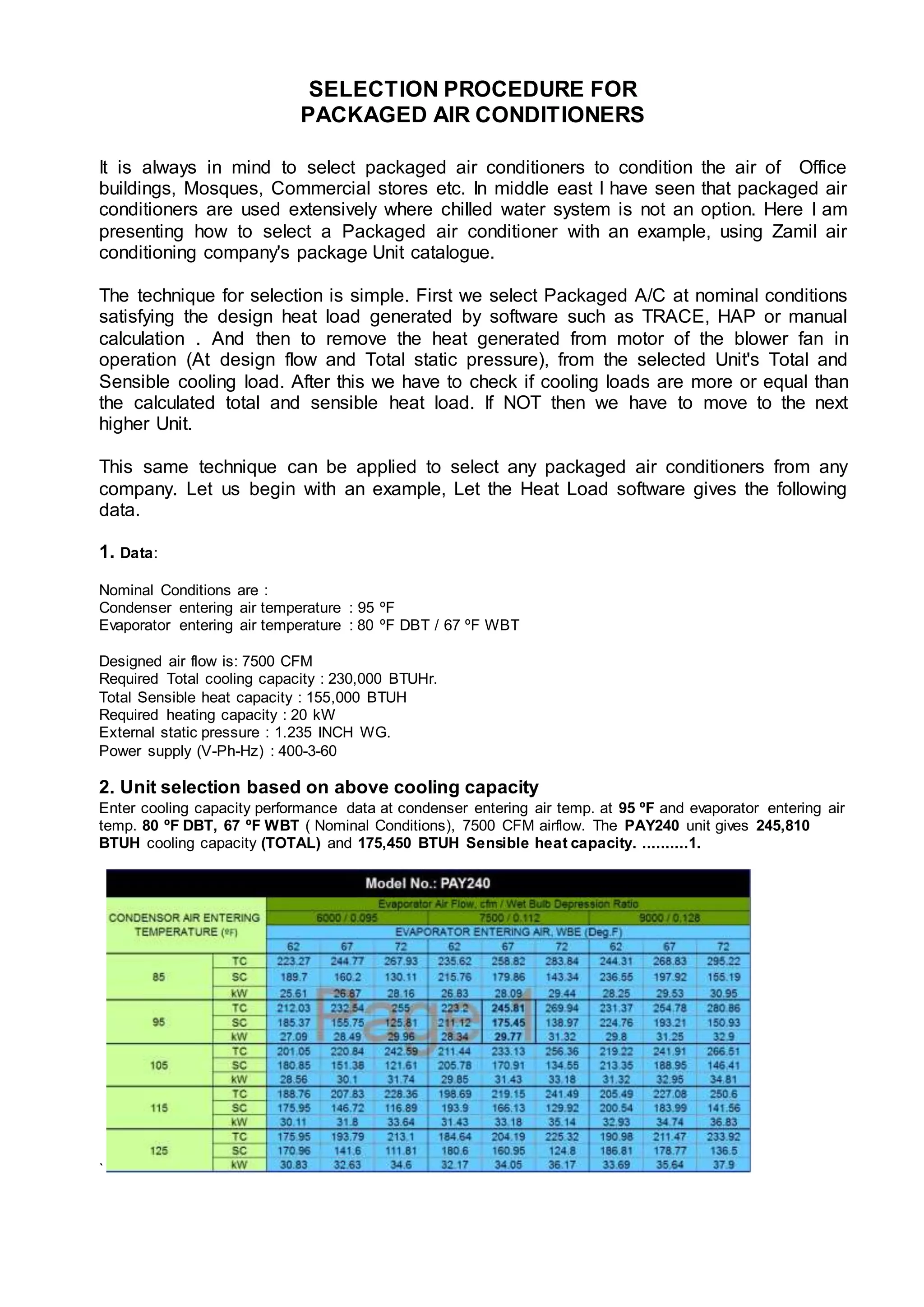
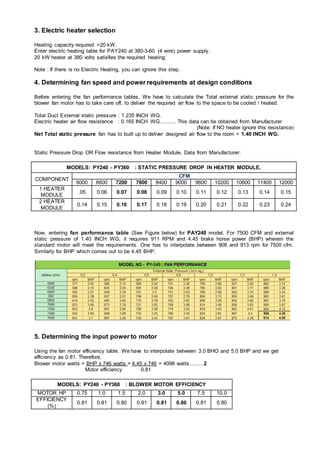
The document provides steps for selecting a packaged air conditioner unit based on design heat load and other criteria. First, a unit is selected that meets the total and sensible cooling load needs at nominal conditions. Then the heat generated by the blower fan is accounted for to determine the net cooling capacities. An electric heater is also selected if needed. Fan speed and power requirements are calculated based on the required air flow and external static pressure. The resulting net cooling capacities are then checked against the design loads to confirm the selected unit is appropriate.