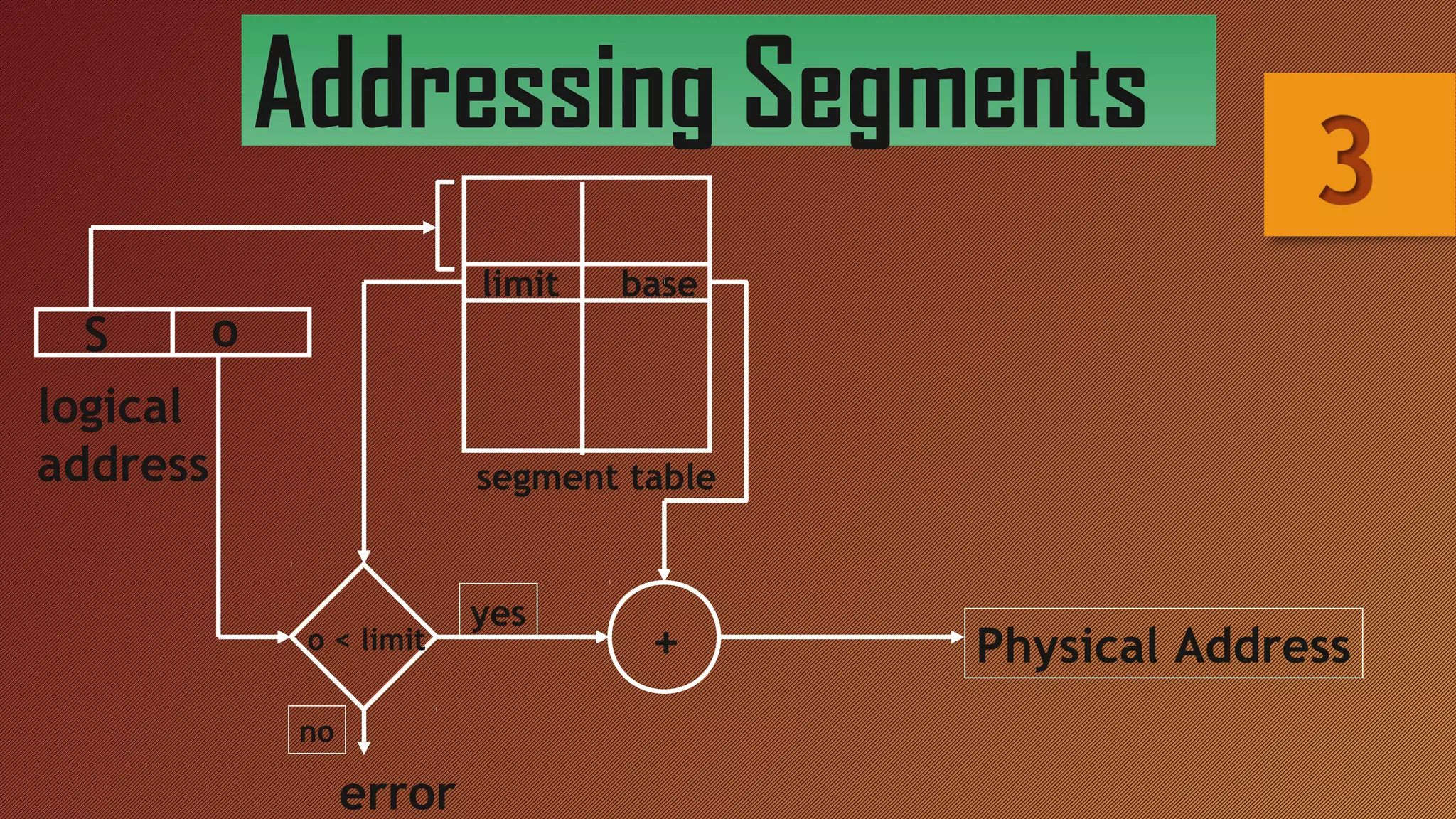
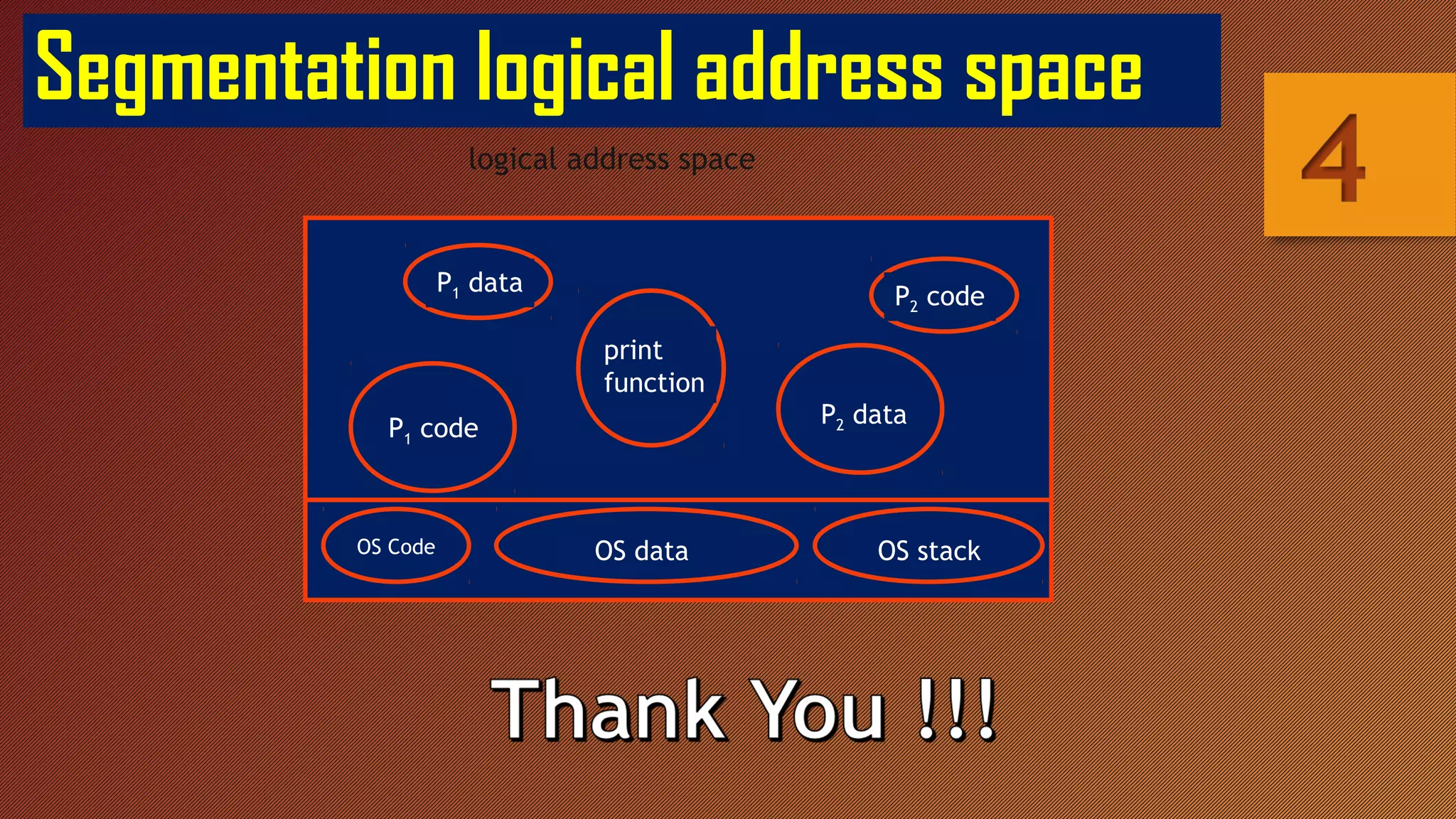
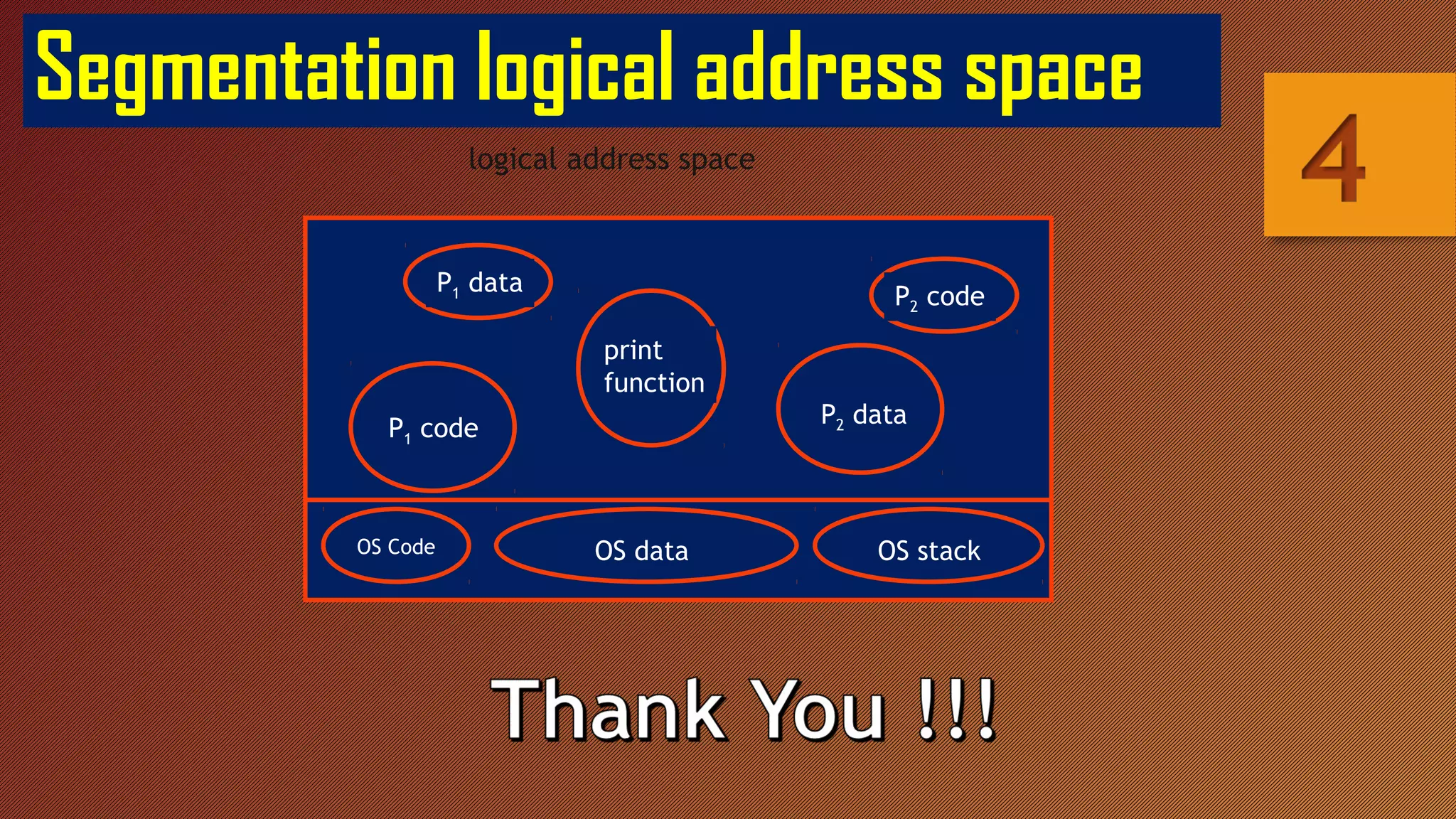
Segmentation breaks memory into logical pieces called segments that each contain related information, such as data segments for each process. Segmentation uses a segment table to translate logical addresses into physical addresses by looking up the base address and limit for each segment number and offset. This allows memory to appear larger than it physically is through segmentation with or without paging.