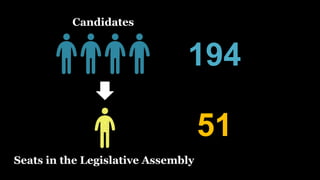
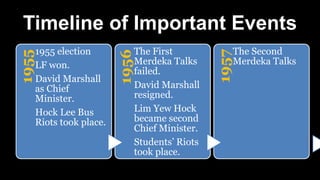
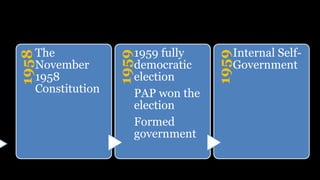
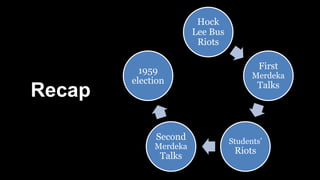
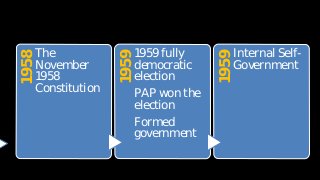
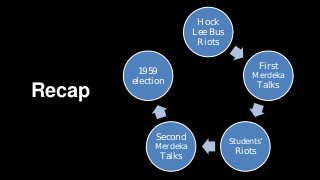
The document summarizes key events in Singapore's path towards self-government, including two rounds of talks with Britain known as the Merdeka Talks. The First Merdeka Talks in 1956, led by then-Chief Minister David Marshall, failed to achieve internal self-government as Britain disagreed to Marshall's demands. The Second Merdeka Talks in 1957, led by Lim Yew Hock, succeeded in gaining internal self-government after the British showed confidence in Lim's ability to suppress riots. This led to Singapore's first elections in 1959 and internal self-government, though Britain retained control over external affairs and defense. The People's Action Party (PAP) led by Lee Kuan Yew won