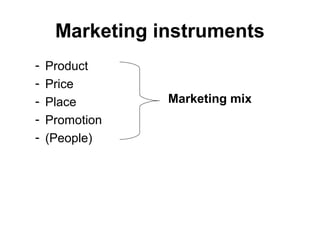
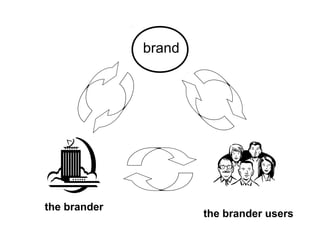
This document provides an introduction to branding concepts through a university course outline. It discusses why brands are important for both consumers and manufacturers in reducing risk and simplifying decisions. Brands help create awareness, knowledge, image, attitude, preference, loyalty and advocacy. The document outlines the course topics on branding management, equity, strategy, research and international aspects. It emphasizes that brands tell stories, have life cycles, personalities, responsibilities and theoretical frameworks. Finally, it discusses how branding becomes more important in entertainment due to increasing choices, commoditization, differentiation needs, and the ability of strong brands to focus employees and build communities.