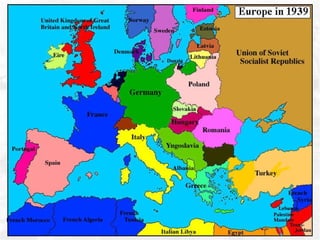
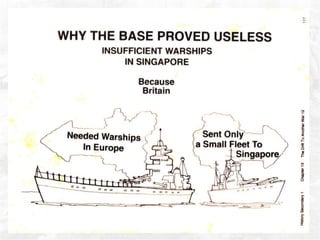
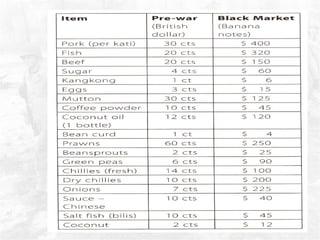
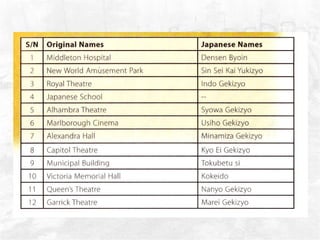
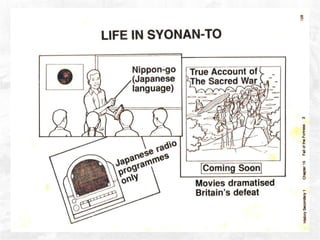
The document summarizes the British defense of Singapore and the reasons for its fall to the Japanese in 1942. It discusses the British strategy of using Singapore as a naval base protected by coastal guns. However, the British were unprepared for jungle warfare and lacked tanks and aircraft. In contrast, the Japanese were well-trained and equipped for jungle combat. The document also outlines the political, economic, and social impacts of Japanese occupation, including rationing, inflation, and efforts to promote Japanese culture in Singapore.