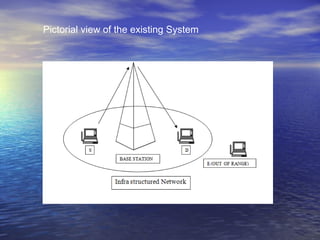
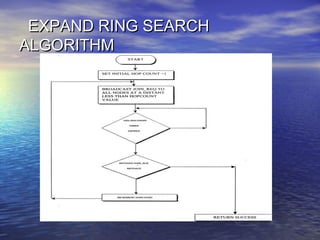
The document discusses secure location-based routing for mobile ad-hoc networks, emphasizing the need for efficient and secure protocols due to the dynamic nature of mobile nodes. It critiques existing systems that rely on fixed infrastructure and proposes an ad-hoc approach where nodes collaborate to forward messages, ensuring security through encryption techniques like RSA. The study concludes that using location information can significantly lower routing overhead and outlines future improvements in dynamic ad-hoc networking and cryptographic security measures.