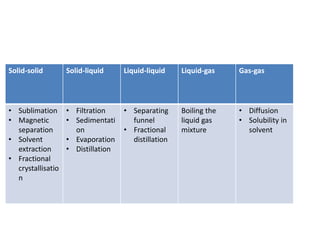
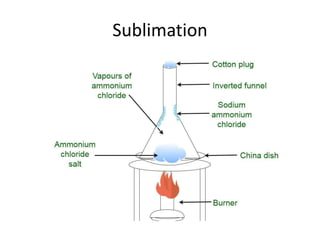
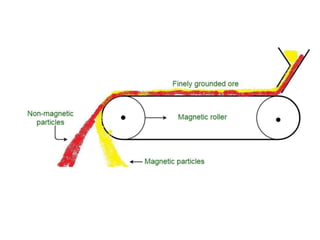
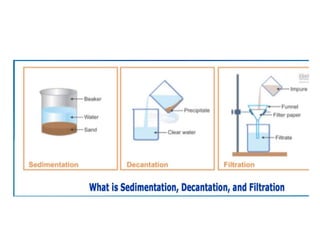
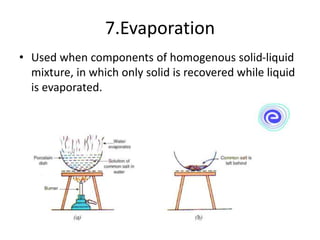
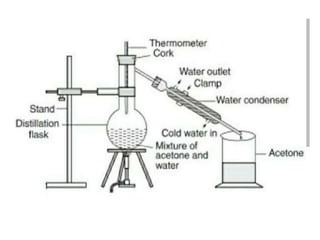
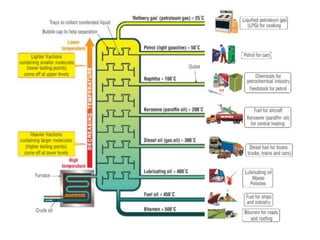
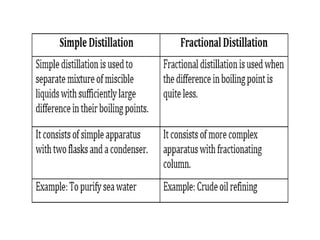
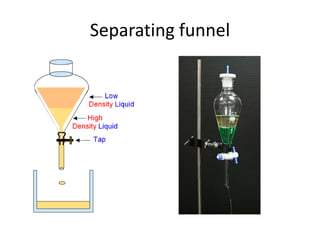
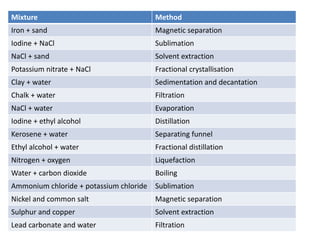
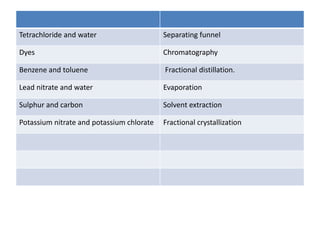
The document provides an overview of various methods used to separate mixtures, including techniques for solid-solid, solid-liquid, liquid-liquid, liquid-gas, and gas-gas separations. Key methods discussed include sublimation, magnetic separation, solvent extraction, filtration, distillation, and chromatography, each suitable for specific types of mixtures. Examples of mixtures and the appropriate separation techniques are also provided to illustrate the concepts.