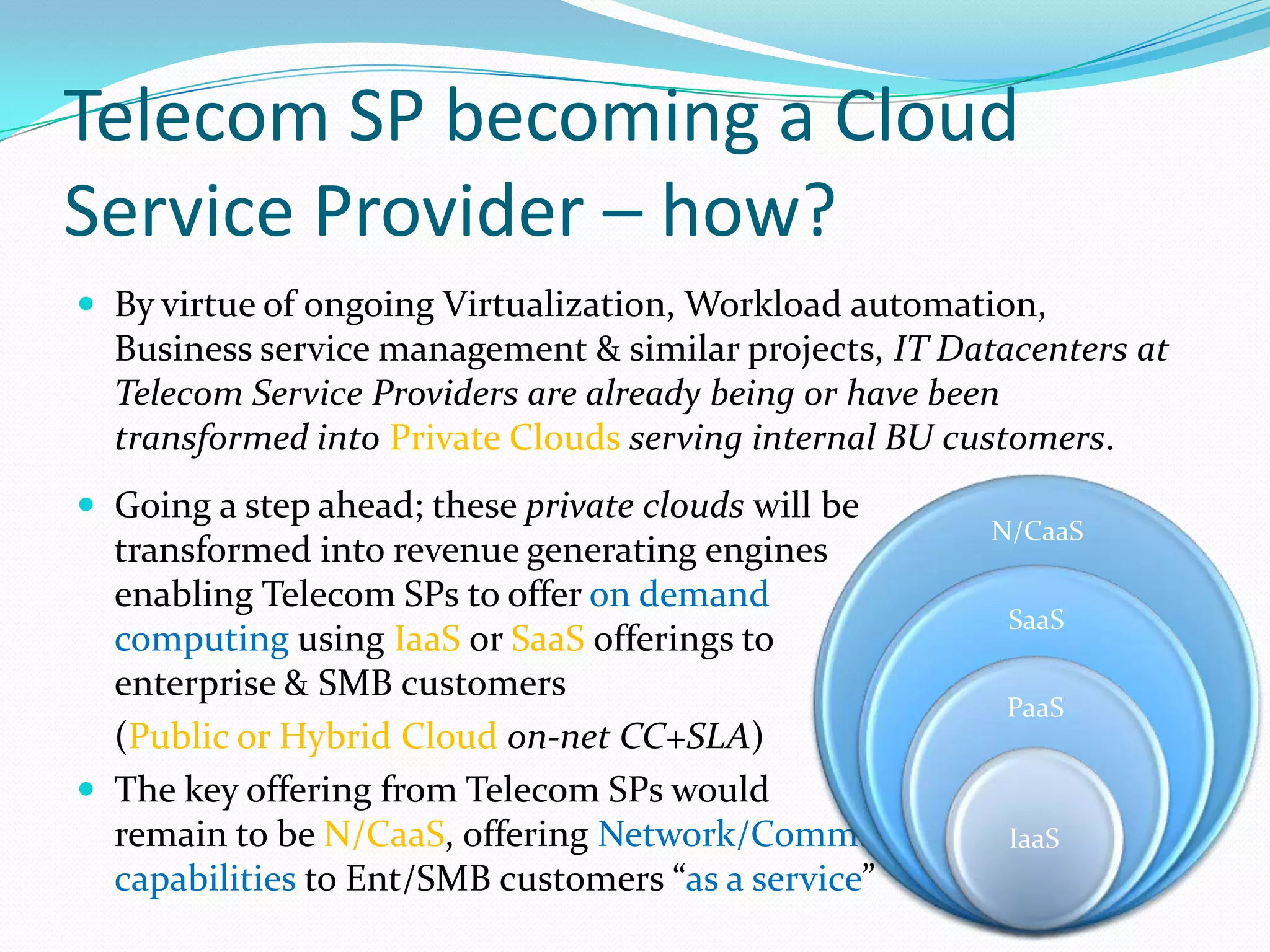
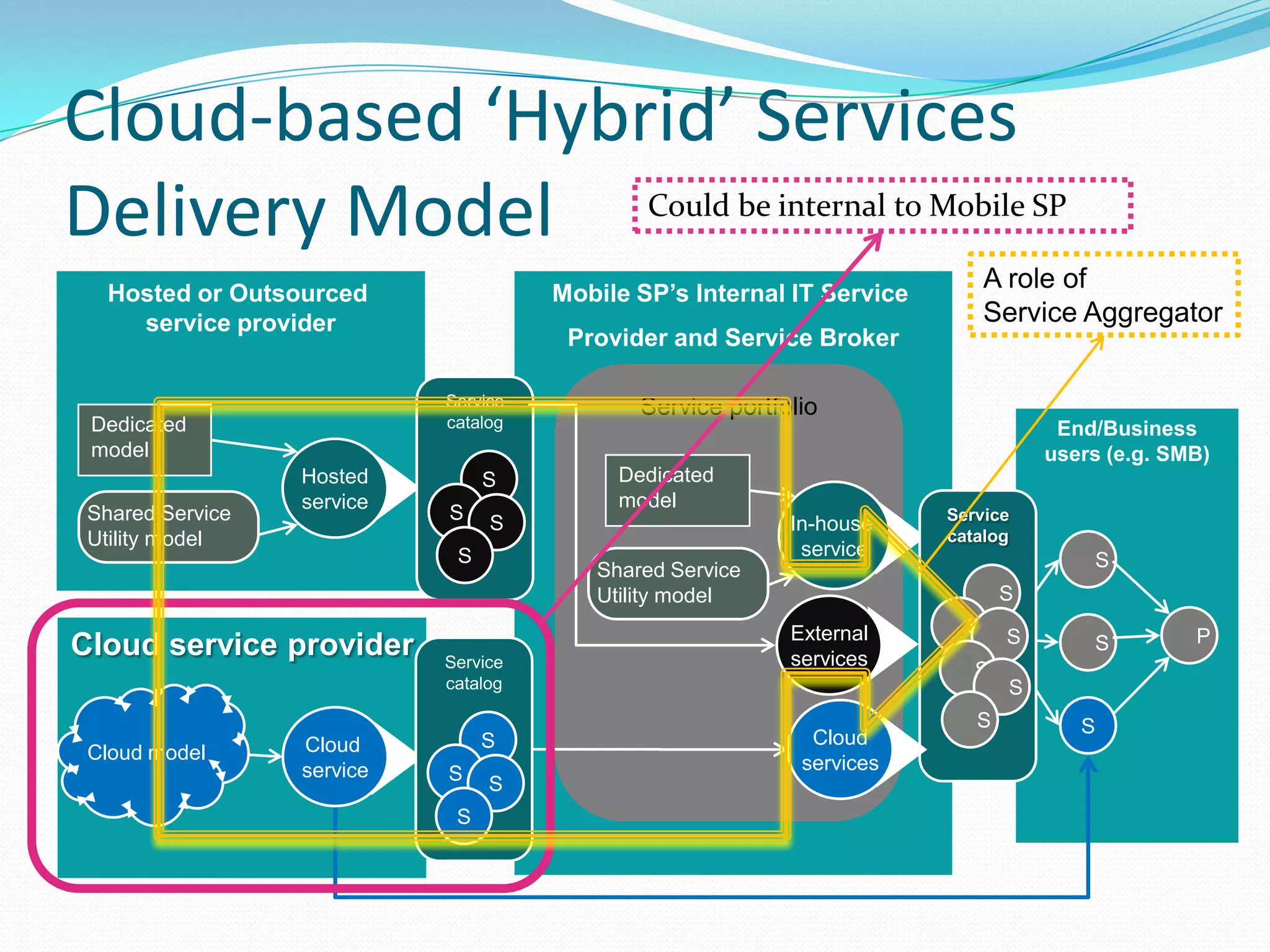
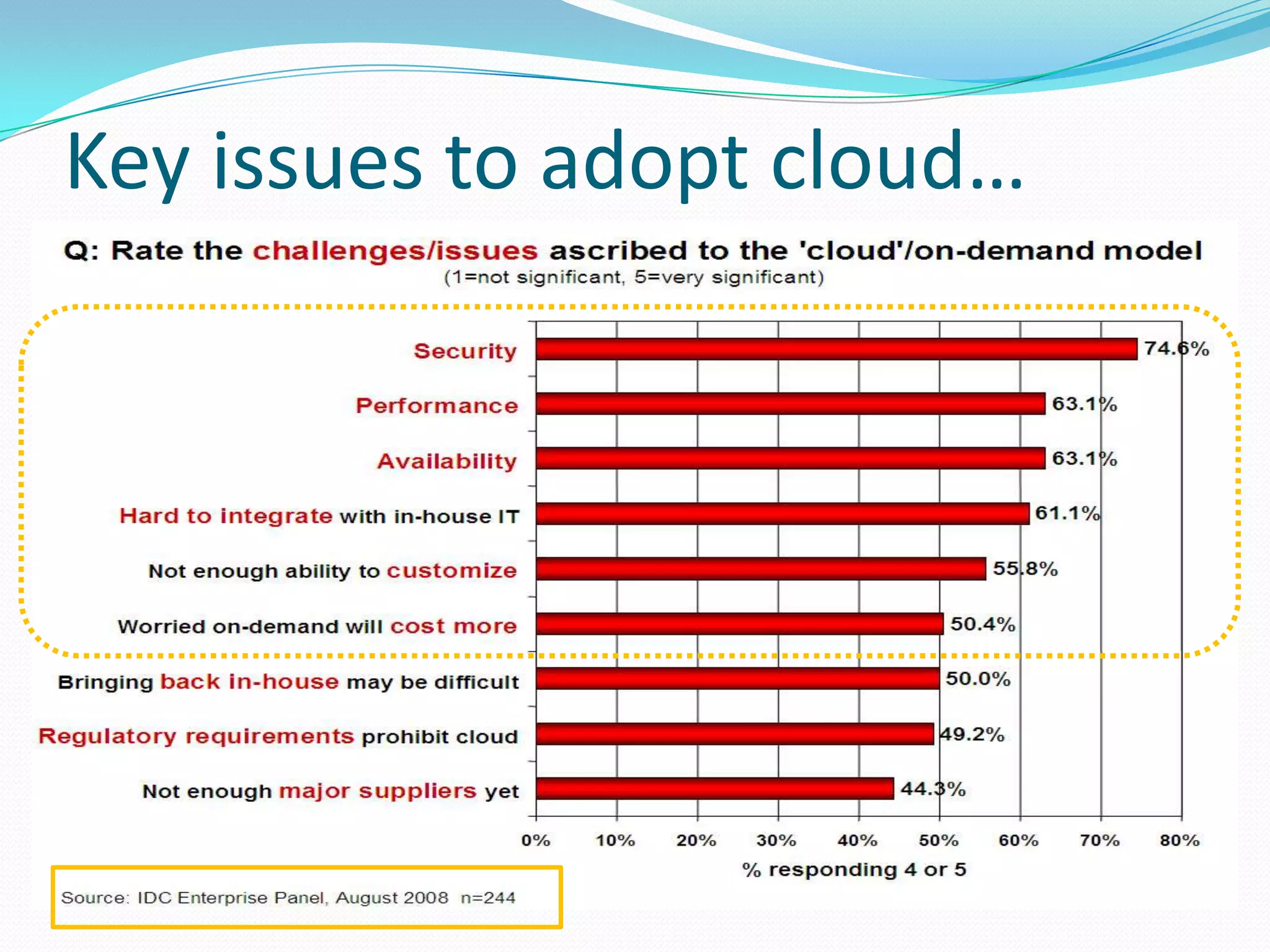
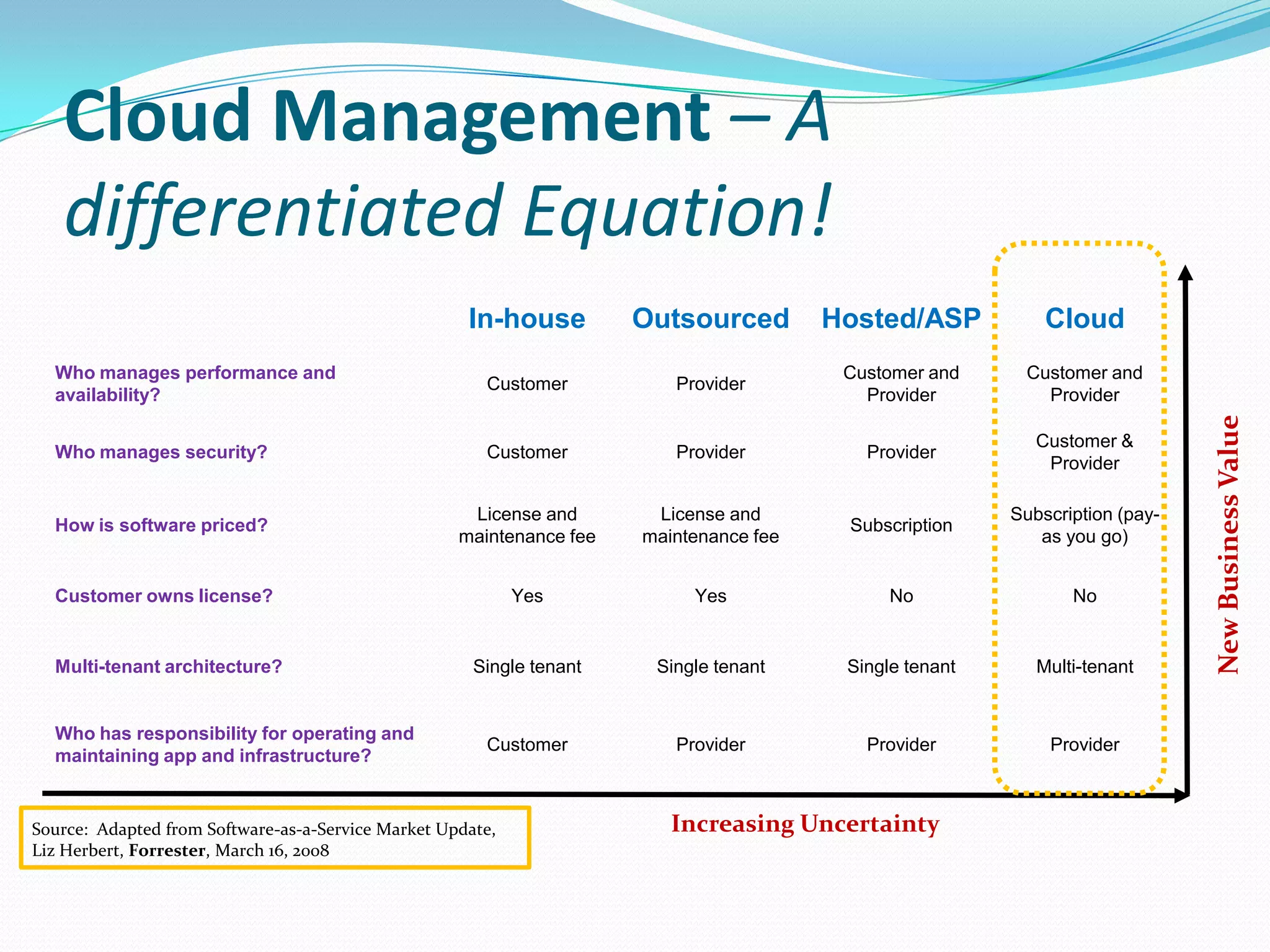
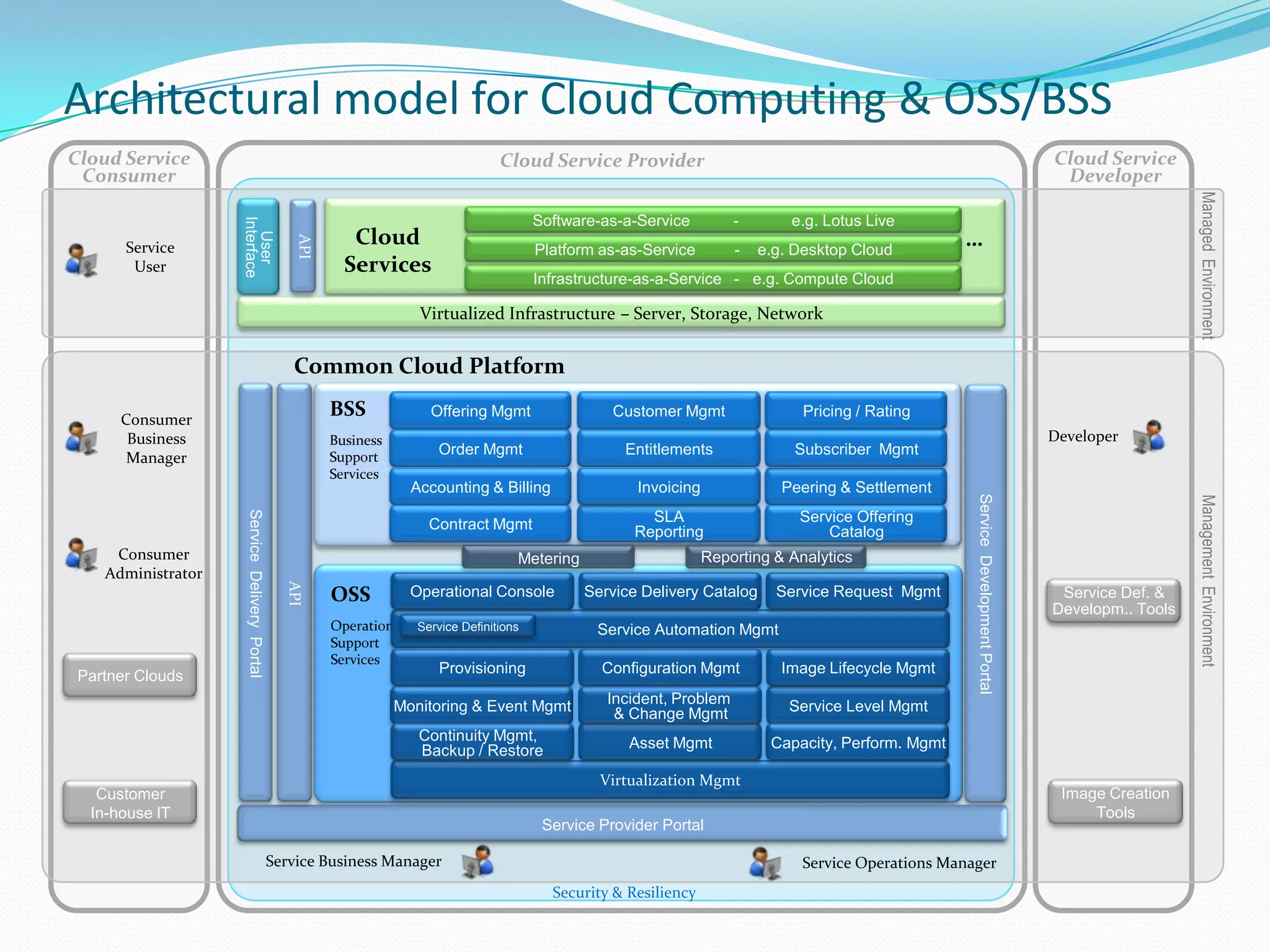
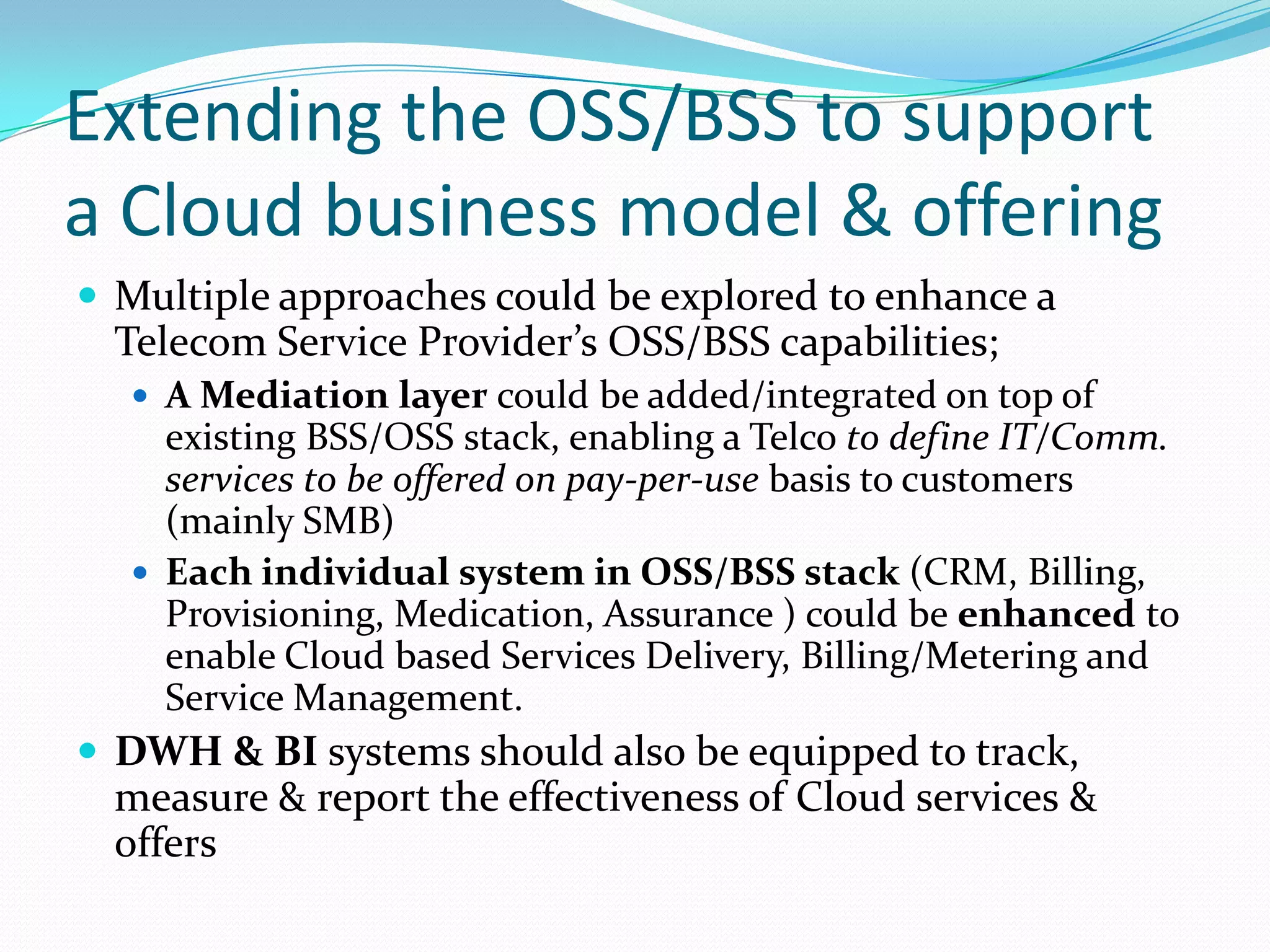
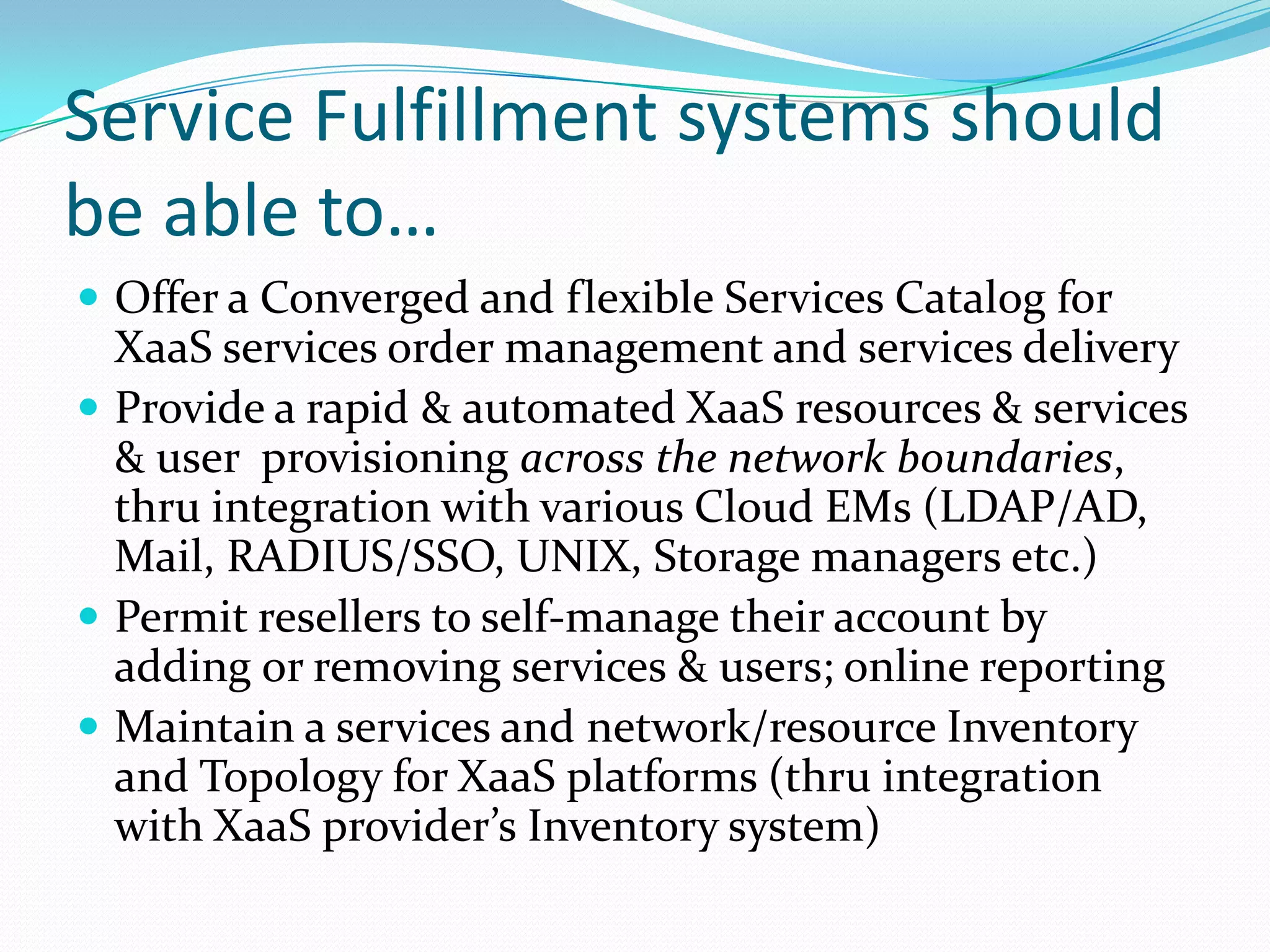
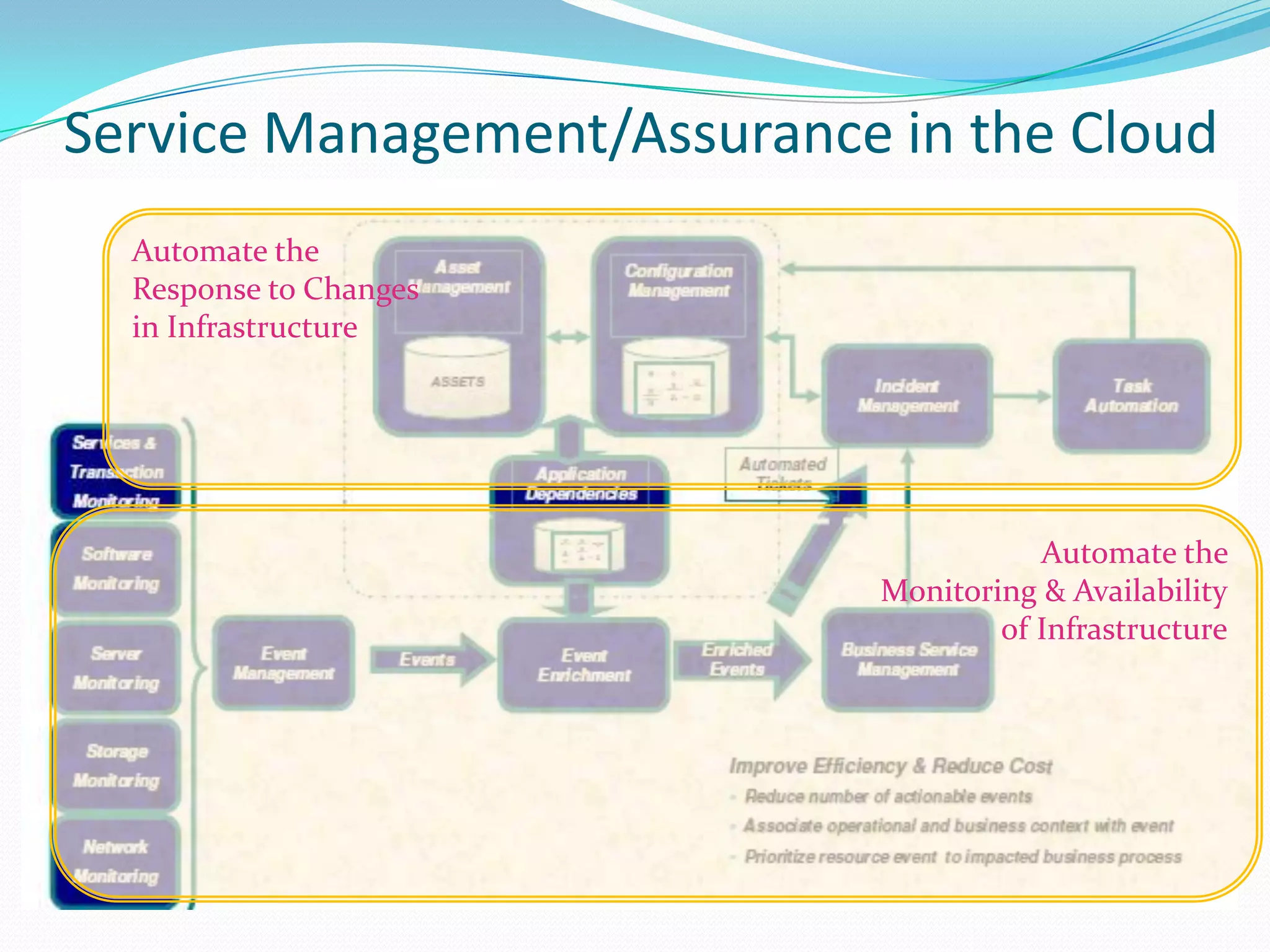
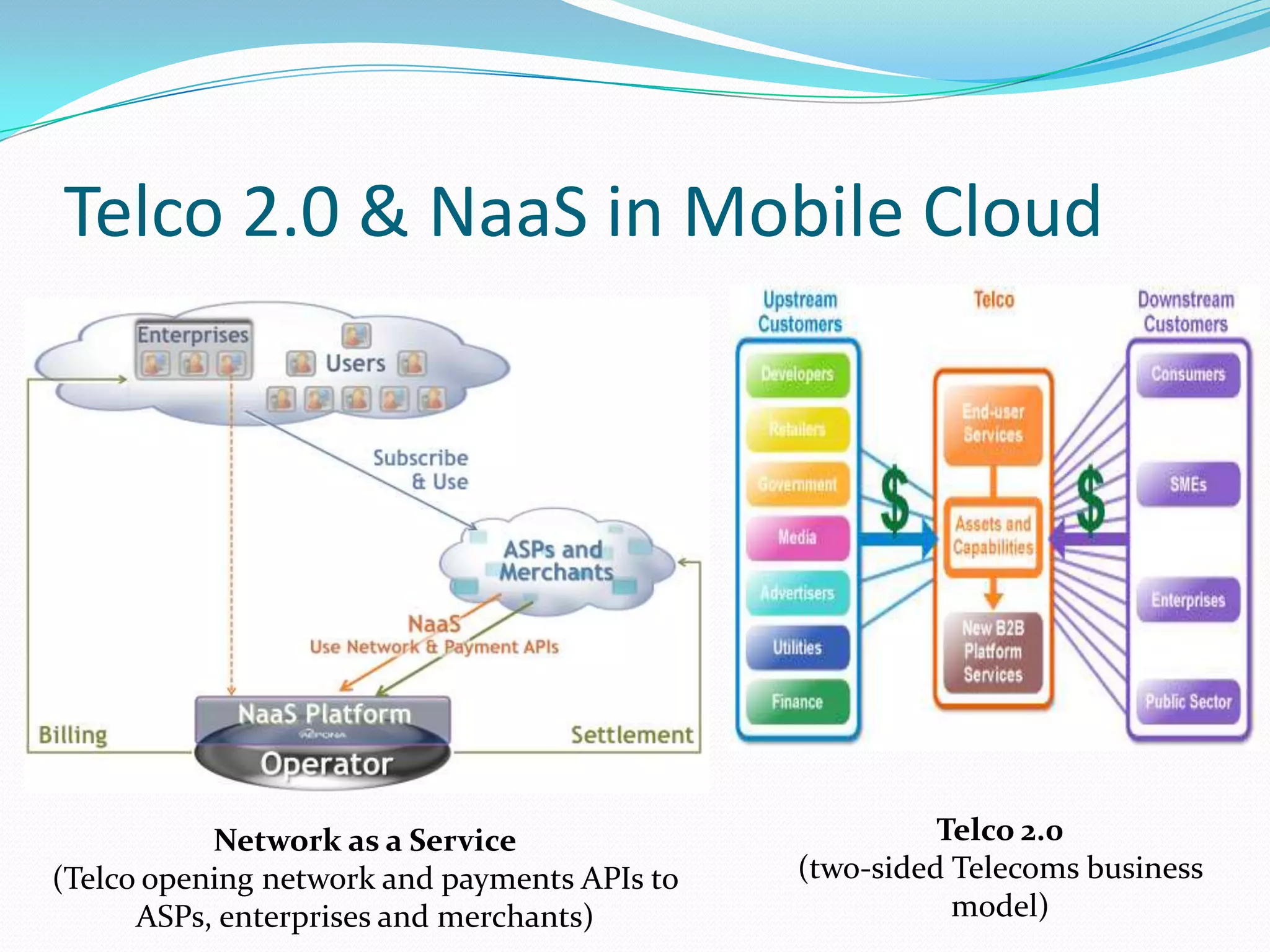
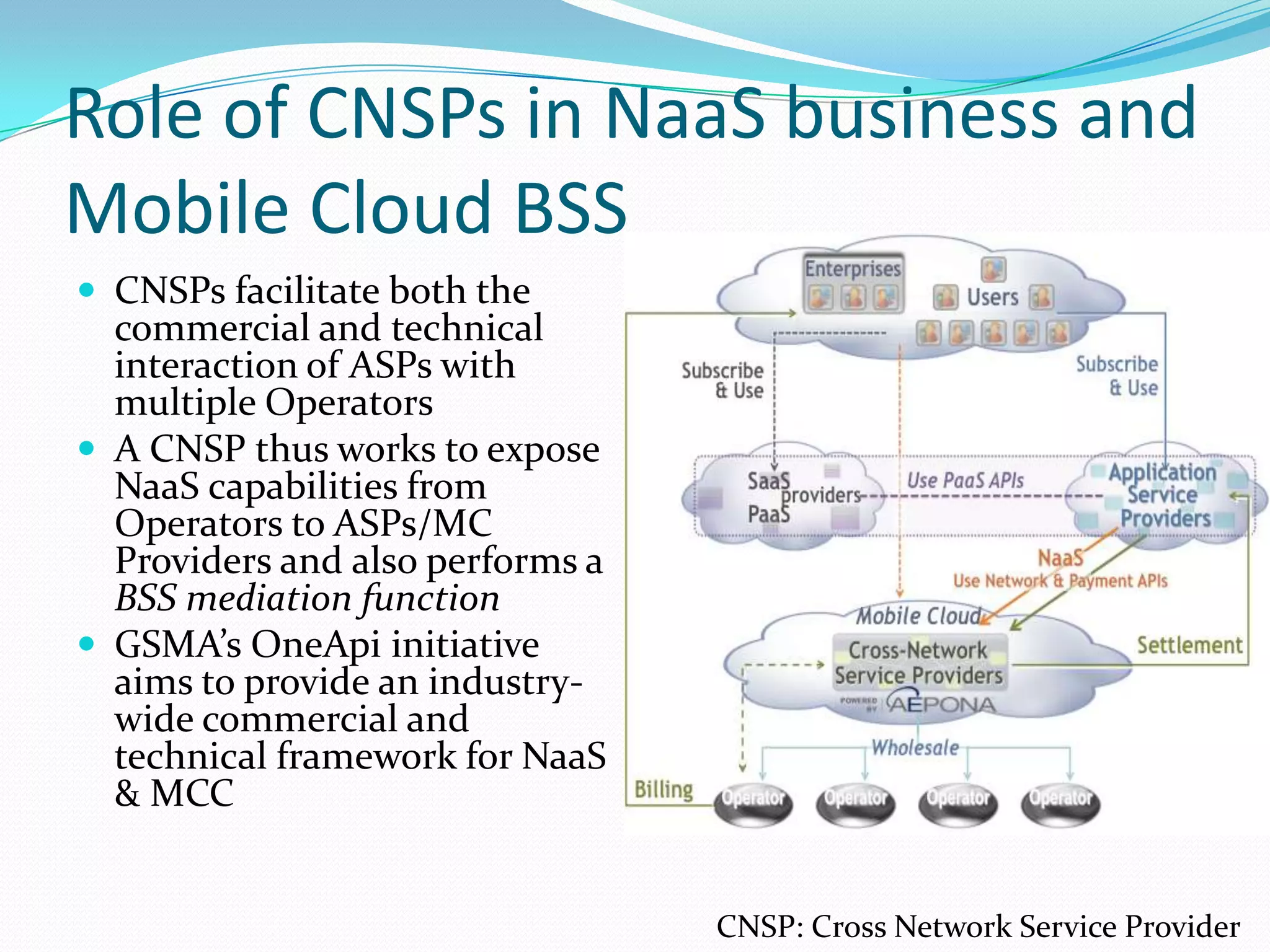
This document discusses how telecom service providers can leverage mobile cloud computing by transforming into cloud service providers. It would allow them to offer infrastructure, platform, and software as a service to enterprise and SMB customers. This transformation requires adapting the OSS/BSS systems to support cloud-based service delivery, billing, and management. Key areas that need enhancement in the OSS/BSS include service catalog, fulfillment, assurance, billing, and support for network as a service business models. Cross-network service providers will also play an important role in facilitating commercial and technical interactions between application service providers and multiple telecom operators in a mobile cloud environment.