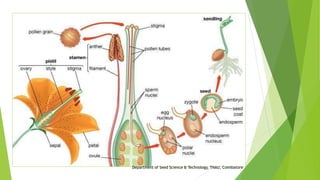
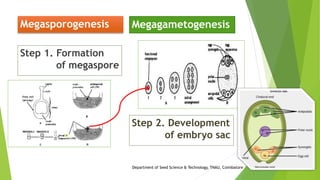
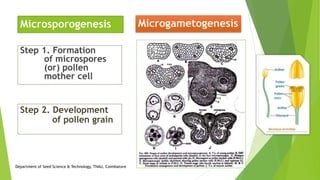
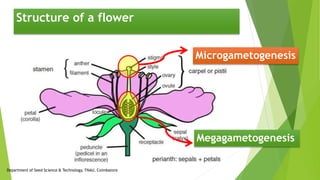
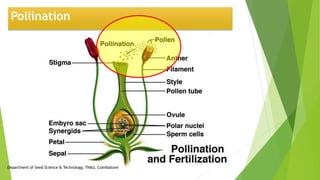
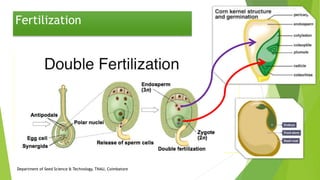
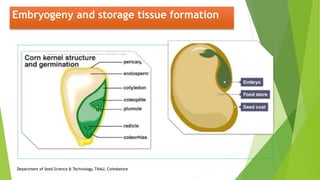
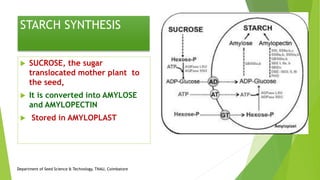
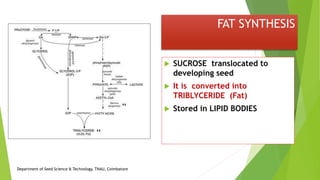
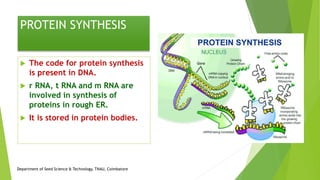
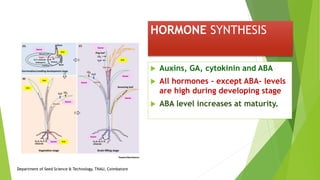
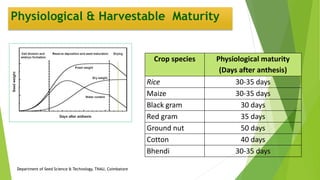
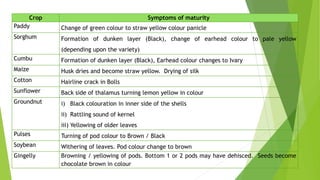
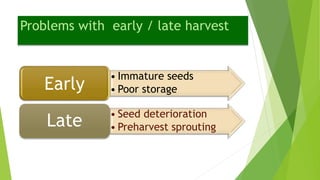
The document discusses the stages of seed development from formation of reproductive organs to maturation. It describes the processes of megasporogenesis and megagametogenesis, microsporogenesis and microgametogenesis which lead to the development of embryo sac and pollen grains. Pollination and fertilization occur, followed by embryogenesis and storage tissue formation as starch, fat, and proteins are deposited in the developing seed. Proper nutrition and irrigation are important for seed development and maturity is reached when seeds reach maximum dry weight and viability. Harvesting before or after physiological maturity can impact seed quality and storage potential.