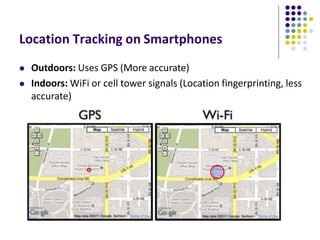
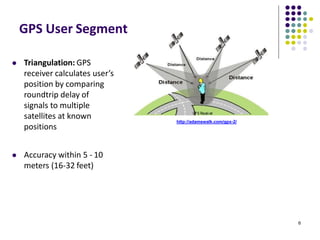
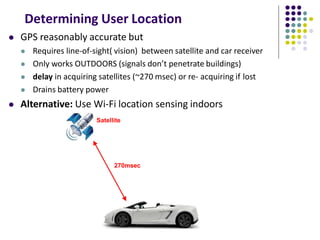
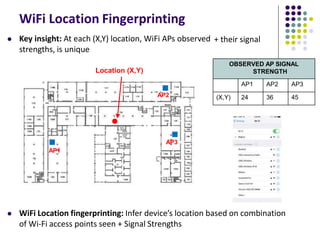
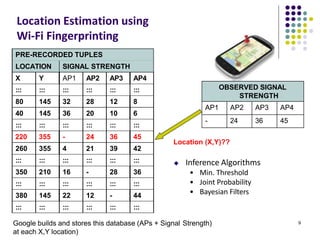
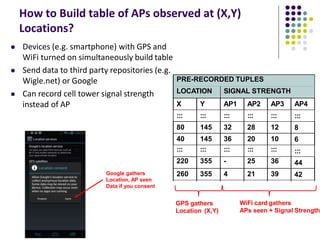
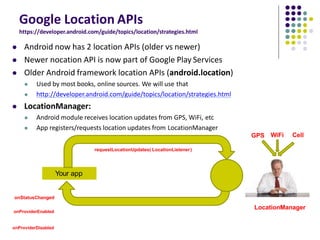
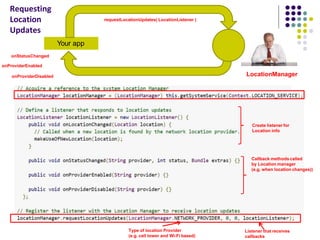
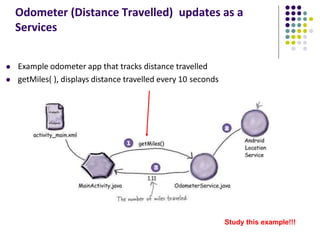
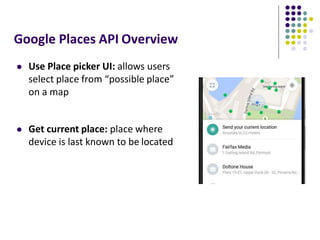
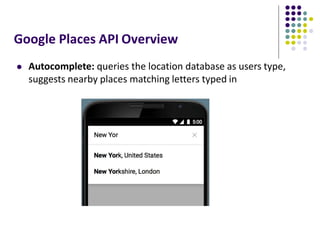
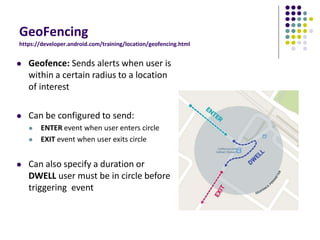
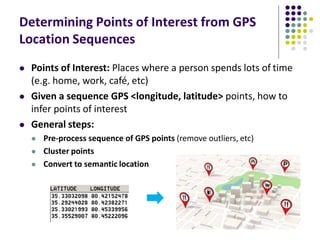
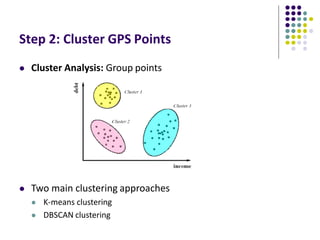
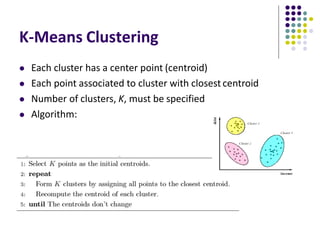
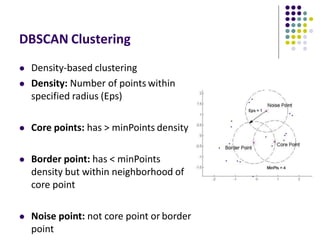
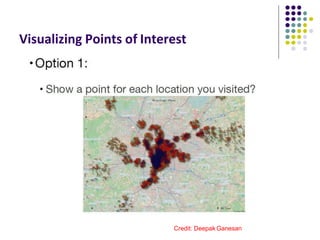
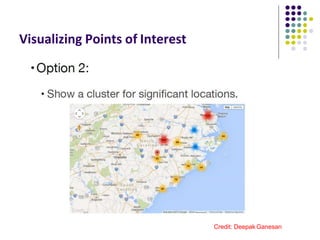
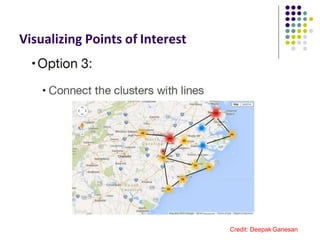
The document discusses location-aware computing and location tracking on smartphones. It describes how GPS and WiFi location fingerprinting are used to determine a user's location outdoors and indoors, respectively. It also discusses how location data is collected and stored by companies like Google to enable location-based services and applications. Finally, it outlines some common techniques for analyzing GPS data to identify points of interest, including preprocessing, clustering algorithms, and converting locations to semantic places.