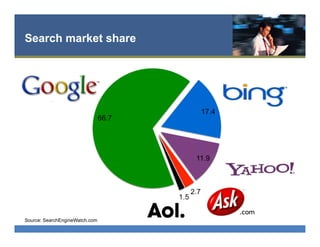
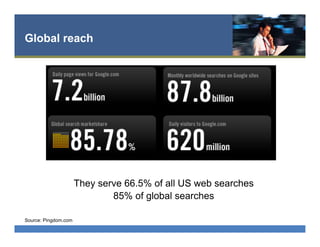
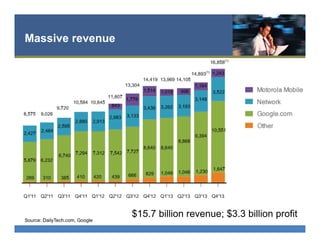
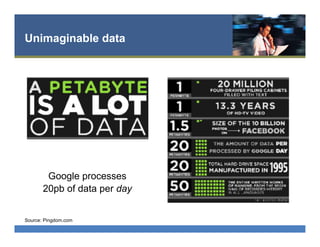
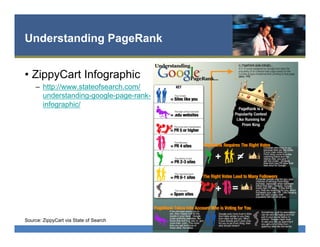
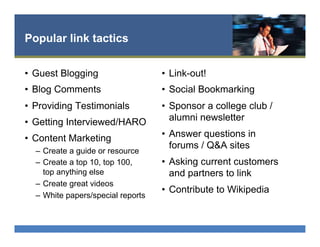
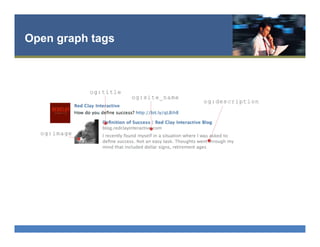
The document provides an overview of search engine optimization (SEO) best practices. It discusses the importance of on-page optimization elements like title tags, meta descriptions, images and body content. It also covers off-page optimization tactics like building high-quality links from relevant sites. Additionally, the document outlines tools for keyword research, site audits and technical SEO checks. The goal is to help websites improve their visibility and rankings on search engines through both on-page and off-page optimization strategies.