This document provides an overview of search engine optimization (SEO), explaining its significance in increasing website visibility through effective keyword usage, links, and crawler-friendly practices. It distinguishes between white hat and black hat SEO methods, emphasizing the importance of abiding by search engine guidelines for long-term success. The document also covers SEO tools and strategies, as well as the critical role of content quality in achieving high search rankings.


























![39
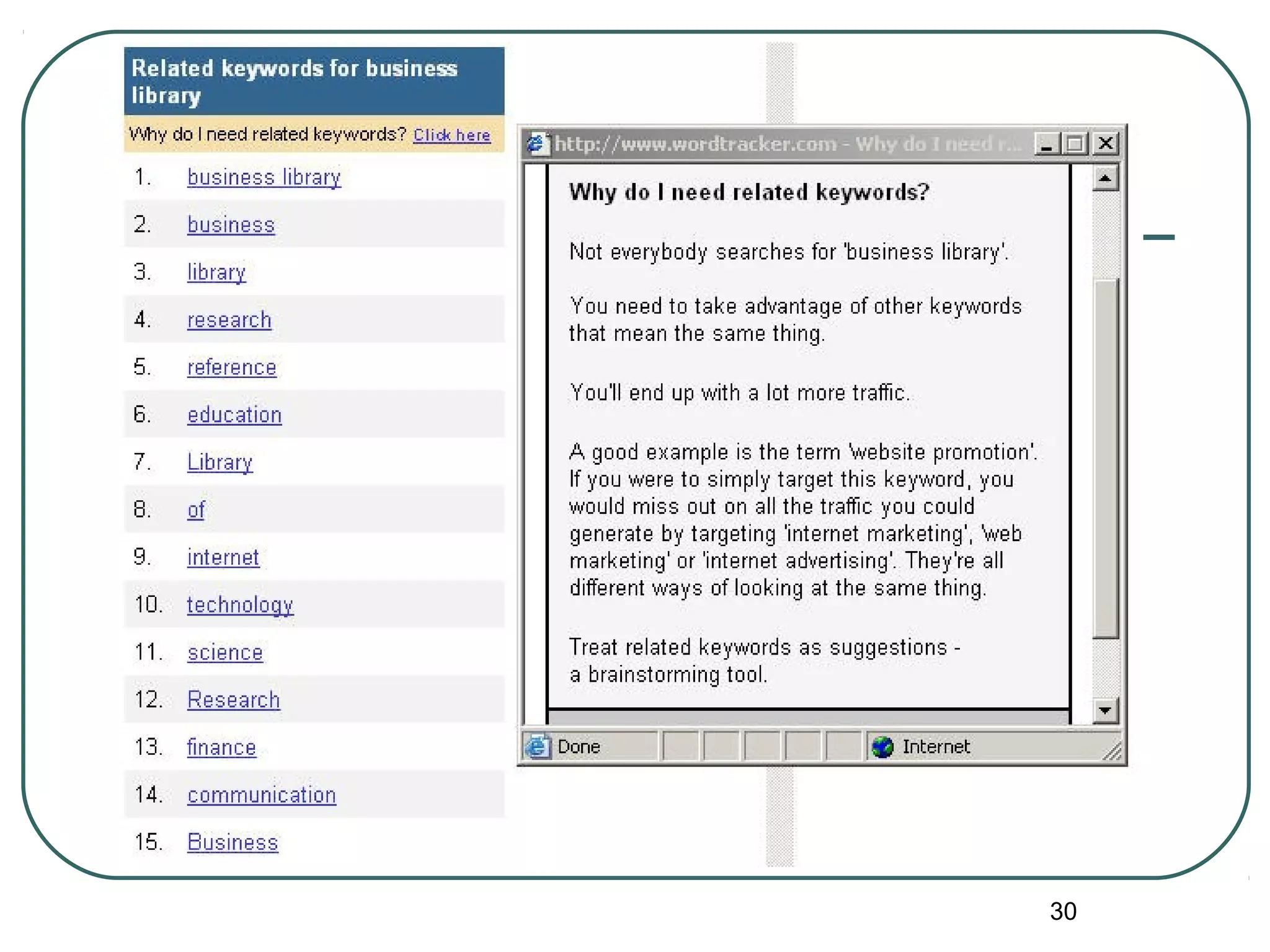
Keyword Tools
Overture tool
http://inventory.overture.com/d/searchinventory/suggestion
Wordtracker tool [recommended]
http://our.affiliatetracking.net/wordtracker/a/12246
Google Sandbox Tool
https://adwords.google.com/select/main?cmd=KeywordSandbox
Espotting Tool
http://www.espotting.com/popups/keywordgenbox.asp
Related Pages
http://www.related-pages.com/adwordskeywords.aspx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seo-beginners-slide-show-150430064824-conversion-gate01/75/Search-Engine-Optimization-Tips-SEO-Tips-For-Beginners-in-2015-39-2048.jpg)