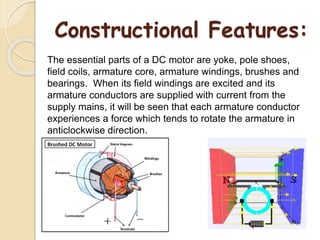
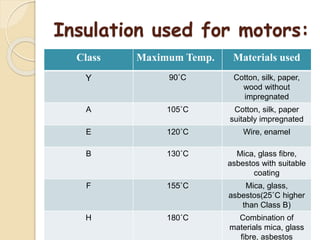
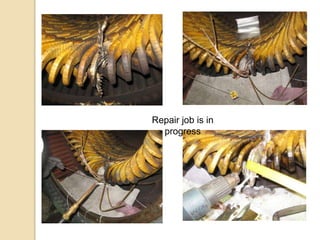
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on the study and repair of motors. It discusses the classification, construction, common failures and insulation of motors. It then describes the rewinding process, bearing replacement, and provides a case study on repairing a 1550 kW HT motor by cutting out the damaged portion and brazing in a new copper strip instead of full rewinding, saving costs and downtime. In conclusion, careful examination and using better materials can improve motor repairs economically.