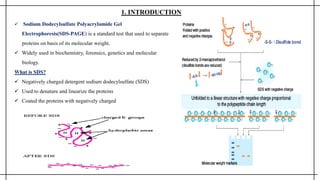
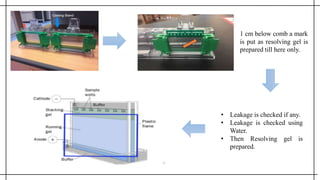
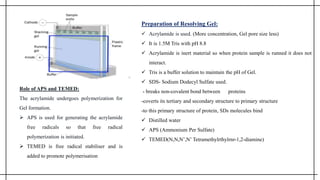
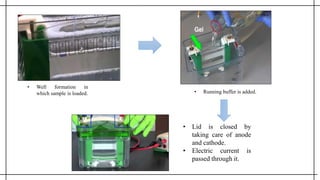
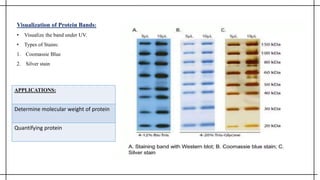
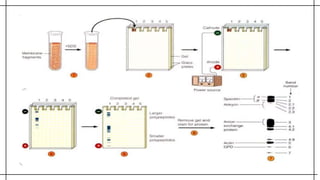
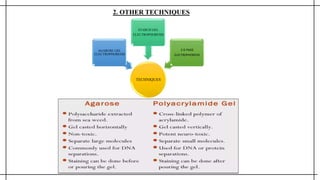
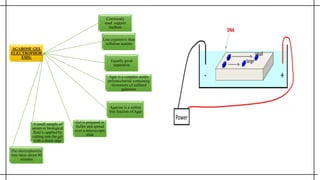
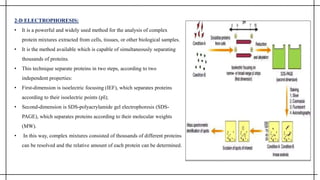
The document outlines advanced techniques in pharmaceutical research, focusing primarily on sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) for protein separation based on molecular weight. It details the preparation of gels, sample processing, and the operational principles of SDS-PAGE, alongside additional techniques like agarose gel and starch gel electrophoresis. Various staining methods used for protein visualization and the applications of these techniques in analyzing complex protein mixtures are also discussed.