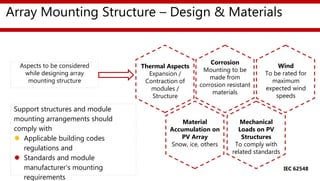
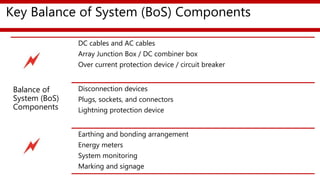
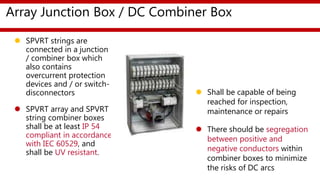
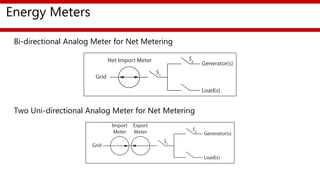
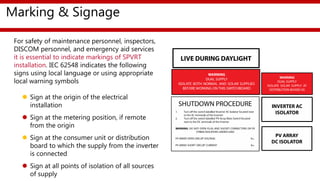
The document provides an overview of a training session on balance of system (BoS) components for solar photovoltaic rooftop (SPVRT) systems. It discusses key BoS components like array mounting structures, DC and AC cables, junction boxes, overcurrent protection devices, disconnectors, lightning protection, earthing, energy meters, system monitoring, and marking/signage. The presentation emphasizes safety, compliance with standards, and proper installation of these components for grid-connected SPVRT systems. It concludes by recapping common questions about SPVRT systems.