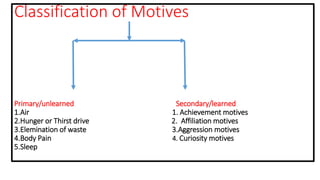
1. The document discusses secondary or learned motives in psychology, including achievement motives, affiliation motives, aggression motives, power motives, and curiosity motives.
2. Achievement motives refer to a drive for excellence and success, with high achievers preferring challenging tasks and feedback. Affiliation motives reflect the basic human need for social connection and approval from others.
3. Aggression motives can arise from intense frustration or exposure to violent media, potentially leading to aggressive behavior. Power motives involve a concern with influence over others, while curiosity motives reflect a desire for status and rank within social groups.