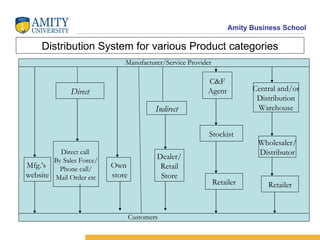
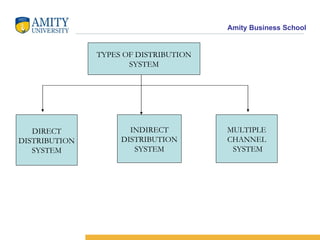
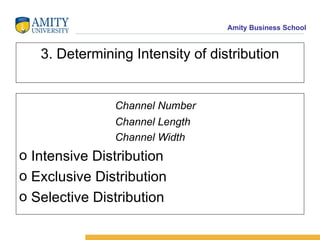
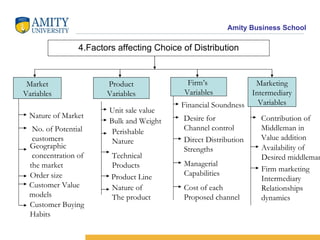
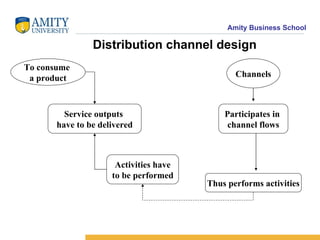
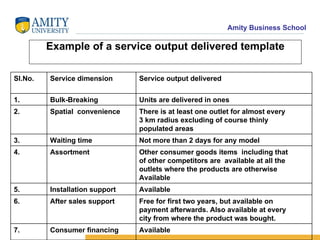
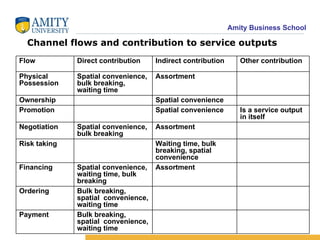
The document discusses various distribution channel design considerations for marketing products. It covers determining distribution objectives, evaluating direct and indirect distribution system alternatives, and factors that affect channel structure choices like market characteristics, product attributes, and firm capabilities. The key aspects of an effective channel design are selecting entities to perform distribution activities and establishing service output levels, activity flows, and performance responsibilities within the channel network.