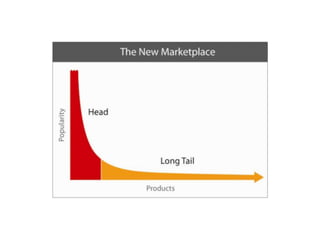
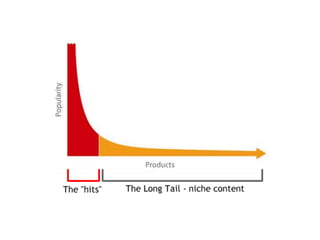
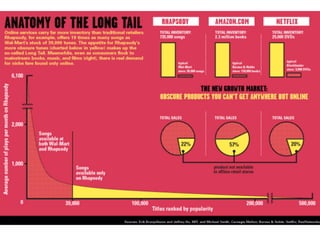
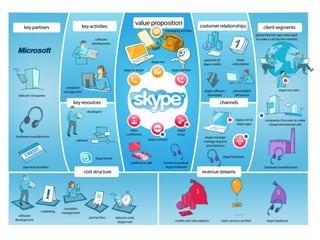
The document discusses various business models including the long tail model, free business models, and the freemium model. It provides examples and explanations of each model. For the long tail model, it explains how this focuses on selling a large number of niche products in lower volumes. For free business models, it discusses how companies like Google started services based on whether people wanted them rather than initial profitability, and how they generate revenue from advertising. The freemium model is described as providing a basic free version with paid upgrades for premium features or to remove advertising.