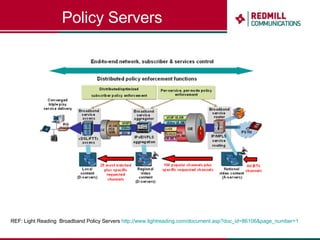
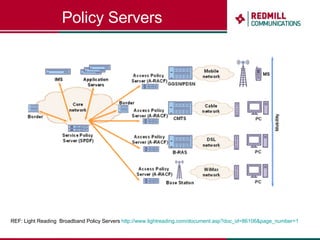
OSS & BSS systems are complicated because they must manage end-to-end telecom services across multiple vendors' elements from ordering to provisioning to payment. Standards bodies like the TM Forum provide reference models and frameworks to help with integration and interoperability, defining common processes, information models, and interfaces. Billing systems construct charging records from different network elements to enable subscriber billing and accounting between operators.