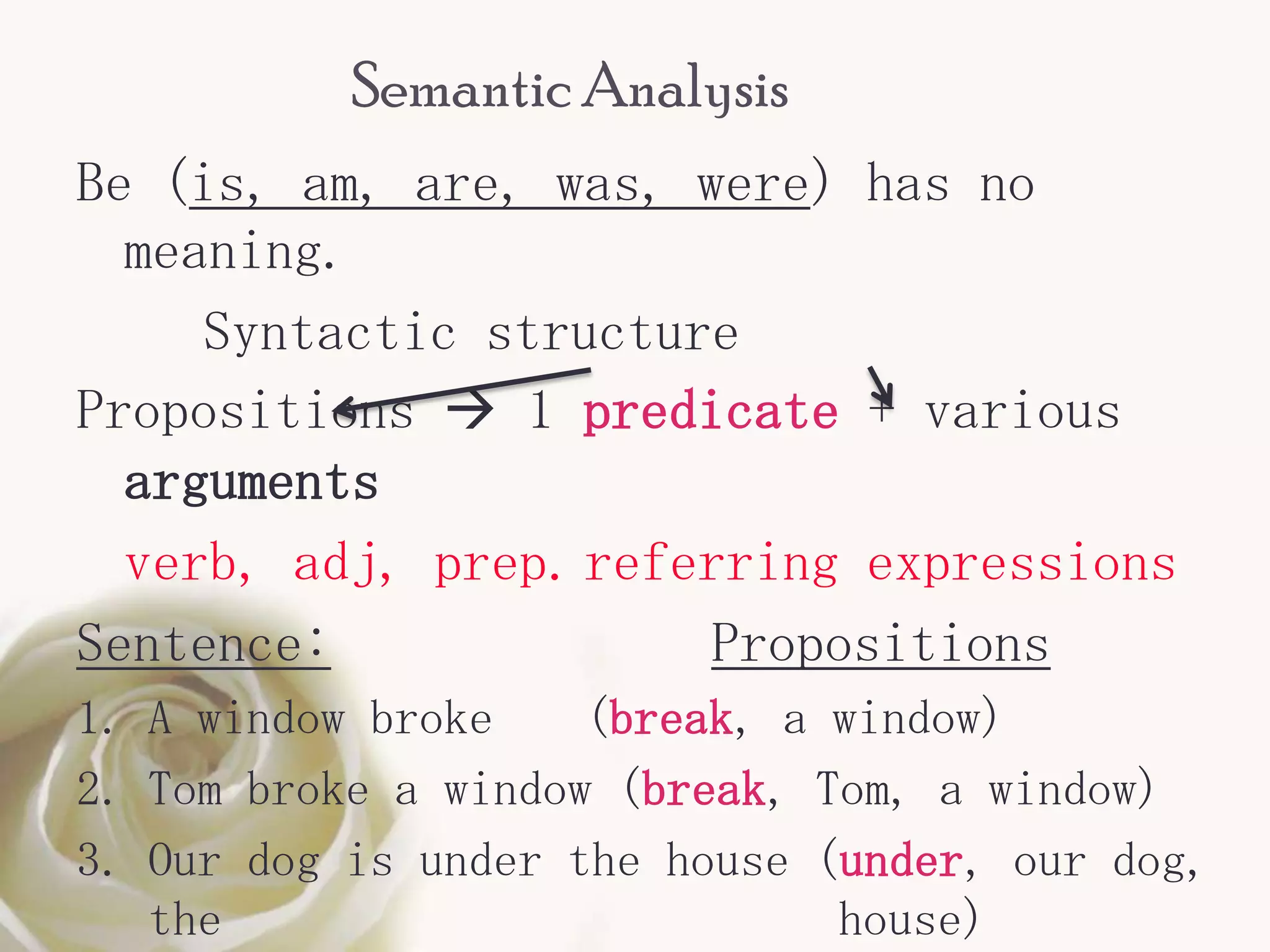
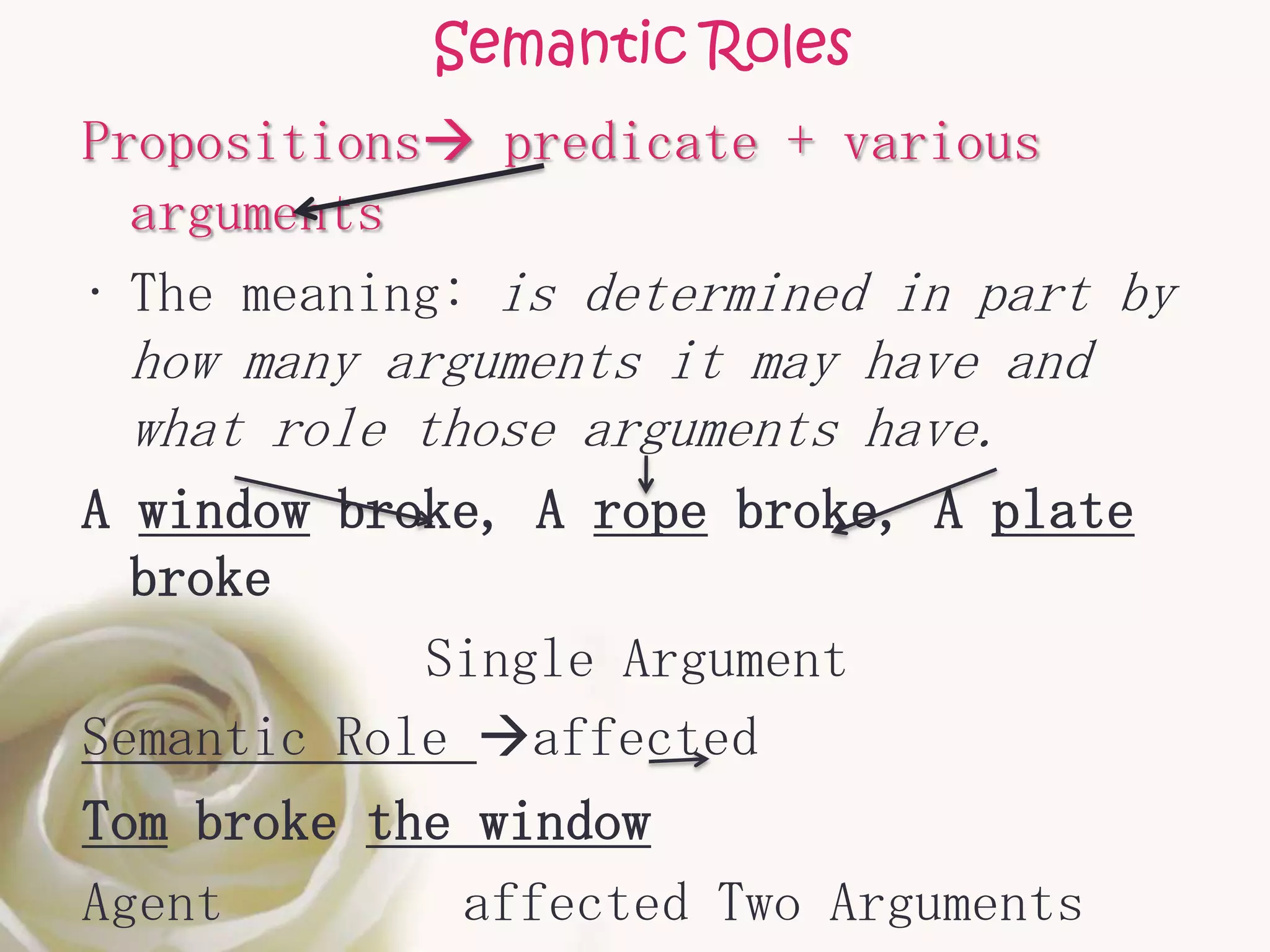
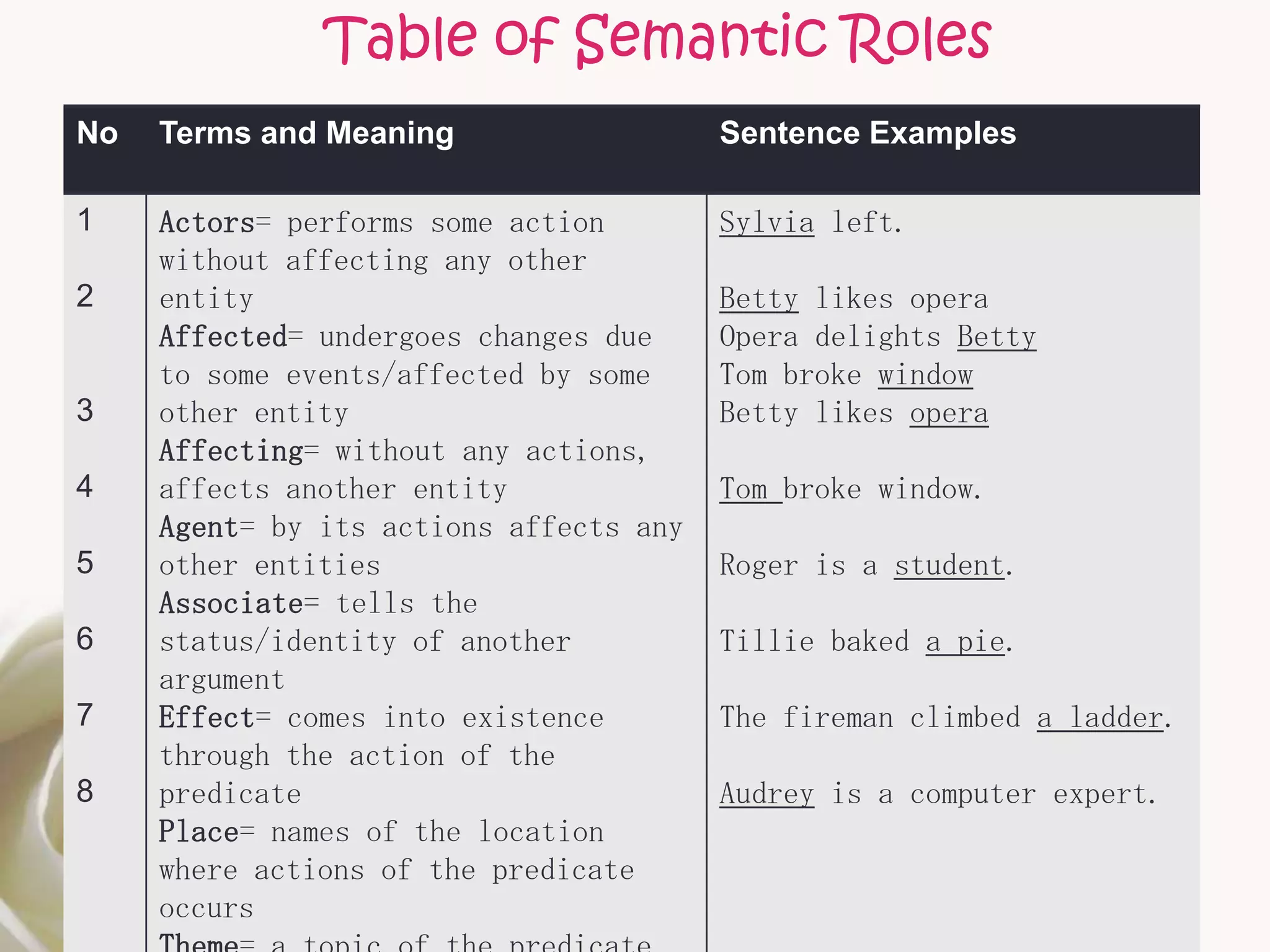
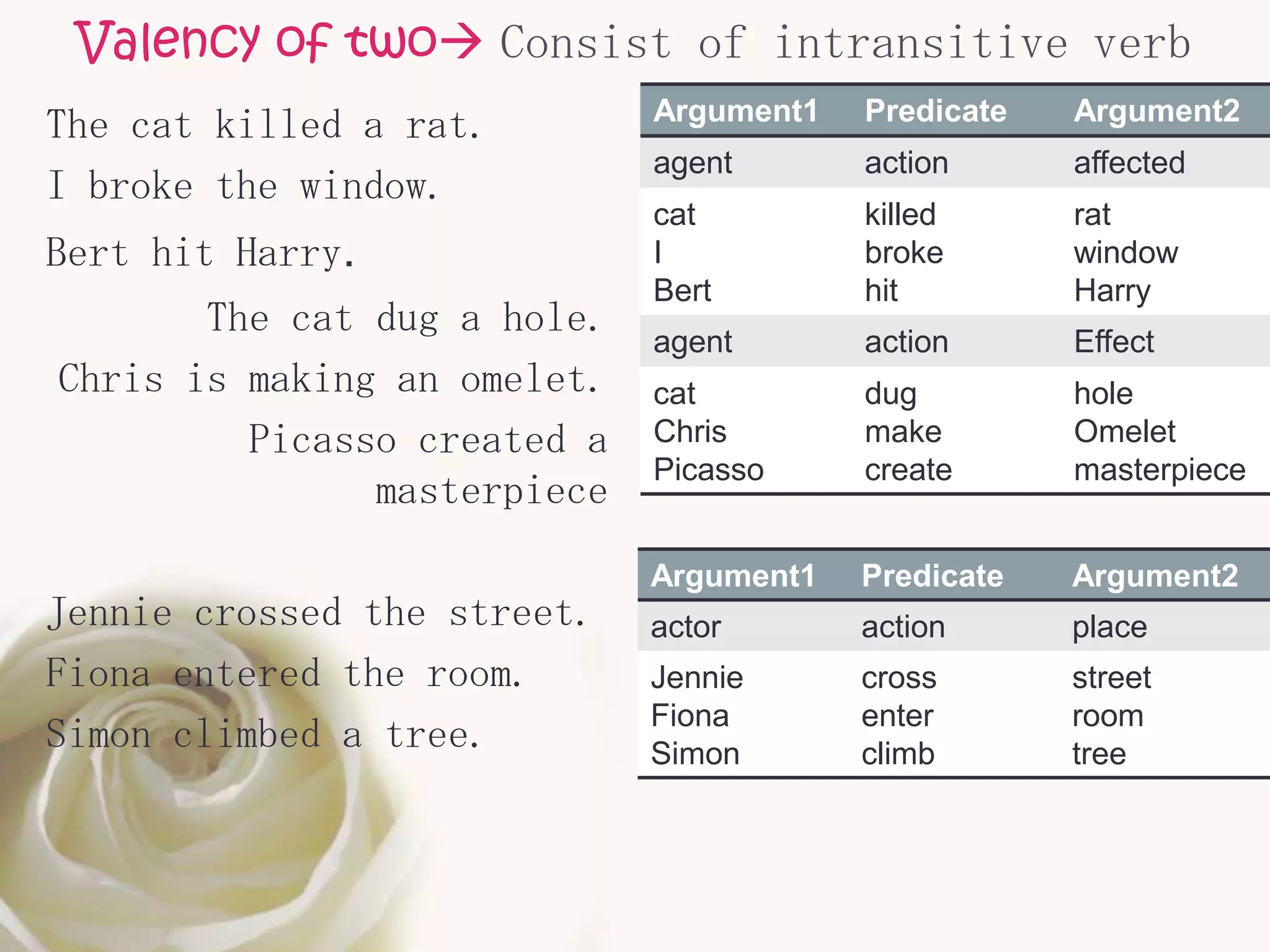
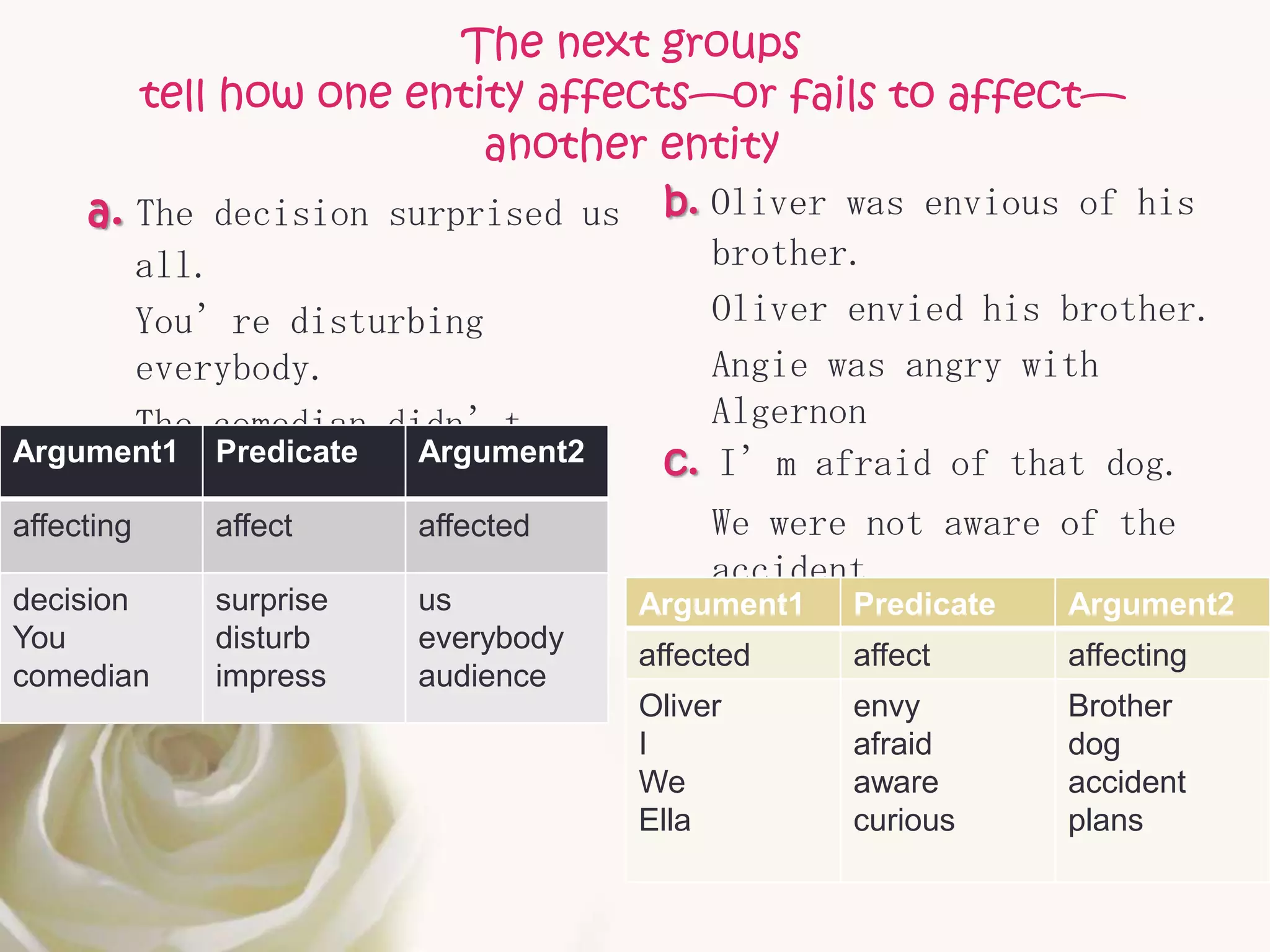
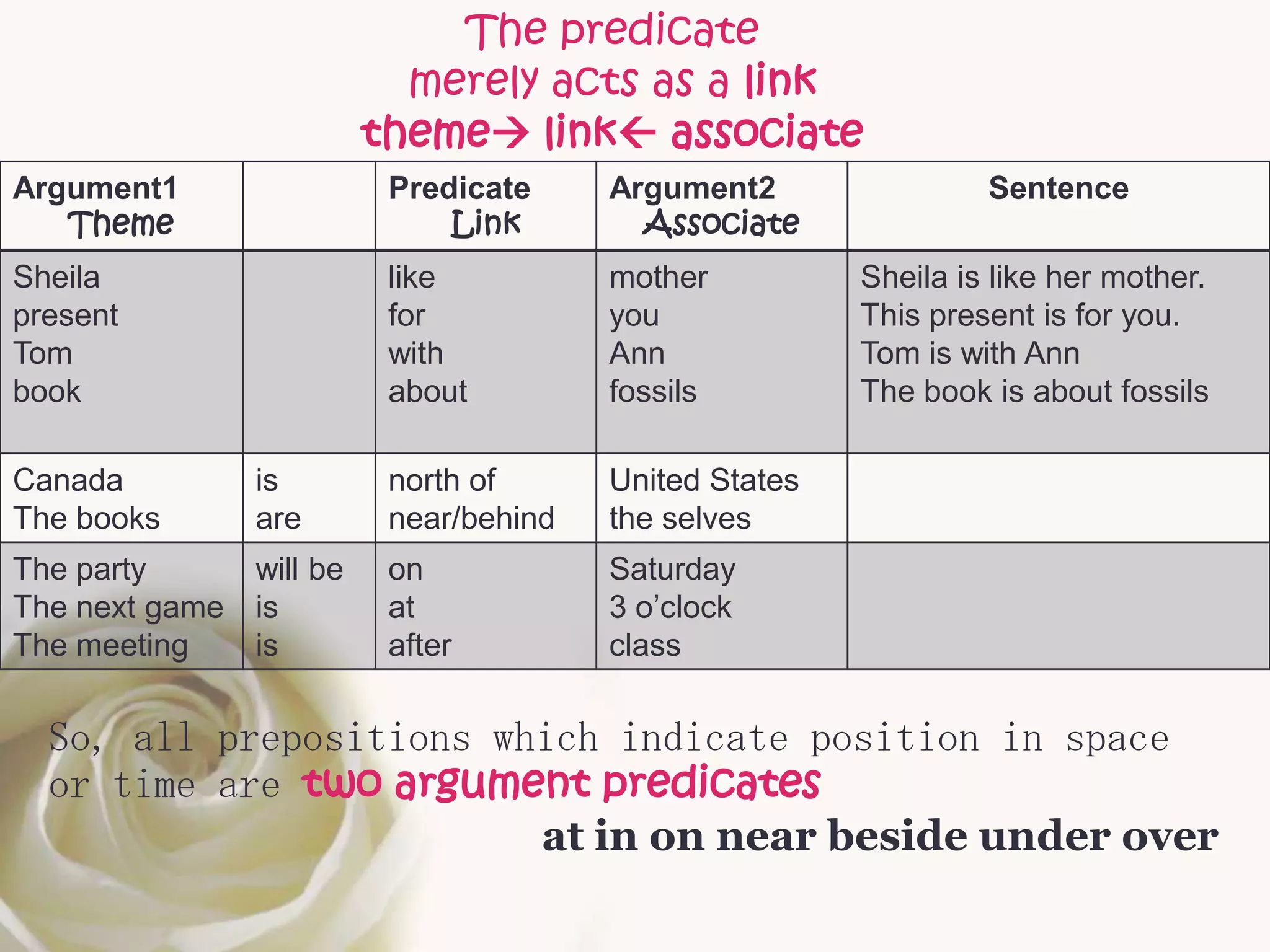
The document discusses semantic roles in language. It begins by defining key terms like sentence, proposition, predicate, and noun phrases. It then explains that a proposition consists of a predicate plus arguments, and discusses how propositions can be expressed through different sentences with varying grammar but conveying the same meaning. The document outlines different semantic roles like agent, patient, and themes and provides examples. It also discusses how the valency of predicates, or number of arguments they can take, can vary and provides a table of common semantic roles.