This document provides information about semen analysis, including:
1. Semen analysis evaluates the quantity and quality of semen and sperm to detect male infertility and check the effectiveness of procedures like vasectomy.
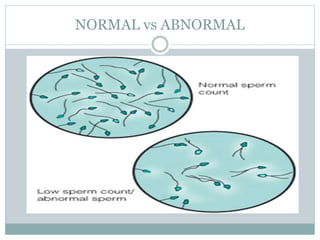
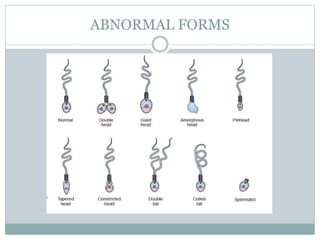
2. Normal parameters include a sperm count of 15 million/ml or more, motility grades of 40% or more, and normal morphology of 4% or more according to WHO standards.
3. Samples should be collected after 2-7 days of abstinence and delivered to the lab within 1 hour to examine volume, pH, viscosity, sperm count, motility, morphology, and presence of other cells. Abnormal results can indicate conditions like infection or abnormalities of the reproductive organs.