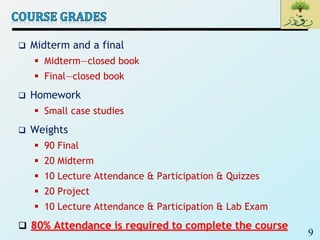
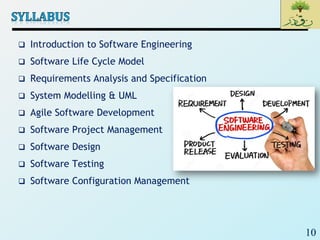
This document provides information about a Software Engineering 1 course. It outlines the course details including the instructor's information, teaching assistants, schedule, required textbooks, assessment breakdown, and course topics. The course aims to teach students how to produce high-quality software within budget and time while dealing with complexity and change. Key topics that will be covered include the software lifecycle, requirements elicitation, modeling and UML, software project management, software design, and software testing. Students are expected to maintain 80% attendance and adhere to other policies like proper attire and no late entries.