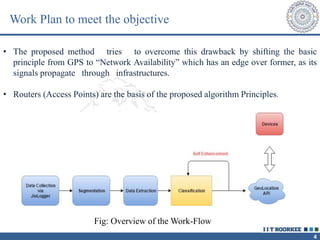
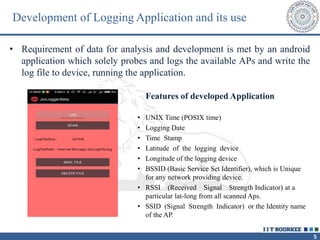
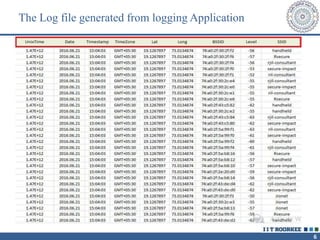
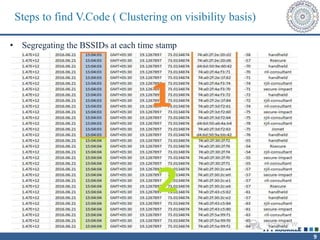
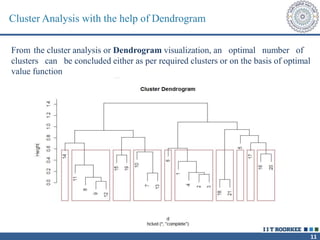
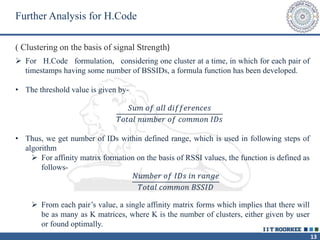
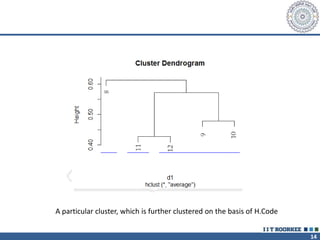
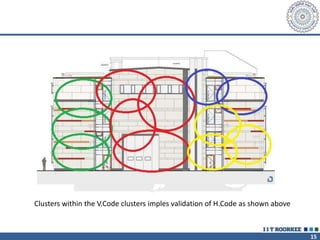
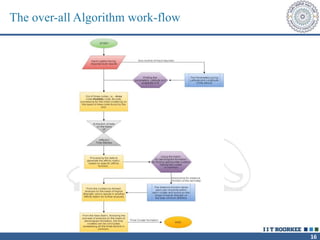
The document describes a call clustering algorithm for Wi-Fi based geolocation. It aims to improve precision of indoor location tracking, which GPS struggles with. The algorithm clusters devices based on observed Wi-Fi access points. It develops three codes - Area, Visibility, and Power codes - to group devices by location, common access points seen over time, and relative signal strengths. Logs of access point observations from an Android app are used to test clustering methods and develop the final algorithm, which can more reliably track indoor location than GPS or other methods.