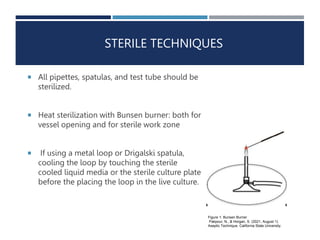
1. The document describes microbiological techniques including sterile techniques, culture media, hypotheses, and experiments.
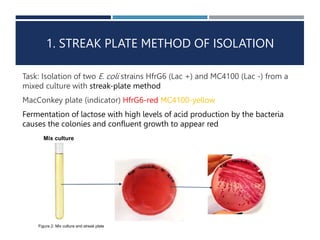
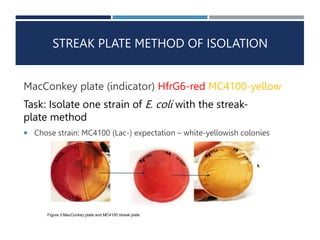
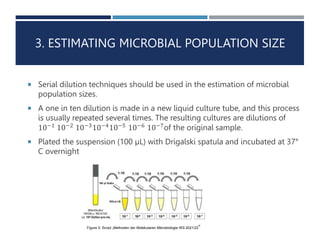
2. The experiments include streak plating two E. coli strains to isolate them, inoculating liquid cultures under sterile conditions, and using serial dilutions to estimate microbial population size.
3. The results supported the hypotheses that sterile techniques yield pure cultures, controls remain sterile, and serial dilutions proportionally estimate populations.