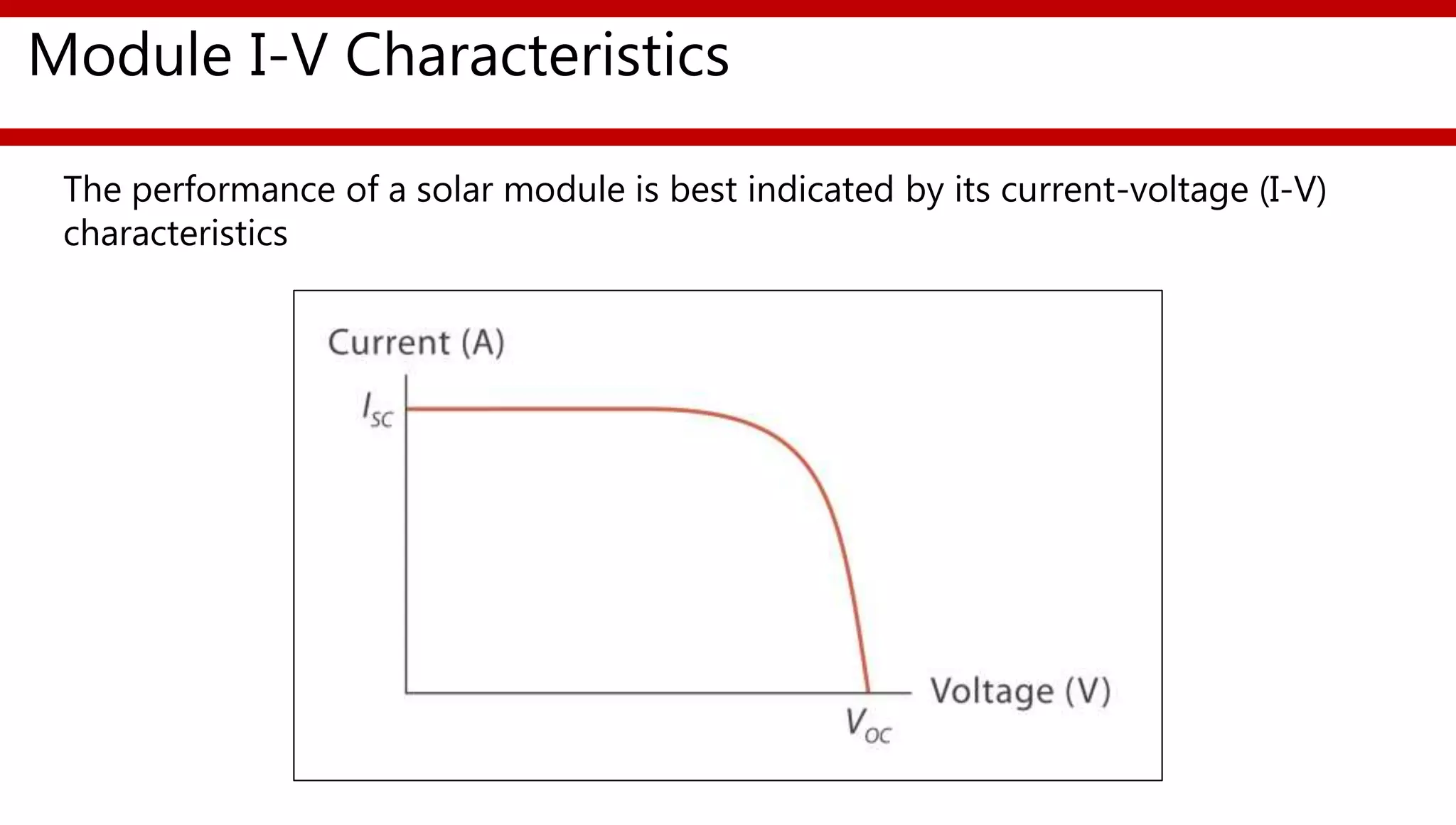
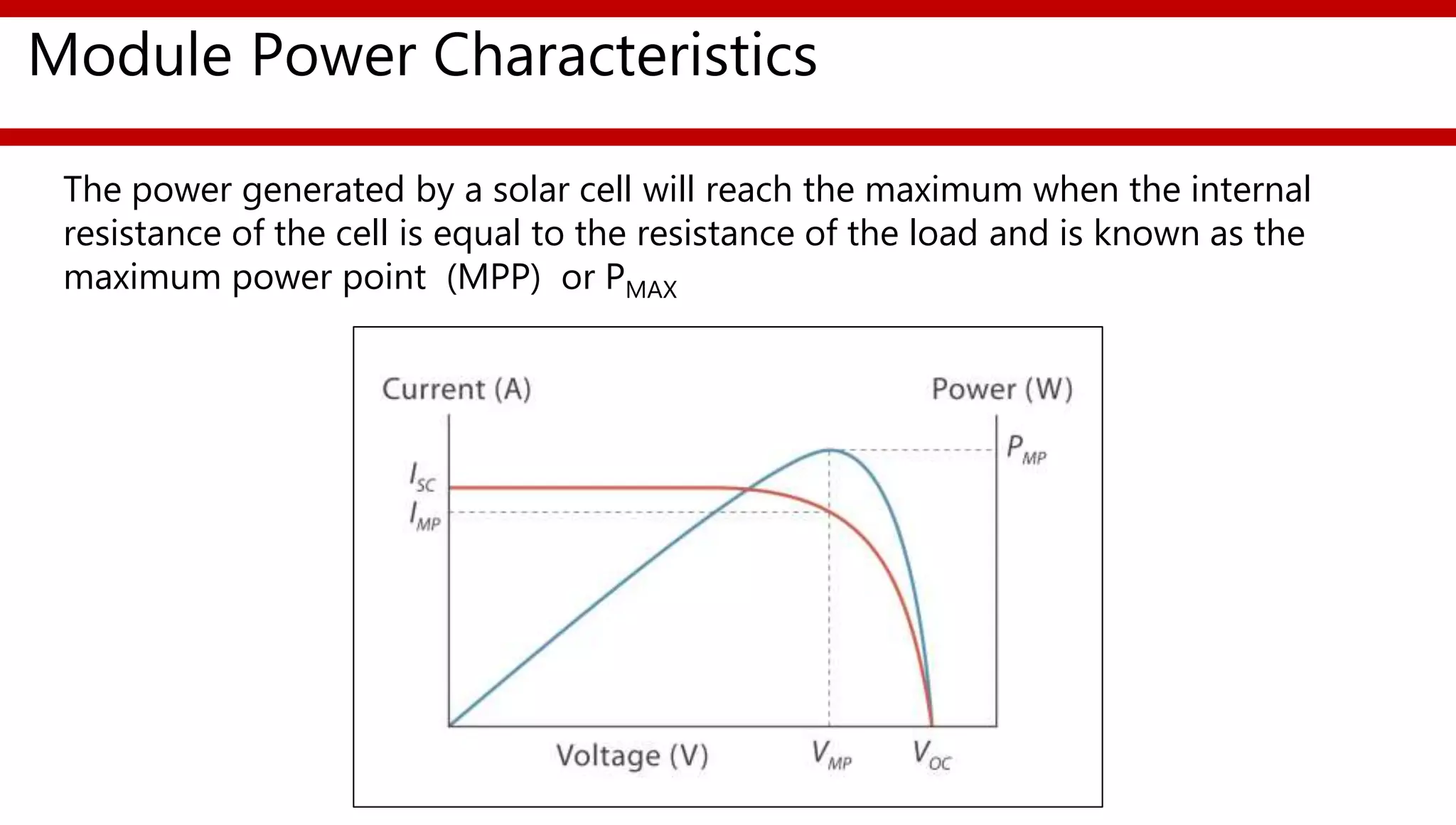
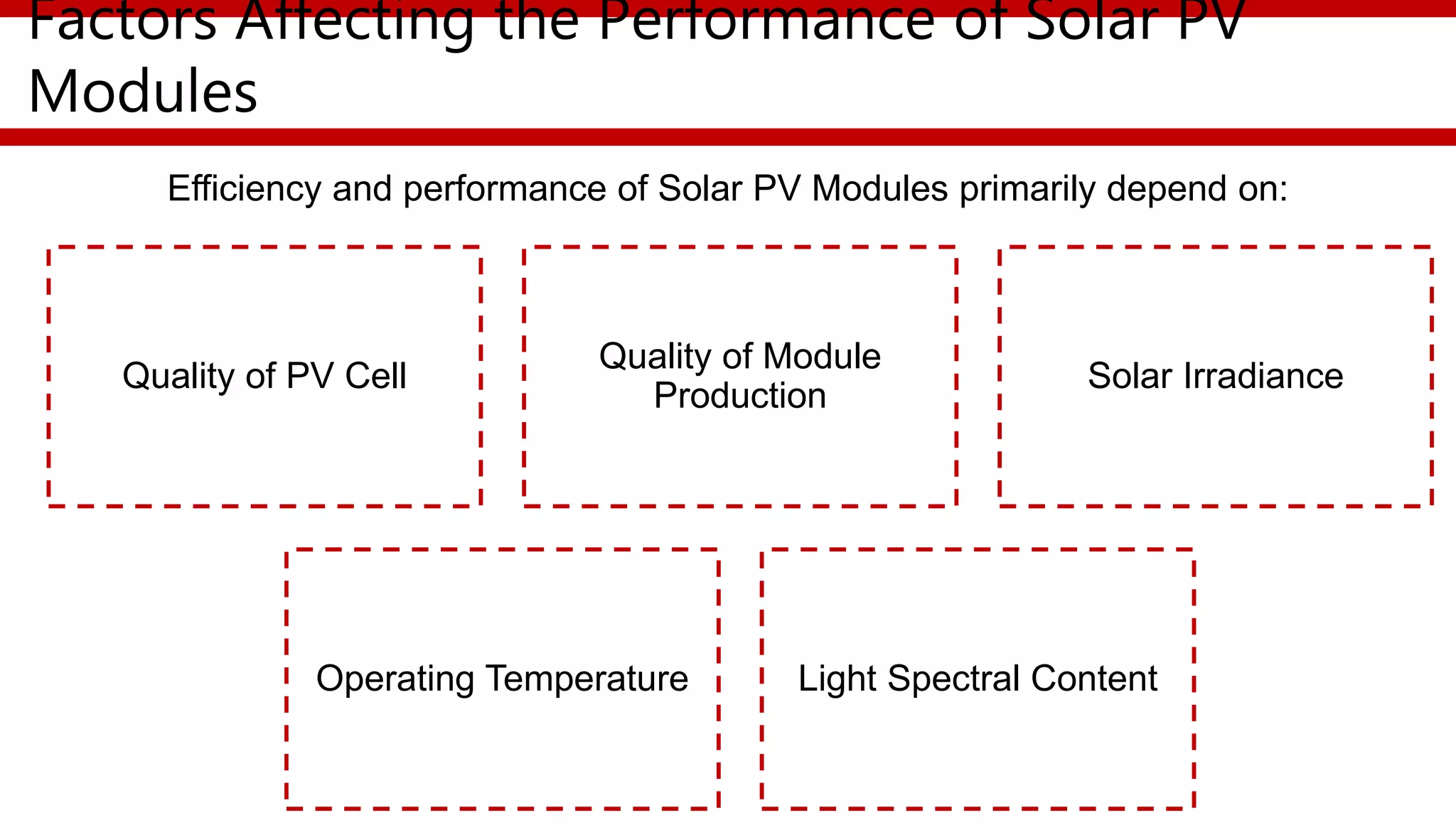
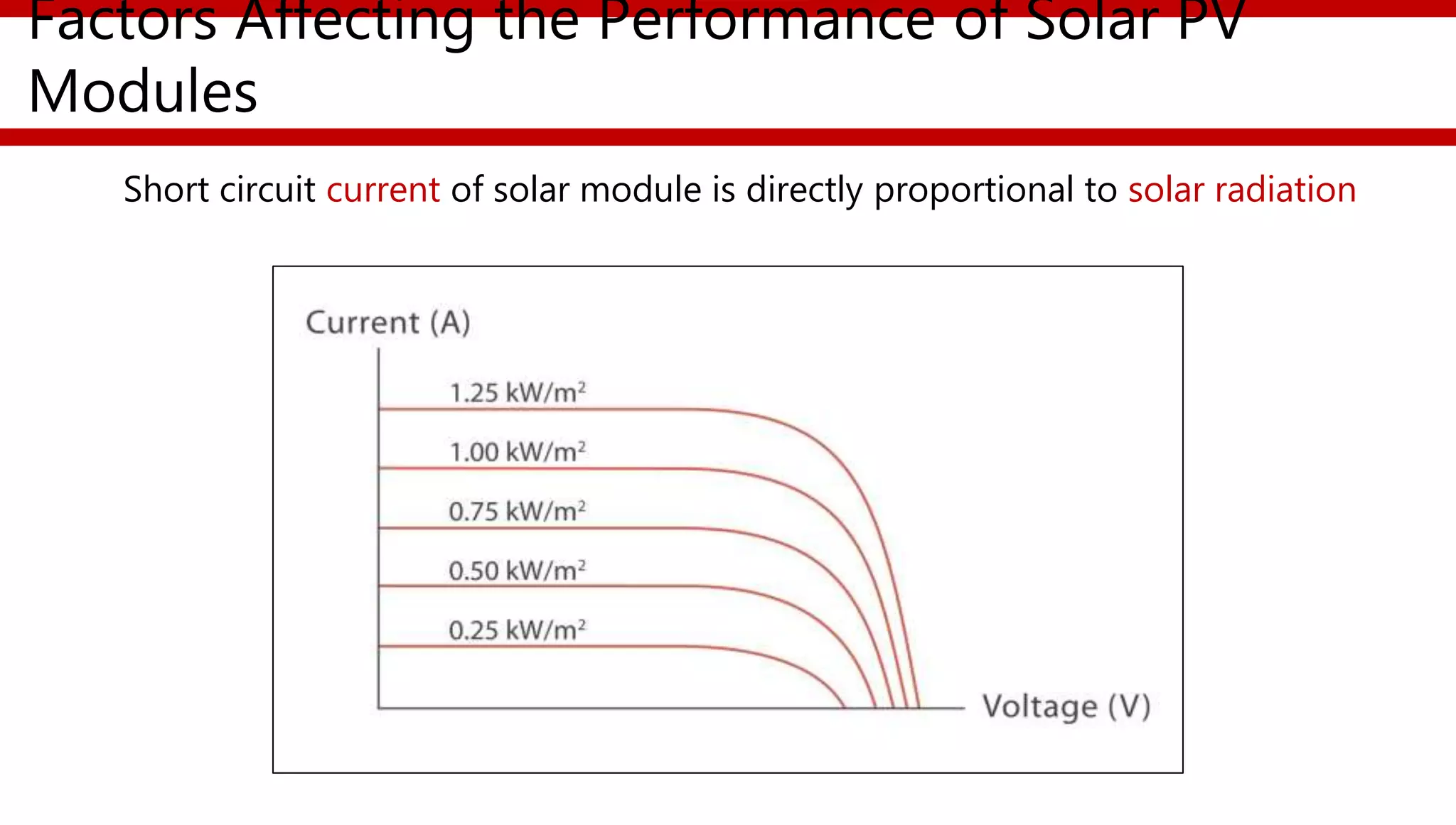
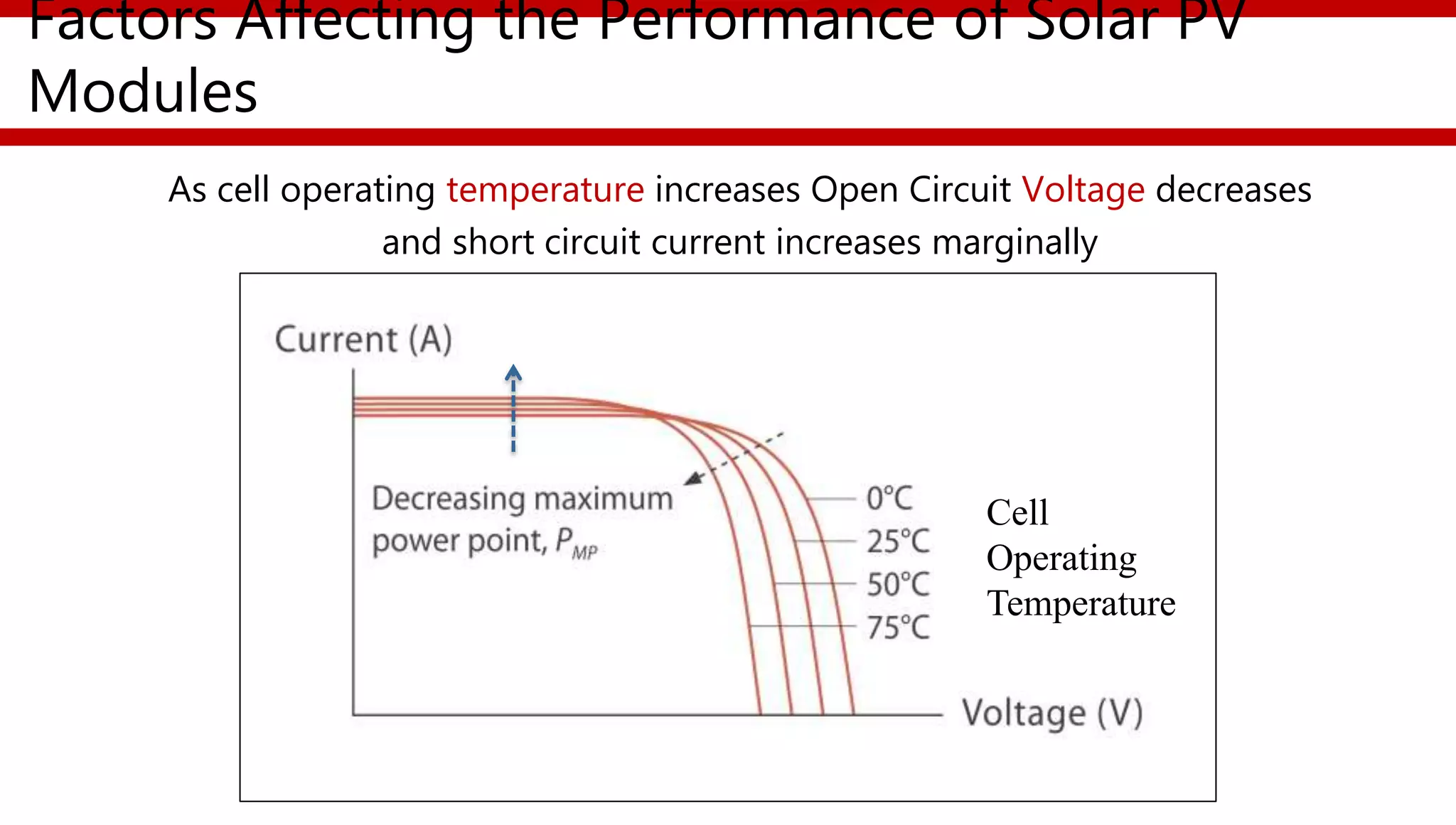
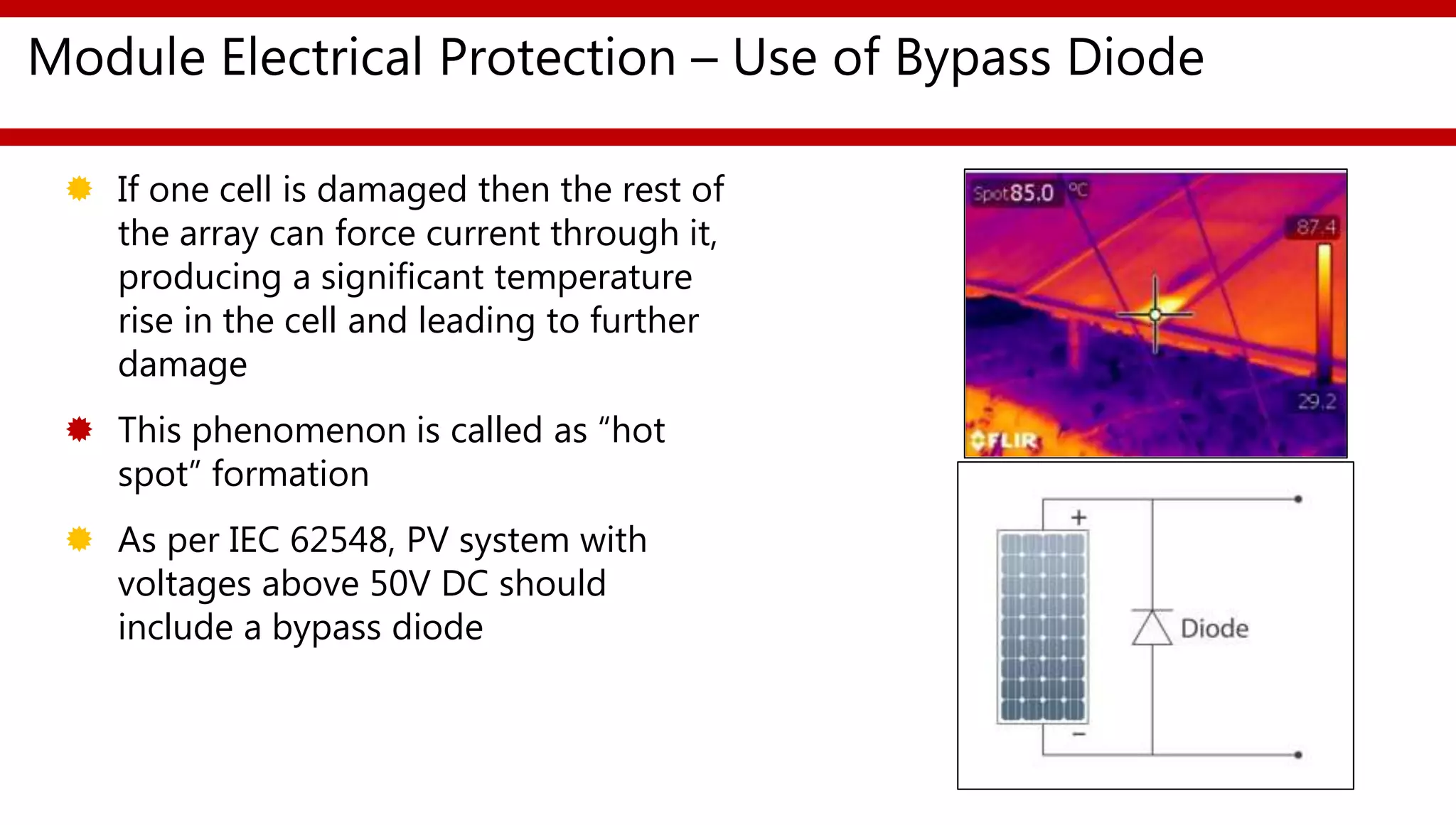
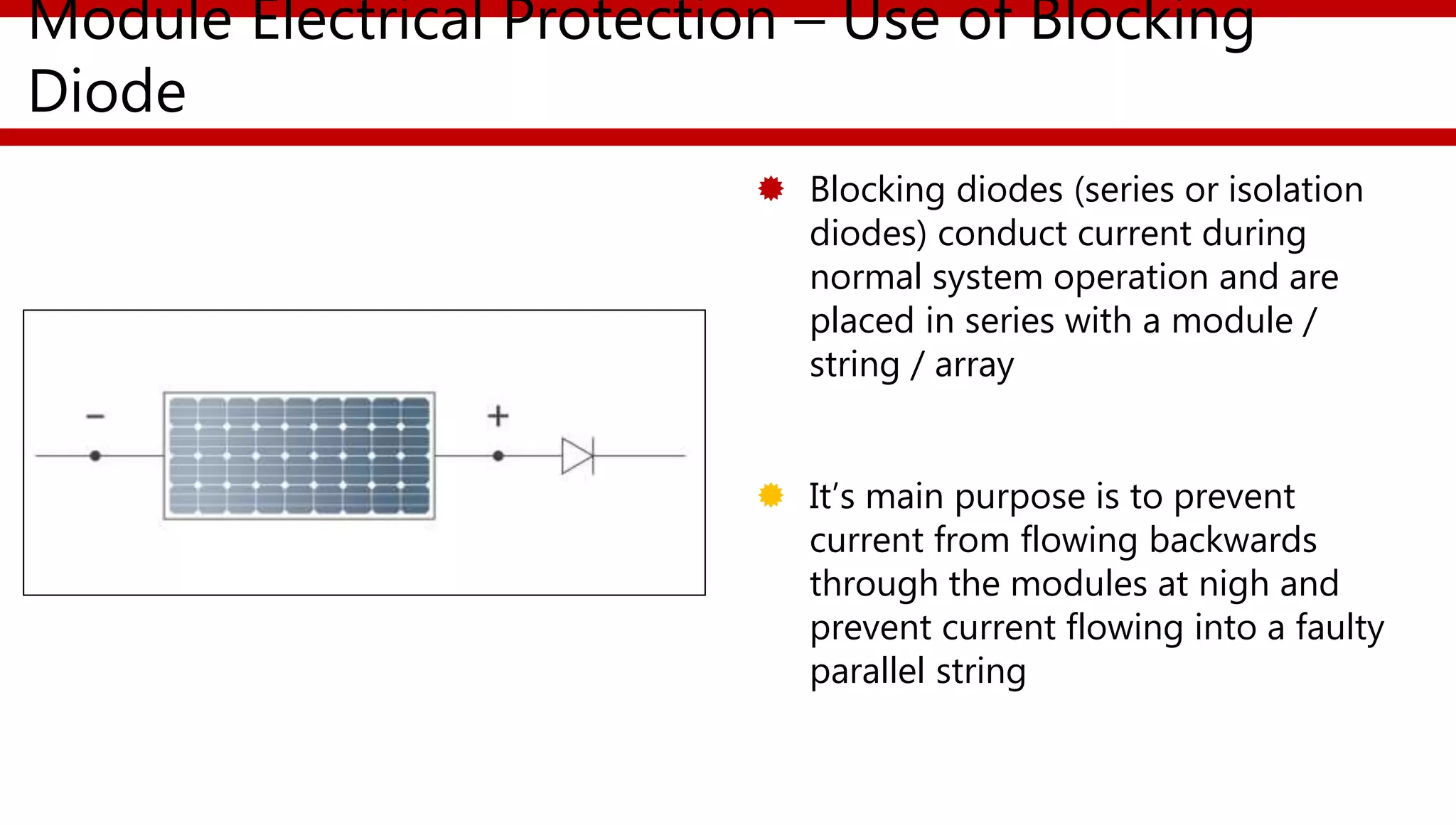
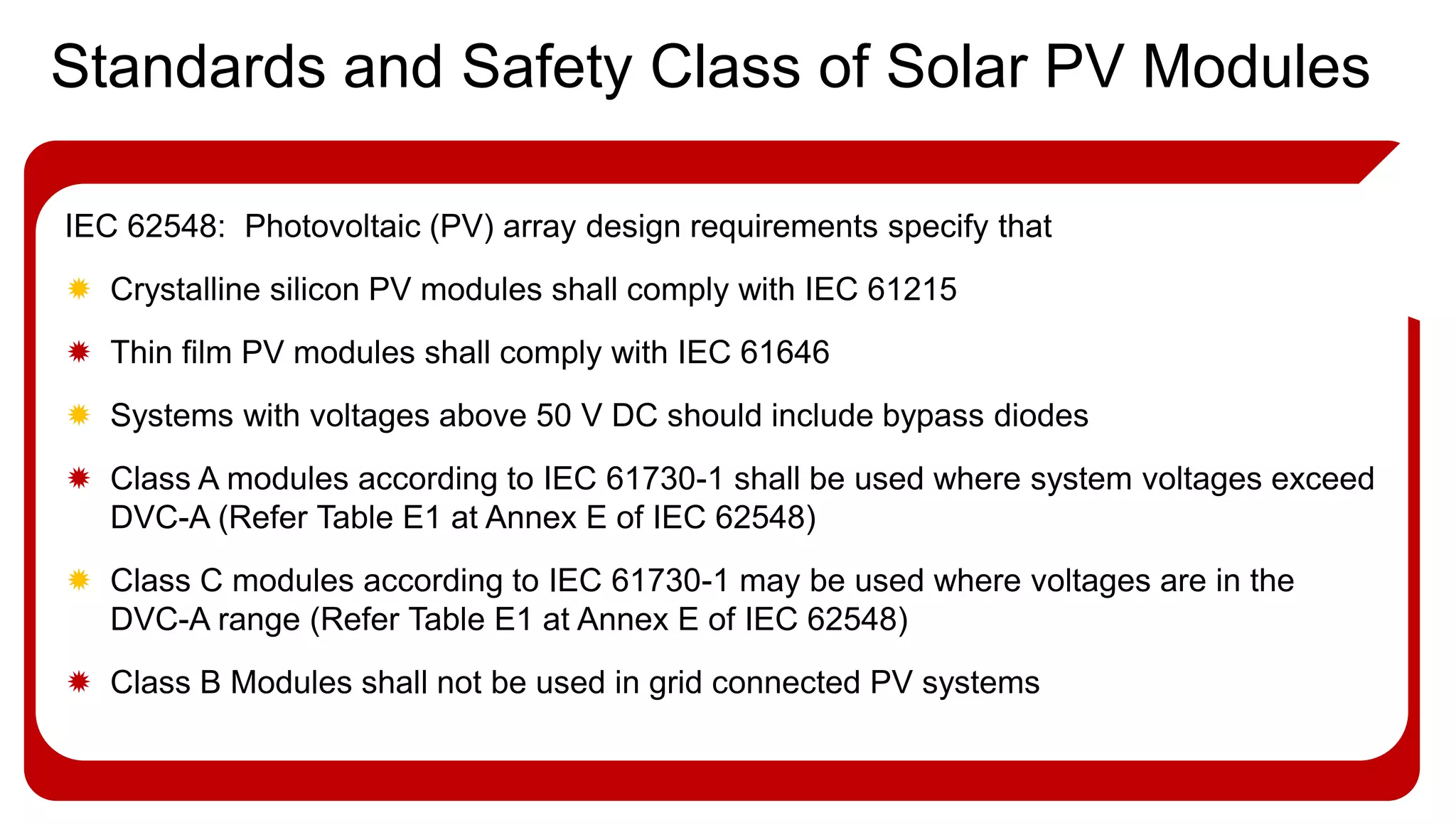
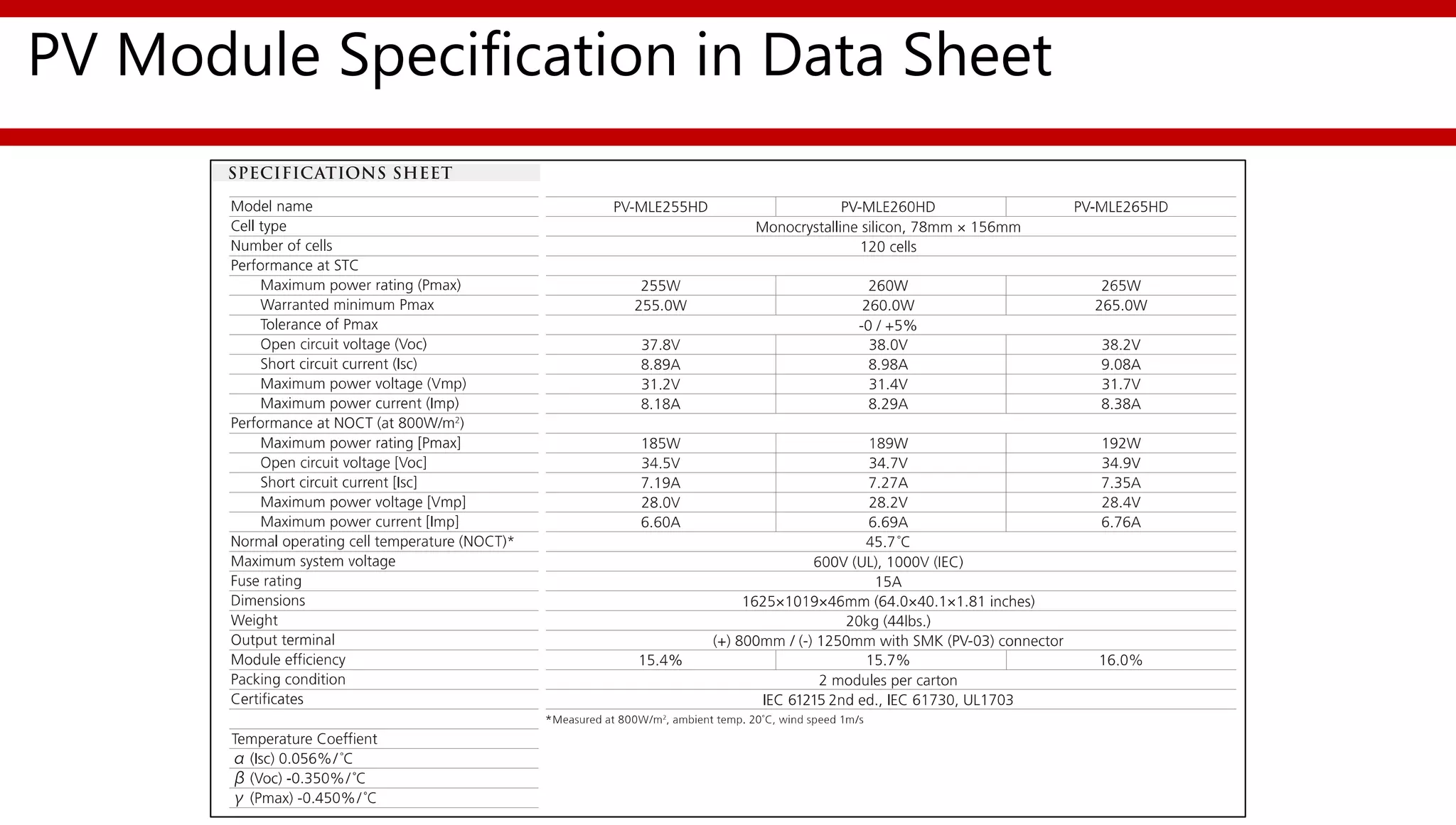
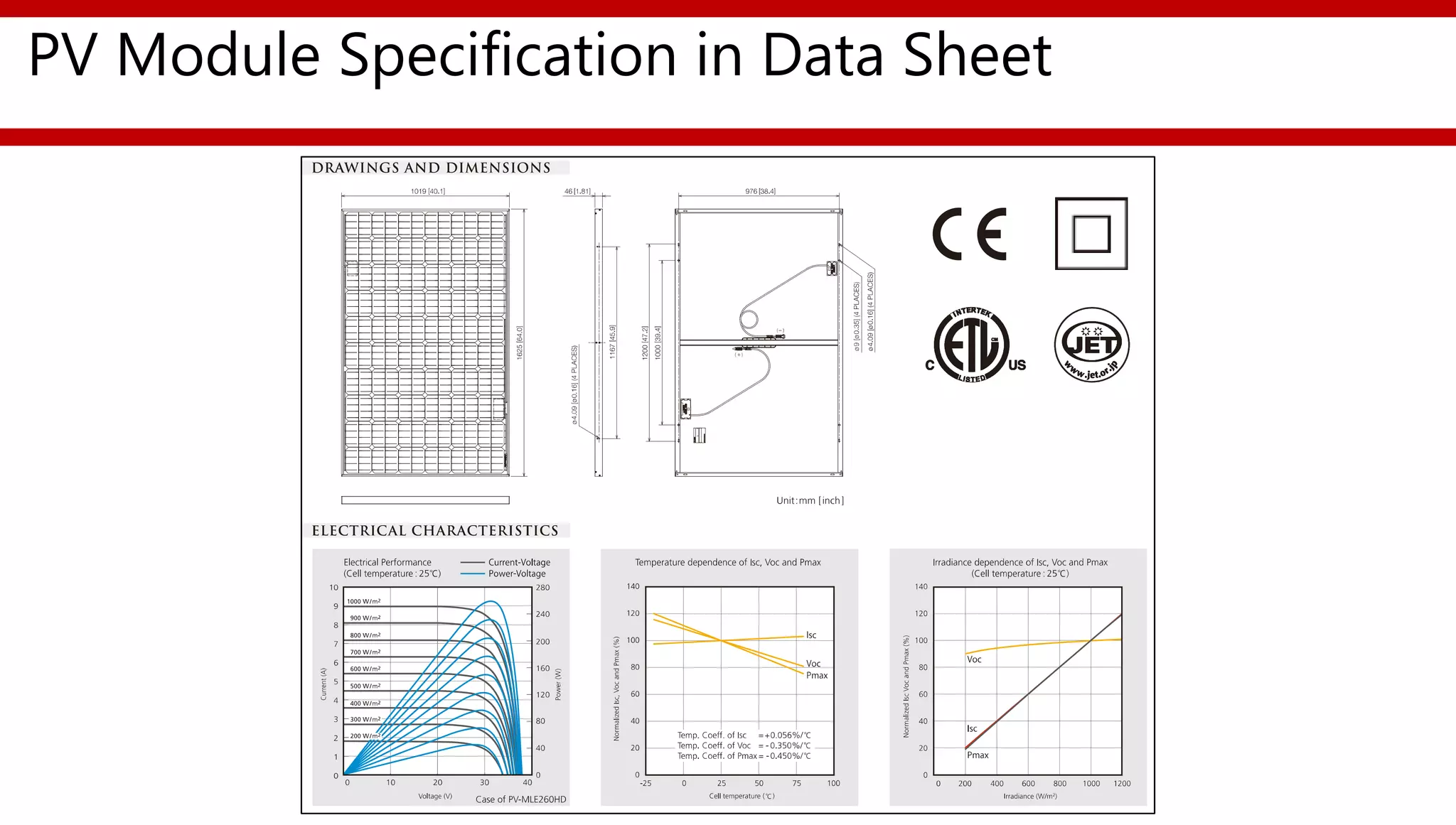
This document provides an overview of different types of solar photovoltaic modules and factors that affect their performance. It discusses mono-crystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous thin film, multi-junction amorphous thin film, CdTe thin film, and CIGS thin film modules. Key factors like quality, temperature, irradiance, and spectral content are covered. The document also outlines standard test conditions, module electrical protection needs, and safety standards.