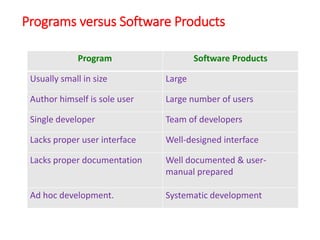
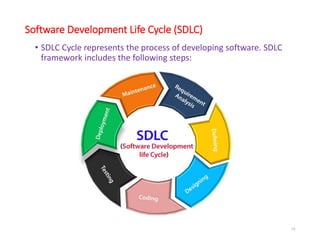
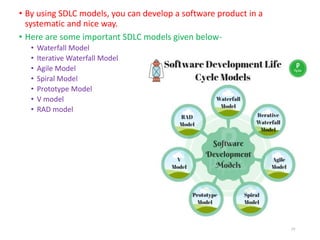
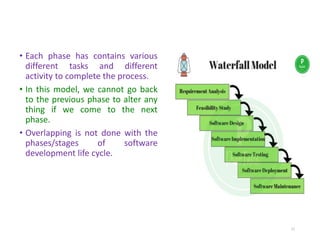
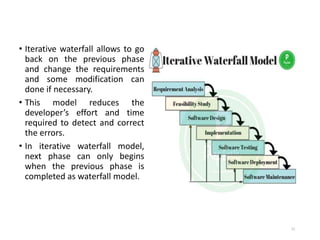
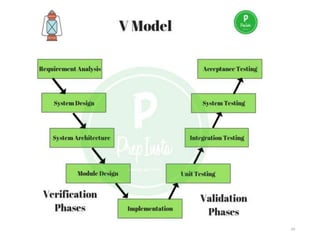
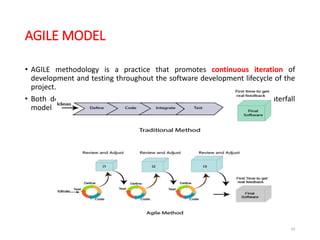
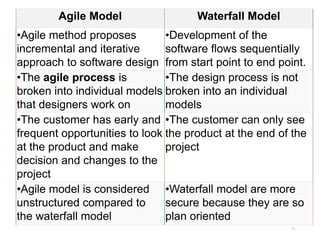
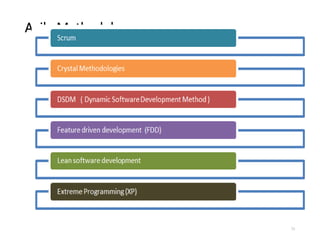
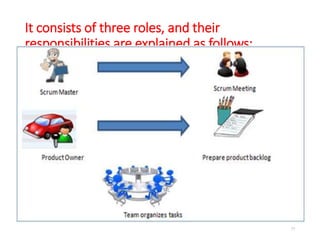
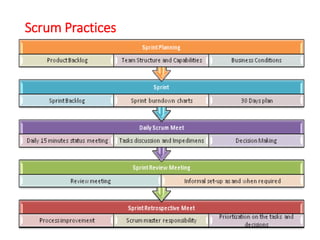
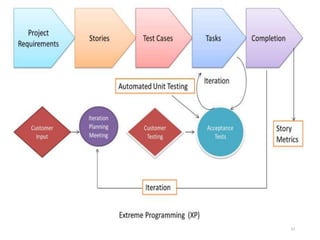
The document outlines the course outcomes and syllabus for a software engineering and project management course. It covers various software development methodologies, including process models like Waterfall, Iterative Waterfall, Spiral, and Prototyping, along with stages of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). Additionally, it discusses the goals, advantages, and disadvantages of software engineering, along with the roles of software engineers and developers.