This study investigates the optimization of physical parameters, specifically the ratio of surface area of copper to the volume of water, which significantly affects the disinfection of water using copper against bacteria like E. coli and Salmonella. Conducted using cylindrical copper jugs and rectangular copper plates, the results indicate that a decreased surface area to volume ratio increases the time required for disinfection, with an optimal ratio of 0.36 achieving maximum bacterial reduction. These findings validate copper's antimicrobial properties and its potential application in safe drinking water storage.

![2 Page 1-10 © MAT Journals 2017. All Rights Reserved
Journal of Civil and Construction Engineering
Volume 3 Issue 2
impact on worldwide access to improved
drinking water sources, there are several
areas that are still unaddressed or are
lacking access to safe drinking water.
Researchers have repeatedly observed that
the microbiological quality of water in
transportation and drinking vessels in the
home is lower than that at the source,
suggesting that contamination may occur
at different stages during the process from
collection of water to consumption (Pruss
et al., 2002; Gundry et al., 2006). Even
though, storage of water has been
recommended as a method of water
purification, contamination of treated or
disinfected water can also occur during
storage due to improper handling. Hence it
is important from a safety point of view to
maintain the quality of drinking water
during storage. Certain heavy metals (like
Silver, Copper, Zinc) are thought to be
antimicrobial and they have great potential
to be used as disinfectant in the treatment
of drinking water. The disinfection using
these metal ions have been studied in
different configuration. The sensitivity of
metals to human and microbial tissues is
different.
MATERIAL & METHODS
Preparation of bacterial culture
Bacterial culture containing E.coli,
Salmonella typhimurium and
Pseudomonas aureofaciens was prepared
by inoculating specific bacteria into
Nutrient Broth (HIMEDIA, Mumbai) from
their respective selective media plates and
incubating for 24 hours in bacteriological
incubator at specific temperatures.
Preparation of test water
In order to prepare sample for testing
appropriate quantity of prepared bacterial
culture was spiked in normal saline
solution (NaCl, 0.85% w/v) which was
autoclaved at 121o
C temperature.
Detection of pH and Copper ion
concentration
pH of the test sample was tested before
and after treatment and was found to rise
by 1 unit[1-20]. Leaching of copper in
treated sample was also tested by
Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical
Emission Spectroscopy and it was found to
be within the BIS permissible limit.
Optimization of physical parameters
With cylindrical copper jug of 1 L.
capacity
A cylindrical jug of 1L. Capacity as shown
in Fig. 1 and a glass beaker as shown in
Fig. 2 were taken. Copper vessel was
wiped with 100% ethanol and then 2-3
times with hot boiling water to remove any
organic or inorganic impurities, if present.
Similar and equal amount of test sample,
say 100 ml (containing E.coli species in it)
was placed in both the copper vessel and
the glass vessel respectively. The glass
vessel was used as negative control. The
depth (d1) upto which test sample was in
contact with copper jug was measured.
Raw sample was withdrawn from both the
containers to determine the initial bacterial
count[21-35]. The sample in both the
containers was stirred with a stirrer for 5
mins and then with a sterile pipette for 10
to 15 seconds, each time before taking the
sample. Sample time points like t=1, t=2,
t=3, t=4, t=5, t=6, t=7 and t=8 hrs were
selected and the sample so taken was
passed from Membrane filtration apparatus
(0.45µm pore size membrane) after desired
serial dilution. The membrane was then
placed on EMB agar petri plates. The plate
was then placed in bacteriological
incubator at 37o
C in inverted position for
24 hours. The bacterial counts were noted
by counting the no. of purple coloured
colonies on plate indicative of E.coli. This
determined the bacterial reduction. The
above set of experiment was repeated by
adding 300 mL of test sample to each
copper jug and the glass beaker
respectively and the depth (d2) upto which](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizationpaper-190606052653/75/Optimization-of-Physical-Parameters-affecting-Disinfection-of-Water-by-Copper-2-2048.jpg)
![3 Page 1-10 © MAT Journals 2017. All Rights Reserved
Journal of Civil and Construction Engineering
Volume 3 Issue 2
test sample was in contact with copper jug
was noted down. Similarly, by adding 600
ml of sample the experiment was carried
out and the depth (d3) was measured. It can
be stated that by changing the volume of
sample in contact, the area of copper jug in
contact with the sample also changes.
Hence, the ratio of surface area of copper
jug in contact to volume of sample in
contact also changes (2.1, 0.92, 0.65). The
details of the same have been presented in
Table 1.
Fig. 1 Cylindrical Copper Jug Fig. 2 Glass beaker used as negative control
Table 1 Calculation of ratio of Surface area of copper in contact to Volume of sample in
contact with cylindrical copper jug
S. No. Volume of
sample in
contact with
copper jug
Radius of
copper jug
Depth of
sample in
copper jug
Area of
copper jug in
contact with
sample
2πr(r+ h)
Ratio pH of sample
(in mL) (in cm.) (in cm.) (in cm2
) (in cm-1
) Initial Final
1 100 5.2 d1 (1.2) 210 2.1 6.5 7.0
2 300 5.2 d2 (3.2) 275 0.92 6.5 7.5
3 600 5.2 d3 (6.8) 392 0.65 6.5 7.5
With rectangular plates of 18 cm x 10
cm
The glass beakers of capacity 2L. were
taken. Test sample of quantity 2L.
(containing E.coli bacterium in it) was
added in each glass beaker. Copper plates
of 99% purity and dimensions 18cm x
10cm (total surface area of 360 cm2
) were
used[36-40]. The plates were wiped with
ethanol and hot boiling water. The
experiment was carried out in batches,
since, the number of plates were limited.
Half copper plate was dipped in 1st
beaker,
1 full plate in 2nd
beaker, 2 full plates in 3rd
beaker, 3 full plates in 4rth
beaker, 4 full
plates in 5th
beaker and no copper plate in
last 6th
beaker which was used as a
negative control. All the beakers were
placed on magnetic stirrer at low stiring as
shown in Fig. 3. Raw sample was](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizationpaper-190606052653/75/Optimization-of-Physical-Parameters-affecting-Disinfection-of-Water-by-Copper-3-2048.jpg)
![4 Page 1-10 © MAT Journals 2017. All Rights Reserved
Journal of Civil and Construction Engineering
Volume 3 Issue 2
withdrawn from the containers to
determine the initial bacterial count. The
sample in the containers was stirred with a
sterile pipette for 10-15 seconds, each time
before taking the sample. Sample
timepoints like t=0.5, t=1.0, t=1.5, t=2.0,
t=2.5, t=3.0, t=3.5, t=4.0, t=4.5 and t=5.0
hrs were selected and the sample so taken
was passed from Membrane filteration
apparatus (0.45µm pore size membrane)
after desired serial dilution[41-47]. The
membrane was then placed on EMB agar
petri plates. The plate was then placed in
bacteriological incubator at 37o
C for 24
hours. The bacterial counts were noted by
counting the no. of purple coloured
colonies on plate indicative of E.coli. This
determined the bacterial reduction.
In this experiment the volume of sample
have been kept constant while the surface
area of copper in contact with sample was
varied by increasing the number of plates
being dipped in beakers. Hence, the ratio
of surface area of copper in contact to
volume of sample in contact varied (0.09,
0.18, 0.36, 0.54 and 0.72). The details of
the same have been presented in Table 2.
Table 2 Calculation of ratio of Surface area of copper plates in contact to Volume of sample
in contact with rectangular copper plates
S. No. Volume of sample
(in cm3
)
Surface Area of copper plate in
contact with sample
(in cm2
)
Ratio
(in cm-1
)
1 2000 180 0.09
2 2000 360 0.18
4 2000 720 0.36
5 2000 1080 0.54
6 2000 1440 0.72
Fig. 3 Beaker with rectangular copper plates & Beaker with negative control](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizationpaper-190606052653/75/Optimization-of-Physical-Parameters-affecting-Disinfection-of-Water-by-Copper-4-2048.jpg)
![5 Page 1-10 © MAT Journals 2017. All Rights Reserved
Journal of Civil and Construction Engineering
Volume 3 Issue 2
RESULTS & DISCUSSION
The results of log10 (No/Nt) reduction
values for E.Coli in different experimental
trials performed by varying the surface
area of copper in contact and volume of
sample in contact (2.1, 0.92, 0.65) with a
cylindrical copper jug of 1L. capacity of
known dimensions have been presented in
the form of graph as shown in Fig. 4.
Fig. 4 E.coli evaluation for surface area and volume variation
It could be observed from Fig. 4 that when
the SA/V ratio was 2.1 then the time taken
for complete 5 log10 reduction was 11 hrs
which indicated very slow disinfection.
There was a sharp decrease in the
concentration of E.coli in 5th
hr of contact
and then the decrease was gradual[48-57].
When the SA/V ratio decreased to 0.92
then the disinfection time reduced to 4 hrs
for the same concentration of E.coli. When
the SA/V ratio was further decreased to
0.65, then 4 log10 reduction took place in
only 1 hr of contact time. Thus, it can be
stated that as the ratio of surface area of
copper in contact to volume of sample in
contact decreases the time taken for
disinfection increases.
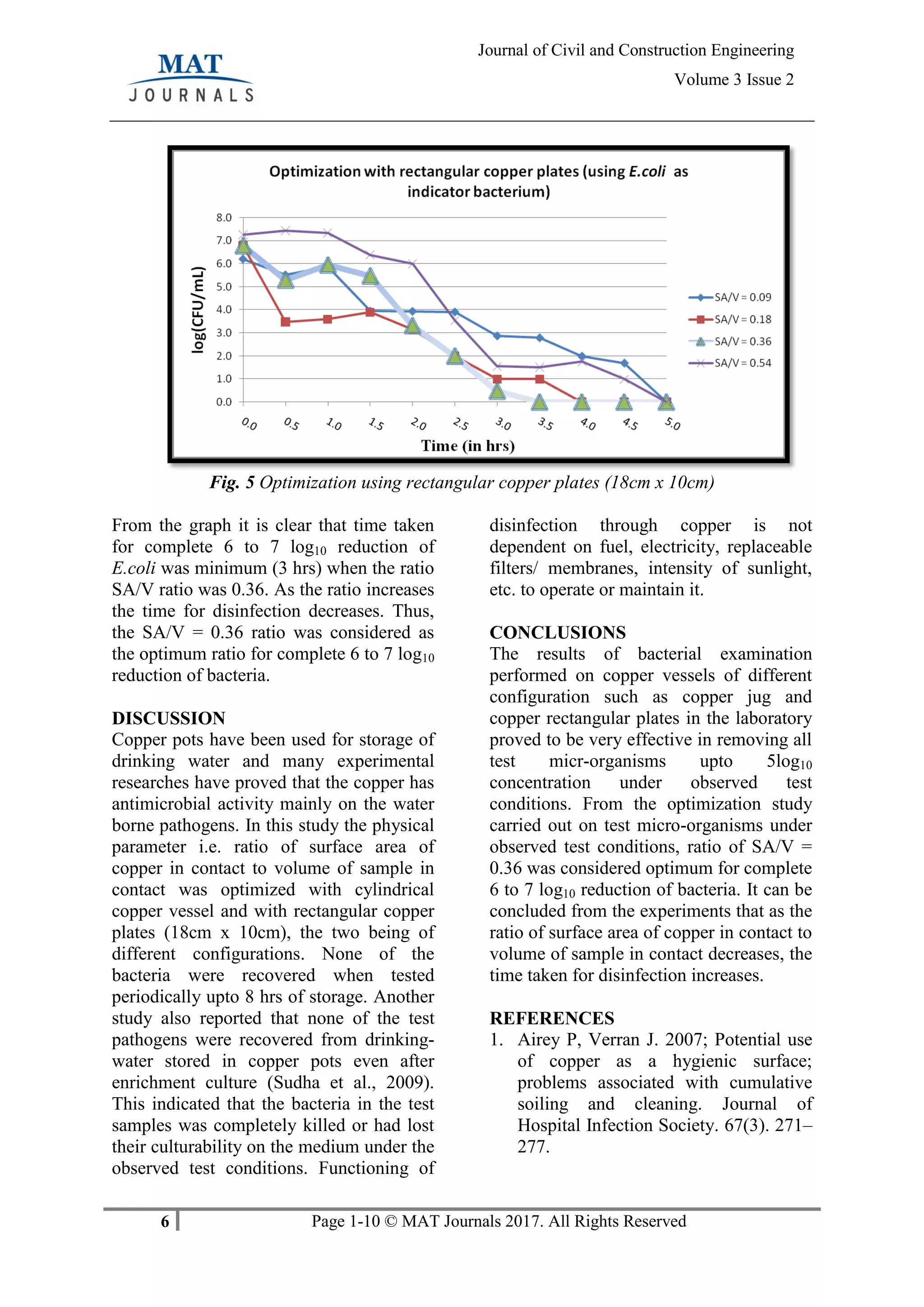
Optimization of physical parameters
using rectangular copper plates (18cm x
10cm)
Optimization study was carried out by
varying the ratio of surface area of copper
in contact to the volume of sample in
contact (0.09, 0.18, 0.36 and 0.54). Surface
area was varied by dipping half, one, two
and three plates in the 2L sample and the
bacterial reduction was noted. It is
presented in the form of graphs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizationpaper-190606052653/75/Optimization-of-Physical-Parameters-affecting-Disinfection-of-Water-by-Copper-5-2048.jpg)
![7 Page 1-10 © MAT Journals 2017. All Rights Reserved
Journal of Civil and Construction Engineering
Volume 3 Issue 2
2. Antimicrobial copper alloy touch
surfaces. Online at
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antimicr
obial_copperalloy_touch_surfaces
(Accessed on November, 2015)
3. Antimicrobial properties of copper.
Online at
https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php/A
ntimicrobial_properties_of_copper&ol
did=633262641(Accessed on
November, 2015)
4. Ashbolt NJ. 2004; Microbial
contamination of drinking water and
disease outcomes in developing
regions. Toxicology. 198(1-3). 229–
238.
5. Beveridge TJ, Murray RE. 1980; Sites
of metal deposition in the cell wall of
Bacillus subtilis. Journal of
Bacteriology. 141(2). 876–87.
6. Blakely T, Hales S, Kieft C, Wilson N,
Woodward A. 2005; The global
distribution of risk factors by poverty
level. Bulletin of the World Health
Organization. 83. 118–126.
7. Borkow G, Gabbay J. 2005; Copper as
a Biocidal Tool. Journal of Current
Medicinal Chemistry. 12(18). 2163-
2175.
8. Bureau of Indian Standards 2005;
Methods of sampling and test (physical
and chemical) for water and
wastewater: Part 42 Copper (first
revision) [IS 3025 (Part 42):1992].
New Delhi: Bureau of Indian
Standards.
9. Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) IS:
10500:2012 (2012) Drinking water
specifications.
10. Clasen T, Roberts I, Rabie T, Schmidt
W, Cairncross S. 2006; Interventions
to improve water quality for preventing
diarrhoea. The Cochrane Library, 3.
11. CPHEEO 1999; Manual on water
supply and treatment, 3rd
edition,
Central Public Health and
Environmental organisation, Ministry
of Urban Development. New Delhi,
India.
12. Curtis V, Cairncross S. 2003; Water,
sanitation, and hygiene at Kyoto.
British Medical Journal. 327. 3–4.
13. Dhanalakshmi T, Rajendran S. 2013;
Antimicrobial Activity of Micro Sized
Copper Particles On Water Borne
Bacterial Pathogens. International
Journal of Scientific & Technology
Research. 2(1). 115-118.
14. Elguindi J, Hao X, Lin Y, Alwathnani
HA, Wei G, Rensing C. 2011;
Advantages and challenges of
increased antimicrobial copper use and
copper mining. Journal of Applied
Microbiology and Biotechnology.
91(2). 237-49.
15. Faúndez G, Troncoso M, Navarrete P,
Figueroa G. 2004; Antimicrobial
activity of copper surfaces against
suspensions of Salmonella enterica
and Campylobacter jejuni. BioMed
Centre Microbiology. 4. 19.
16. Ford TE. 1999; Microbiological safety
of drinking water: United States and
global perspectives. Journal of
Environmental Health Perspectives
107 (1) 191-206.
17. Freeman MC, Trinies V, Boisson S,
Mak, G, Clasen T. 2012; Promoting
Household Water Treatment through
Women's Self Help Groups in Rural
India: Assessing Impact on Drinking
Water Quality and Equity. Journal of
plos one. 7(9).
18. Grass G, Rensing C, Solioz M. 2011;
Metallic Copper as an Antimicrobial
Surface. Journal of Applied and
Environmental Microbiology. 77(5).
1541–1547.
19. Guentzel MN. 1996; Escherichia,
Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia,
Citrobacter, and Proteus. Medical
Microbiology. 4th ed. The University
of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston.
20. Gundry S, Wright A, Conroy R, Du
PM, Genthe B, Moyo S. 2006;
Contamination of drinking water
between source and point of use in
rural households of South Africa and](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizationpaper-190606052653/75/Optimization-of-Physical-Parameters-affecting-Disinfection-of-Water-by-Copper-7-2048.jpg)


