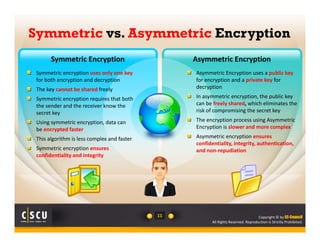
A survey of 500 IT security specialists found that roughly 40% believe they could hold their employer's network hostage by withholding encryption keys after leaving the company. Additionally, one third were confident they could bring a company to a halt with little effort using their knowledge of encryption keys and certificates. The study highlighted the need for companies to properly manage and monitor who has access to encryption keys to avoid security breaches.